SERPINE1 Antibodies
Background
SERPINE1 (serine protease inhibitor E1) is a glycoprotein encoded by human genes, mainly functioning as a plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1). This protein regulates the fibrinolysis process by specifically inhibiting tissue-type and urokinase-type plasminogen activators, which is crucial for maintaining the balance between coagulation and anticoagulation. Its abnormal expression is closely related to thrombosis, tissue fibrosis and tumor progression. For example, under hypoxic conditions, it can induce overexpression of SERPINE1 through the HIF-1α pathway to promote disease development. As the main regulator of the fibrinolytic system in serum, the study of the molecular mechanism of this gene provides important targets for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases and cancer, and the analysis of its tertiary structure also promotes the development of related inhibitor drugs.
Structure of SERPINE1
SERPINE1 is a glycoprotein with a molecular weight of approximately 45 kDa. The actual measured value often fluctuates within the range of 42 to 55 kDa due to differences in glycosylation.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Bovine |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 45 | 44 | 44 | 46 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Containing nine beta fold and three reaction center ring | The sequence of the reaction center loop is highly conserved | Glycosylation sites similar to humans | Species-specific variation was found in the C-terminal domain |
This protein is composed of 379 amino acids, and its three-dimensional structure is characterized by a central β -barrel-shaped fold. The active center contains a unique flexible hinge region that can trap the target protease. The key functional sites are composed of arginine-346 and histidine-343 on the reaction center ring. These two residues achieve specific and irreversible inhibition of plasminogen activators through steric hindrance effects.
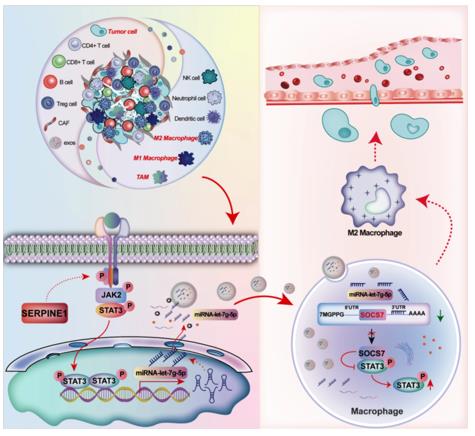 Fig. 1 SERPINE1 in Gastric Cancer Exosomes Drives Macrophage M2 Polarization.1
Fig. 1 SERPINE1 in Gastric Cancer Exosomes Drives Macrophage M2 Polarization.1
Key structural properties of SERPINE1:
- Central β -barrel-shaped folded core structure
- Highly flexible active center ring (reaction center ring)
- "Entrapment" mechanism of protease binding sites
- Key arginine - 346 residues mediated irreversible inhibition
Functions of SERPINE1
The main function of SERPINE1 (plasminogen activator inhibitor-1) is to maintain vascular homeostasis by inhibiting the fibrinolytic system. However, it is also widely involved in a variety of pathophysiological processes, including tissue remodeling, inflammatory responses and tumor progression.
| Function | Description |
| Fibrinolytic inhibition | As a major physiological inhibitor, it irreversibly binds to and neutralizes tissue type (tPA) and urokinase type (uPA) plasminogen activators. |
| Thrombus stability | By inhibiting plasmin production, it stabilizes the formed fibrin thrombus and prevents its premature degradation. |
| Regulation of cell migration | Regulate UPA-mediated extracellular matrix degradation and affect the processes of cell adhesion, diffusion and migration. |
| Promotion of tissue fibrosis | Overexpressed under pathological conditions, it inhibits the degradation of matrix proteins and promotes collagen deposition and tissue fibrosis. |
| Participation in wound healing | By controlling proteolytic activity, it participates in the dynamic balance process of tissue repair and remodeling. |
The inhibitory kinetics of SERPINE1 exhibits a unique "trapping" mechanism. Its interaction with the target protease shows a slow binding but irreversible characteristic, which contrasts sharply with the rapid reversible equilibrium of typical serine protease inhibitors, establishing its core position in thrombotic and fibrotic diseases.
