CD6 Antibodies
Background
CD6 is a transmembrane glycoprotein mainly expressed on the surface of T lymphocytes. As a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, its structure contains three scavenger receptor cysteine-rich domains. The protein encoded by this gene plays a key role in the formation of immune synapses by mediating the interaction between antigen-presenting cells and T cells, and also participates in the regulation of T cell activation and differentiation as a costimulatory molecule. Research has found that CD6 gene polymorphisms are associated with susceptibility to autoimmune diseases, including multiple sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis. Due to its significant role in immune regulation, CD6 has become a key research target for the treatment of autoimmune diseases. The development of related monoclonal antibody drugs has entered the clinical trial stage, providing a new direction for precise immunotherapy.
Structure of CD6
CD6 is a transmembrane glycoprotein with a molecular weight of approximately 105-130 kDa, and its differences mainly stem from the varying degrees of glycosylation modification.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 105-130 | 110-135 | 108-132 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains three SRCR domain structure | Highly homologous to human CD6 | Extracellular region structure highly conservative |
The CD6 protein is composed of 668 amino acids, and its extracellular region contains three highly conserved scavenger receptor cysteine-enriched (SRCR) domains, forming an extended rod-like structure. This protein is linked to multiple phosphorylation sites in the intracellular segment through the transmembrane region. Among them, serine at position 629 is the main site for PKC-mediated phosphorylation and directly regulates T cell activation signal transduction. The third SRCR domain is a key region for binding to the ligand CD166/ALCAM, and this specific interaction is an important molecular basis for the formation of immune synapses.
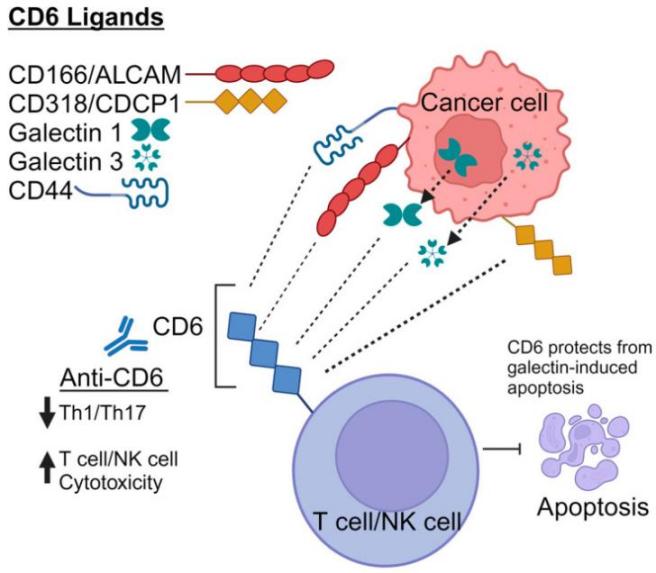 Fig. 1 Schematic representation of endogenous CD6 ligands.1
Fig. 1 Schematic representation of endogenous CD6 ligands.1
Key structural properties of CD6:
- Extracellular region contains three cysteine enrichment of scavenger receptor (SRCR) domain structure
- Transmembrane regions anchor proteins to cell membranes
- Intracellular section contains conservative phosphorylation sites, but the signal transduction of T cell activation
Functions of CD6
The main function of CD6 is to act as a T-cell co-stimulatory receptor to participate in the regulation of immune responses, and it is also involved in pathophysiological processes such as immune tolerance and inflammatory responses.
| Function | Description |
| Immune synaptic formation | By binding to the ligand CD166 through the extracellular SRCR domain, it promotes stable contact between T cells and antigen-presenting cells. |
| Regulation of T cell activation | Transmit co-stimulatory signals, coordinate with TCR signals to regulate T cell proliferation and differentiation, and determine the intensity of immune response. |
| Maintenance of immune tolerance | Participate in thymus negative selection, affect the clearance of autoreactive T cells, and prevent the occurrence of autoimmune diseases. |
| Regulation of inflammatory response | Mediates the migration and retention of lymphocytes at the site of inflammation and regulates the degree of local immune cell infiltration. |
| Therapeutic targets for diseases | As potential therapeutic targets for autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis and psoriasis, related antibody drugs have entered clinical research. |
The binding of CD6 to the ligand CD166 shows moderate affinity, and its signal output intensity is dynamically regulated by the phosphorylation state of intracellular serine segments. This characteristic enables it to precisely control the activation threshold of immune responses and avoid excessive immune reactions.
