JAK3 Antibodies
Background
JAK3 is a tyrosine kinase mainly present in hematopoietic cells such as lymphocytes, and it participates in the signaling of cytokine receptors by forming complexes with other members of the JAK family. This protein plays a core role in the immune system. The signaling pathway it mediates can activate STAT transcription factors, thereby regulating the proliferation, differentiation and survival processes of lymphocytes. The JAK3 gene mutations associated with X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency disease were first identified in 1995. These mutations can cause abnormal development of immune cells, making it an important research subject for primary immunodeficiency diseases. Specific inhibitors of JAK3 have been developed for anti-rejection treatment in organ transplantation. Their high tissue distribution specificity makes them ideal models for studying immune regulatory mechanisms and developing targeted drugs, providing an important perspective for understanding cytokine signaling networks.
Structure of JAK3
JAK3 is a tyrosine kinase with a molecular weight of approximately 125 kDa. Its precise molecular weight may vary slightly due to different transcript splicing methods and post-translational modifications such as phosphorylation.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 125 | 124.5 | 124.8 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains the JH2 pseudokinase domain | The JH1 kinase domain is highly conserved | The JH7 domain has a species-specific sequence |
This protein is composed of 1,124 amino acids, and its polypeptide chain folds into a typical kinase globular structure. The tertiary structural feature of JAK3 lies in its C-terminal dual-kinase domain: JH1 (true kinase domain) is responsible for catalytic activity, while the adjacent JH2 (pseudo-kinase domain) plays a crucial role in self-inhibitory regulation. Within the JH1 domain, the phosphorylation status of specific tyrosine residues on the activation loop (such as Y980 and Y981) directly determines its kinase activity. This sophisticated molecular switch composed of JH2 and JH1 is the structural basis for regulating the JAK-STAT signaling pathway and maintaining immune homeostasis.
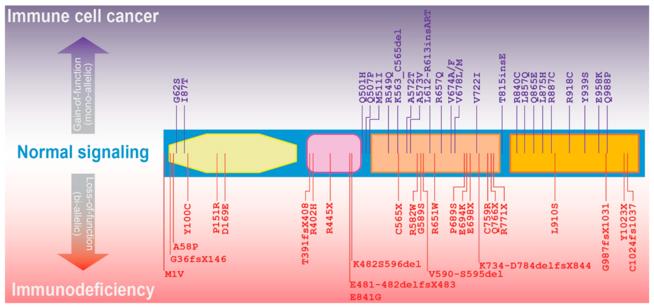 Fig. 1 JAK3 mutations associated with immune cell diseases.1
Fig. 1 JAK3 mutations associated with immune cell diseases.1
Key structural properties of JAK3:
- Modular JH domain assembly
- Mechanism of allosteric inhibition of the JH1 catalytic center by the JH2 domain
- The tyrosine phosphorylation regulatory node of the kinase active center
Functions of JAK3
The core function of JAK3 is to transduct cytokine signals to regulate the development of immune cells. However, it is also deeply involved in various pathophysiological processes such as the maintenance of immune homeostasis and the balance between cell proliferation and apoptosis.
| Function | Description |
| Immune signal transduction | Mediate the intracellular signaling of γc chain cytokines such as IL-2, IL-4, and IL-7, and activate the JAK-STAT pathway. |
| Lymphocyte development | T cells in the thymus and peripheral B cells positive/negative selection key regulatory role. |
| Maintenance of immune tolerance | By regulating the function of Treg cells and the expression of Foxp3, the occurrence of autoimmune reactions can be prevented. |
| Balance of proliferation and apoptosis | The last activation to STAT5 phosphorylation, drive cell cycle D1 protein expression, while the signal attenuation induced Bim mediated apoptosis. |
| Targeted therapy node | Become organ transplantation rejection and autoimmune disease treatment of important drug targets, and its inhibition can selectively block lymphocyte activation. |
Unlike the widespread expression of JAK1/2, the expression of JAK3 is strictly confined to the hematopoietic system. The loss of its function can lead to severe combined immune deficiency, a feature that highlights its non-redundancy in the immune system.
