PCCB Antibodies
Background
The β subunit and α subunit encoded by the PCCB gene jointly form mitochondrial propionyl-coA carboxylase (PCC), which, as A member of the biotin-dependent carboxylase family, is mainly distributed in the mitochondrial matrix of tissues such as the liver and kidneys. The protein encoded by it catalyzes the conversion of propionyl-CoA to D-methylmalonyl-CoA and plays A key role in branched-chain amino acid metabolism, odd-chain fatty acid oxidation and cholesterol synthesis pathways. Mutations in this gene can disrupt the propionic acid metabolic pathway, leading to abnormal accumulation of propionic acid and its metabolites, and triggering methylmalonic acidemia with homocysteinemia (cblC type), an autosomal recessive genetic disorder. In 1999, researchers first clarified its molecular characteristics through complementary DNA cloning technology. Subsequent studies revealed the correlation between the gene mutation spectrum and clinical manifestations, providing an important molecular basis for neonatal genetic disease screening, targeted therapy and genetic diagnosis.
Structure of PCCB
The molecular weight of the β subunit protein encoded by the PCCB gene is approximately 58 kDa, and its size varies among different species. This protein, together with the α subunit encoded by the PCCA gene, constitutes A total propionyl-coA carboxylase enzyme of approximately 76 kDa. The following are the comparative data among various species:
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Bovine |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 58.2 | 57.9 | 58.1 | 58.3 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains 539 amino acids | Conservative sequences are highly similar | Enzyme activity area highly conservative | The binding domains of biotin are consistent |
The PCCB protein is composed of 539 amino acids, and its three-dimensional structure contains highly conserved biotin-binding domains and ATP-binding domains. The protein core is composed of multiple α -helices and β -folds, forming a stable bifunctional enzyme activity center. The C-terminal region contains a characteristic biotin carboxycarrier protein domain, which is covalently linked to a biotin cofactor through a conserved lysine residue. The N-terminal region forms A propionyl-CoA binding pocket, which is jointly maintained by arginine and glutamic acid residues for substrate-specific recognition.
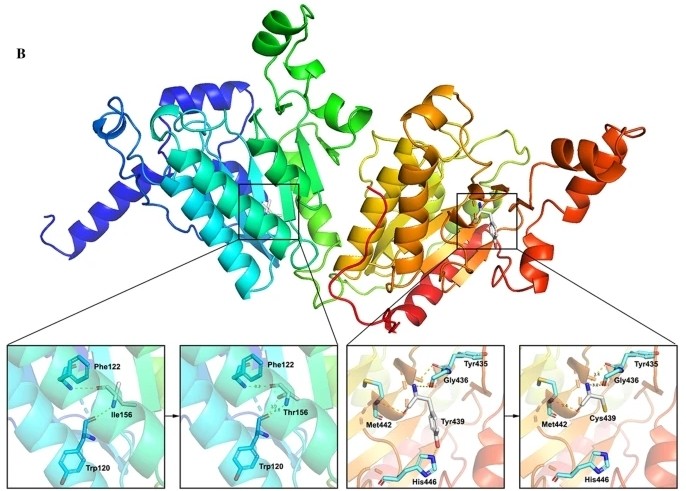 Fig. 1 Three-dimensional structure modeling of the PCCB protein with isoleucine 156 and tyrosine 439 framed.1
Fig. 1 Three-dimensional structure modeling of the PCCB protein with isoleucine 156 and tyrosine 439 framed.1
Key structural properties of PCCB:
- Conserved biotin carboxylase domains and carboxyltransferase domains
- Propionyl-coa binding channels are composed of hydrophobic amino acids
- Lysine residues are covalently linked to biotin cofactors
Functions of PCCB
PCCB gene encoding protein is the core functions of catalytic propionyl coenzyme A carboxylation reactions. However, this enzyme is also involved in a variety of physiological processes, including maintaining energy homeostasis and regulating the toxicity of organic acids.
| Function | Description |
| Propionic Acid Metabolism | Catalyzing the carboxylation of propionyl-CoA to methylmalonyl-CoA is A key step in the decomposition of odd-chain fatty acids and branched-chain amino acids. |
| Energy Metabolic Support | Provide the Krebs cycle succinyl coa precursor, safeguard cell energy continuous production of ATP. |
| Organic Acid Detoxification | Prevent the abnormal accumulation of metabolic intermediates such as propionic acid in the body to avoid metabolic acidosis and neurotoxic damage. |
| Metabolite Balance | By regulating the level of methylmalonyl-CoA, it indirectly affects the homeostasis of metabolic pathways such as gluconeogenesis and fatty acid synthesis. |
| Association With Genetic Diseases | Defects in this gene result in methylmalonic acidemia, which affects multiple systems throughout the body and is particularly dysfunctional in tissues with high energy requirements. |
The carboxylation reaction catalyzed by PCCB enzyme exhibits typical dual-substrate cooperative kinetic characteristics, which are quite different from the allosteric regulation mechanisms of many metabolic enzymes, reflecting its functional positioning as a key enzyme in basic catabolism.
