FANCE functions as an essential part of the Fanconi anemia DNA repair pathway which mainly exists in proliferating cells and tissues. The protein functions as a vital component for DNA cross-link repair and genomic stability maintenance which protects against chromosomal abnormalities and cancer formation. The protein complex of FANCE works to detect DNA damage for repair purposes which enables normal cell division and prevents excessive genetic mutations. Research on Fanconi anemia patients led to the initial discovery of FANCE which has since become a focus of extensive DNA repair mechanism studies. The discovery of FANCE has led to major breakthroughs in understanding cellular genetic maintenance processes and DNA damage responses which benefits cancer research and therapeutic development.
FANCE is a relatively small protein with a molecular weight of approximately 55 kDa. This weight may slightly vary between species due to differences in glycosylation patterns or minor variations in amino acid sequence.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 60 | 60 | 60 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Composed of 536 amino acids, with a disordered region between residues 170 and 270 | Contains 536 amino acids, with a structure highly similar to human FANCE | Similar structure to human FANCE, with minor variations in non-critical regions |
The protein FANCE (Fanconi Anemia Complementation Group E) is a key component of the Fanconi anemia (FA) DNA repair pathway and plays a crucial role in maintaining genomic stability. FANCE contains multiple conserved domains and displays a complex structure essential for its function. The protein structure of FANCE contains binding regions for other FA proteins which assemble into a central complex that enables DNA repair. The protein contains specific domains which enable it to move to areas where DNA damage occurs. The protein functions as a vital component in cells to stop chromosomal problems and defend against cancer development. FANCE works with other FA pathway proteins to control DNA interstrand cross-link repair which maintains cell cycle progression and prevents genomic instability.
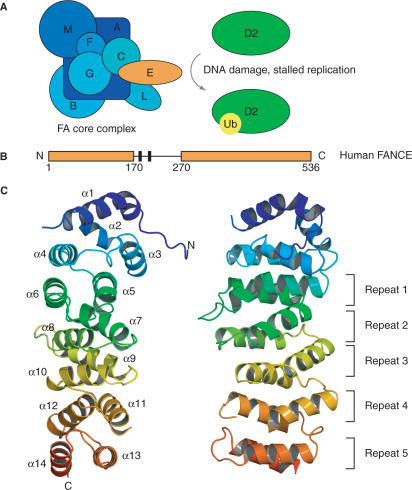 Fig. 1 Structure of human FANCE.1
Fig. 1 Structure of human FANCE.1
Key structural properties of FANCE:
FANCE's primary function is DNA repair via the Fanconi anemia pathway. However, it is also involved in various cellular processes, including maintaining genomic stability and responding to DNA damage.
| Function | Description |
| DNA Repair | Critical for repairing DNA interstrand cross-links |
| Genomic Stability | Prevents chromosomal abnormalities and maintains genome integrity |
| Pathway Regulation | Serves as a key regulator in the Fanconi anemia pathway |
| Protein Interactions | Forms complexes with other FA proteins to mediate repair |
| Response to DNA Damage | Localizes to sites of DNA damage to initiate repair processes |
The function of FANCE in DNA repair is essential for maintaining genomic stability, in contrast to other proteins that may have broader roles, indicating its specialized role in preventing chromosomal abnormalities.
1. Lin, Bo, et al. "Integrated analysis of FANCE expression and its regulatory role in the immune microenvironment of oral squamous cell carcinoma." Oncology Letters 29.3 (2025): 160. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2025.14906
This article presents an integrated analysis of FANCE expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma, highlighting its regulatory role in the immune microenvironment. FANCE antibody was used as a key marker to investigate the protein's expression patterns and interactions with immune cells, demonstrating its significance in understanding tumor-immune dynamics and identifying potential therapeutic targets.
2. Nookala, Ravi K., Shobbir Hussain, and Luca Pellegrini. "Insights into Fanconi Anaemia from the structure of human FANCE." Nucleic Acids Research 35.5 (2007): 1638-1648. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkm033
This article offers in-depth structural insights into human FANCE, shedding light on the molecular basis of Fanconi Anaemia. The study pinpoints key structural components of FANCE that underpin its role in DNA repair processes and highlights its significance in maintaining genome stability. These findings provide novel perspectives on the molecular mechanisms of Fanconi Anaemia and suggest potential therapeutic avenues for associated conditions.
3. Yin, Huan, Zhixian Zhou, and Chun Fu. "Fance deficiency impaired DNA damage repair of prospermatogonia and altered the repair dynamics of spermatocytes." Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology 22.1 (2024): 113. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12958-024-01284-w
This article investigates the impact of FANCE deficiency on DNA damage repair in prospermatogonia and spermatocytes. The study demonstrates that FANCE deficiency impairs DNA damage repair in prospermatogonia and alters the repair dynamics of spermatocytes, highlighting the critical role of FANCE in maintaining genomic integrity during spermatogenesis. The findings provide insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying reproductive cell development and the consequences of FANCE dysfunction.
4. Takahashi, Junichi, et al. "Fanconi anemia complementation group E, a DNA repair-related gene, is a potential marker of poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma." Oncology 100.2 (2022): 101-113. https://doi.org/10.1159/000520582
The research examines how Fanconi Anemia Complementation Group E (FANCE) functions in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The research demonstrates that FANCE functions as a prognostic indicator for poor outcomes in HCC patients because it belongs to the DNA repair gene family. The research shows that higher FANCE expression levels correlate with more severe tumor progression and shorter patient survival times which makes it important for both outcome prediction and treatment planning.
Company A specializes in the production of high-quality FANCE antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
For further information regarding our FANCE antibodies, custom services, or technical assistance, please reach out to us via info@creative-biolabs.com.
Reference