Applications of SERPINE1 and SERPINE1 Antibody in Literature
1. Zhang, Dan, et al. "Therapy-induced senescent tumor cell-derived extracellular vesicles promote colorectal cancer progression through SERPINE1-mediated NF-κB p65 nuclear translocation." Molecular Cancer 23.1 (2024): 70. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-024-01985-1
Studies have shown that senescent tumor cells induced by anti-cancer treatment release extracellular vesicles rich in SERPINE1. SERPINE1 in these vesicles can bind to p65, activating the NF-κB signaling pathway and thereby promoting the progression of colorectal cancer. Inhibiting SERPINE1 can block this effect.
2. Ye, Zhenzhen, et al. "Gastric cancer-derived exosomal let-7 g-5p mediated by SERPINE1 promotes macrophage M2 polarization and gastric cancer progression." Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research 44.1 (2025): 2. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-024-03269-4
Studies have found that gastric cancer cells activate the JAK2/STAT3 pathway by highly expressing SERPINE1, promoting the packaging of let-7g-5p into exosomes. After the exosome is taken up by macrophages, let-7g-5p enhances STAT3 phosphorylation by inhibiting SOCS7, thereby driving macrophages to polarize to the M2 type and promoting tumor progression.
3. Wang, Luning, et al. "RBM4 regulates cellular senescence via miR1244/SERPINE1 axis." Cell death & disease 14.1 (2023): 27. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-023-05563-z
Studies have shown that the deletion of RNA-binding protein RBM4 promotes the degradation of primary miR-1244, resulting in a reduction of its mature bodies. This weakens the inhibitory effect of miR-1244 on the key aging factor SERPINE1, upregulates the expression of SERPINE1, and ultimately induces the senescence of lung cancer cells and inhibits tumor progression.
4. Pavón, Miguel Angel, et al. "uPA/uPAR and SERPINE1 in head and neck cancer: role in tumor resistance, metastasis, prognosis and therapy." Oncotarget 7.35 (2016): 57351. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.10344
Studies have shown that in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, uPA/uPAR and its inhibitor SERPINE1, although functionally contradictory, are both highly expressed and can promote tumor metastasis and lead to a poor prognosis. The mechanism lies in the fact that SERPINE1 can activate pro-cancer signals independently of the uPA inhibitory function. Both can serve as prognostic biomarkers and potential therapeutic targets.
5. Li, Lingqin, et al. "Identification and validation of SERPINE1 as a prognostic and immunological biomarker in pan-cancer and in ccRCC." Frontiers in pharmacology 14 (2023): 1213891. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2023.1213891
Studies have shown that SERPINE1 is abnormally highly expressed in various cancers and is associated with a poor prognosis. Its expression is regulated by gene copy number amplification and DNA hypomethylation. Studies have confirmed that SERPINE1 plays a key role in the malignant progression of tumors and immunosuppression by influencing immune regulation, immune cell infiltration and tumor mutational burden.
Creative Biolabs: SERPINE1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality SERPINE1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom SERPINE1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our SERPINE1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Ye, Zhenzhen, et al. "Gastric cancer-derived exosomal let-7 g-5p mediated by SERPINE1 promotes macrophage M2 polarization and gastric cancer progression." Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research 44.1 (2025): 2. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-024-03269-4
Anti-SERPINE1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-DES Monoclonal Antibody (440) (CBMAB-AP1857LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC3 Recombinant Antibody (315304) (CBMAB-1214-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-BMI1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-P026) (CBMAB-P0108-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CCDC6 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-0106) (CBMAB-C5397-CQ)

-
Rat Anti-EMCN Recombinant Antibody (28) (CBMAB-E0280-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CEMIP Recombinant Antibody (3C12) (CBMAB-K0296-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A950) (CBMAB-A4388-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (SN3) (CBMAB-C1037-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-FLT1 Recombinant Antibody (11) (CBMAB-V0154-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-CAMK2A Recombinant Antibody (BA0032) (CBMAB-0137CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ACKR3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-261265) (CBMAB-C1023-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CGAS Recombinant Antibody (CBFYM-0995) (CBMAB-M1146-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ATF4 Recombinant Antibody (D4B8) (CBMAB-A3872-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CASQ1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0863) (CBMAB-C0918-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-DLL4 Recombinant Antibody (D1090) (CBMAB-D1090-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL6 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0442) (CBMAB-0445-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-AK4 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180419) (CBMAB-A1891-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-DLC1 Recombinant Antibody (D1009) (CBMAB-D1009-YC)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Recombinant Antibody (CBC05) (CBMAB-CR005LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BHMT Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0547) (CBMAB-0550-YY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