Applications of JAK3 and JAK3 Antibody in Literature
1. Velatooru, Loka Reddy, et al. "New JAK3-INSL3 fusion transcript—an oncogenic event in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma." Cells 12.19 (2023): 2381. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12192381
The article indicates that in the study of mycosis fungoides, the newly discovered JAK3-INSL3 fusion transcript has been confirmed to be carcinogenic. The five-year survival rate of patients with high expression of this fusion gene was significantly reduced. Gene knockout experiments confirmed that it could promote the proliferation and tumorigenesis ability of tumor cells.
2. Kumar, Narendra, et al. "Mucosal implications of oral Jak3-targeted drugs in COVID patients." Molecular Medicine 31.1 (2025): 203. https://doi.org/10.1186/s10020-025-01260-z
The article indicates that in COVID-19 infection, the overactivation of the JAK3 signaling pathway can exacerbate inflammation and tissue damage, making JAK3 inhibitors a potential therapeutic option. However, its oral preparations carry the risk of side effects such as immunosuppression, and it is necessary to explore optimization strategies to balance efficacy and safety.
3. Liongue, Clifford, et al. "Janus kinase 3 (JAK3): a critical conserved node in immunity disrupted in immune cell cancer and immunodeficiency." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25.5 (2024): 2977. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052977
The article indicates that JAK3 is the core medium for cytokine signal transduction and is crucial for the development and function of immune cells. Its gain-of-function mutations can cause malignant diseases such as leukemia, while loss-of-function mutations lead to severe combined immunodeficiency.
4. Yuan, Shengnan, et al. "PHF6 and JAK3 mutations cooperate to drive T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia progression." Leukemia 36.2 (2022): 370-382. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41375-021-01392-1
The article indicates that in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia, JAK3 mutations often coexist with PHF6 deletion. Research has found that the deletion of PHF6 aggravates the JAK3-driven leukemia process by inhibiting the Bai1-Mdm2-P53 pathway. The combined use of JAK3 inhibitors and MDM2 inhibitors can effectively alleviate the condition.
5. Smedley, William, and Amiya Patra. "JAK3 Inhibition Regulates Stemness and Thereby Controls Glioblastoma Pathogenesis." Cells 12.21 (2023): 2547. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12212547
The article indicates that JAK3 inhibitors can significantly inhibit the cell proliferation and tumor sphere formation of glioblastoma, weaken its stem cell characteristics, and induce cell differentiation, providing a potential new treatment strategy for this fatal brain tumor.
Creative Biolabs: JAK3 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality JAK3 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom JAK3 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our JAK3 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Liongue, Clifford, et al. "Janus kinase 3 (JAK3): a critical conserved node in immunity disrupted in immune cell cancer and immunodeficiency." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25.5 (2024): 2977. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052977
Anti-JAK3 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-HTLV-1 gp46 Recombinant Antibody (CBMW-H1006) (CBMAB-V208-1154-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALPL Antibody (B4-78) (CBMAB-1009CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-1728) (CBMAB-2077-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD33 Recombinant Antibody (6C5/2) (CBMAB-C8126-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AMOT Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A564) (CBMAB-A2552-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ACKR3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-261265) (CBMAB-C1023-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCNH Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1054) (CBMAB-C1111-FY)

-
Rat Anti-EMCN Recombinant Antibody (28) (CBMAB-E0280-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AKT1/AKT2/AKT3 (Phosphorylated T308, T309, T305) Recombinant Antibody (V2-443454) (PTM-CBMAB-0030YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CRTAM Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2235) (CBMAB-C2305-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ATF4 Recombinant Antibody (D4B8) (CBMAB-A3872-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BANF1 Recombinant Antibody (3F10-4G12) (CBMAB-A0707-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AFM Recombinant Antibody (V2-634159) (CBMAB-AP185LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-B2M Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0059) (CBMAB-0059-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-DLC1 Recombinant Antibody (D1009) (CBMAB-D1009-YC)

-
Rat Anti-CD34 Recombinant Antibody (MEC 14.7) (CBMAB-C10196-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADRB2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180026) (CBMAB-A1420-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ACE2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179293) (CBMAB-A0566-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-DMD Recombinant Antibody (D1190) (CBMAB-D1190-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ARID1B Recombinant Antibody (KMN1) (CBMAB-A3546-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