Applications of CD6 and CD6 Antibody in Literature
1. Gurrea-Rubio, Mikel, David A. Fox, and Javier S. Castresana. "CD6 in Human Disease." Cells 14.4 (2025): 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14040272
The article indicates that CD6 is a surface protein expressed on lymphocytes such as T cells, and it participates in the processes of lymphocyte activation, proliferation and adhesion through its interaction with its ligands. It is related to the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases and is a potential target for cancer immunotherapy.
2. Aragón-Serrano, Lucía, et al. "CD6 and its interacting partners: newcomers to the block of Cancer immunotherapies." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24.24 (2023): 17510. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417510
The article indicates that CD6 is a signal transduction receptor mainly expressed in T cells, and its ligands are highly expressed in various cancer cells. This makes it an emerging therapeutic target for hematological malignancies and solid tumors. This review summarizes a variety of anti-cancer immune strategies targeting CD6, including monoclonal antibodies, soluble bait receptors, and CAR-T cell therapy.
3. Gonçalves, Carine M., et al. "CD6, a rheostat-type signalosome that tunes T cell activation." Frontiers in immunology 9 (2018): 2994. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.02994
The article indicates that CD6 is an important glycoprotein on the surface of T cells and is involved in T cell activation and immune response. Its intracellular tail can recruit various signal-effector molecules, which have a regulatory effect on TCR signal transduction. Compared with the inhibitory receptor CD5 of the same family, the specific function (inhibition or antagonism) of CD6 in T cell signal transduction remains controversial and is currently the focus of research.
4. Santos, Rita F., et al. "The CD6 interactome orchestrates ligand-independent T cell inhibitory signaling." Cell Communication and Signaling 22.1 (2024): 286. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12964-024-01658-y
The article indicates that CD6 is a new type of "switch" scaffold receptor, and its function is dual. On the one hand, it exerts constitutive inhibitory effects through intracellular regions, setting the threshold for T cell activation; On the other hand, the binding of its extracellular region to CD166 can enhance the adhesion of T cells to APCs, but this LIGAND-dependent regulation is independent of TCR signaling.
5. Gurrea-Rubio, Mikel, et al. "Ligands of CD6: Roles in the pathogenesis and treatment of cancer." Frontiers in immunology 15 (2025): 1528478. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1528478
The article indicates that CD6 is an important regulatory molecule of T cells, participating in intercellular interactions by binding to CD166, CD318 and the possible new ligand CD44. These ligands are highly expressed on various cancer cells and are associated with poor prognosis and metastasis, making CD6 and its ligands a new focus in cancer research and immunotherapy.
Creative Biolabs: CD6 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality CD6 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom CD6 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our CD6 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Gurrea-Rubio, Mikel, David A. Fox, and Javier S. Castresana. "CD6 in Human Disease." Cells 14.4 (2025): 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14040272
Anti-CD6 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-CCDC6 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-0106) (CBMAB-C5397-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CCDC25 Recombinant Antibody (CBLC132-LY) (CBMAB-C9786-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A950) (CBMAB-A4388-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD8 Recombinant Antibody (C1083) (CBMAB-C1083-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD164 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0077) (CBMAB-C0086-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ESR1 Recombinant Antibody (Y31) (CBMAB-1208-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP1B3 Recombinant Antibody (1E9) (CBMAB-A4021-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV-5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-503417) (CBMAB-V208-1369-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BAD (Phospho-Ser136) Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0138) (CBMAB-0139-YY)

-
Rat Anti-EPO Recombinant Antibody (16) (CBMAB-E1578-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-B2M Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0059) (CBMAB-0059-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-HTLV-1 gp46 Recombinant Antibody (CBMW-H1006) (CBMAB-V208-1154-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AKT1/AKT2/AKT3 (Phosphorylated T308, T309, T305) Recombinant Antibody (V2-443454) (PTM-CBMAB-0030YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AP4E1 Recombinant Antibody (32) (CBMAB-A2996-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BACE1 Recombinant Antibody (CBLNB-121) (CBMAB-1180-CN)

-
Rabbit Anti-ABL1 (Phosphorylated Y185) Recombinant Antibody (V2-443434) (PTM-CBMAB-0001YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ABCA3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-178911) (CBMAB-A0145-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ADGRE2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-261270) (CBMAB-C0813-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CA9 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-2079) (CBMAB-C0131-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC3 Recombinant Antibody (315304) (CBMAB-1214-CN)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