Applications of PCCB and PCCB Antibody in Literature
1. Zhang, Wendiao, et al. "Human forebrain organoid-based multi-omics analyses of PCCB as a schizophrenia associated gene linked to GABAergic pathways." Nature Communications 14.1 (2023): 5176. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-40861-2
This study found through multi-omics analysis that the mitochondrial gene PCCB is a risk gene for schizophrenia (SCZ). SNPS related to SCZ affect the transcriptional activity of PCCB. Knockdown of PCCB leads to abnormal neural function of human forebrain organoids, damage to GABAergic synaptic pathways and reduced synchrony of neural networks, suggesting that mitochondrial function is involved in the pathogenesis of SCZ through the GABA pathway.
2. Li, Yingxuan, et al. "Novel compound heterozygous variants in the PCCB gene causing adult-onset propionic acidemia presenting with neuropsychiatric symptoms: a case report and literature review." BMC Medical Genomics 15.1 (2022): 59. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12920-022-01202-2
This study reports a case of adult propionic acidemia caused by a novel compound heterozygous mutation of the PCCB gene. The patient developed the disease at the age of 21 and presented with neuropsychiatric symptoms. This finding, in combination with a literature review, indicates that PCCB gene mutations are associated with the phenotype of late-onset disease, expanding the pathogenic mutation spectrum and phenotypic understanding of this gene.
3. Tajima, Go, et al. "Current perspectives on neonatal screening for propionic acidemia in Japan: An unexpectedly high incidence of patients with mild disease caused by a common PCCB variant." International Journal of Neonatal Screening 7.3 (2021): 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns7030035
The article indicates that neonatal screening has found that propionic acidosis caused by the c.1304T>C variant of the PCCB gene has an incidence rate as high as approximately 1 in 45,000 in Japan. Most patients carrying this variant are asymptomatic, but the risk of cardiac complications is of concern, and related cardiac phenotypic studies are ongoing.
4. Zhang, Wendiao, et al. "Human forebrain organoids-based multi-omics analyses reveal PCCB's regulation on GABAergic system contributing to schizophrenia." Research Square (2023): rs-3. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-2674668/v1
This study reveals for the first time that the mitochondrial gene PCCB is a risk gene for schizophrenia (SCZ). Its decreased expression inhibits the GABAergic system by affecting the tricarboxylic acid cycle, leading to SCZ-related phenotypes such as excessive neuronal activity and weakened network synchrony in human brain organoids, clarifying a new mechanism by which PCCB regulates the GABA pathway to participate in diseases.
5. García-Tenorio, Emilio M., et al. "Novel CRISPR-Cas9 iPSC knockouts for PCCA and PCCB genes: advancing propionic acidemia research." Human Cell 38.3 (2025): 64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-025-01193-z
In this study, a PCCB gene knockout cell line was successfully constructed in healthy IPscs using CRISPR-Cas9 technology. This model accurately simulates the molecular characteristics of propionic acidemia, providing an ideal in vitro research platform for in-depth study of disease mechanisms and development of new therapies.
Creative Biolabs: PCCB Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality PCCB antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom PCCB Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our PCCB antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Li, Yingxuan, et al. "Novel compound heterozygous variants in the PCCB gene causing adult-onset propionic acidemia presenting with neuropsychiatric symptoms: a case report and literature review." BMC Medical Genomics 15.1 (2022): 59. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12920-022-01202-2
Anti-PCCB antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-CA9 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-2079) (CBMAB-C0131-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ALPL Antibody (B4-78) (CBMAB-1009CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CD1C Recombinant Antibody (L161) (CBMAB-C2173-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CAPZB Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0944) (CBMAB-C2381-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CFL1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1771) (CBMAB-C1833-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CASQ1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0863) (CBMAB-C0918-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-Acetyl-α-Tubulin (Lys40) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623485) (CBMAB-CP2897-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-Acetyl-Histone H3 (Lys36) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623395) (CBMAB-CP0994-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-APP Recombinant Antibody (DE2B4) (CBMAB-1122-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-CARTPT Recombinant Antibody (113612) (CBMAB-C2450-LY)

-
Rat Anti-EMCN Recombinant Antibody (28) (CBMAB-E0280-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-APCS Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A663) (CBMAB-A3054-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP1B1 Recombinant Antibody (E4) (CBMAB-0463-LY)

-
Rat Anti-CD63 Recombinant Antibody (7G4.2E8) (CBMAB-C8725-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BHMT Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0547) (CBMAB-0550-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-C5AR1 Recombinant Antibody (R63) (CBMAB-C9553-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-FAS2 Monoclonal Antibody (1D4) (CBMAB-0071-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-ADAM29 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179787) (CBMAB-A1149-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CRTAM Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2235) (CBMAB-C2305-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATM Recombinant Antibody (2C1) (CBMAB-A3970-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






