MMP9 Antibodies
Background
MMP-9, also known as gelatinase B, is a zinc and calcium ion-dependent hydrolytic protease and an important member of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMPs) family. It mainly participates in the degradation and remodeling of the extracellular matrix (ECM), capable of decomposing various matrix components such as gelatin, type IV collagen, and elastin, and plays a key role in physiological processes such as tissue repair, angiogenesis, and inflammatory responses. MMP-9 was initially widely studied for its role in tumor metastasis, and its overexpression is closely related to various pathological processes such as cancer invasion, diabetic nephropathy and cardiovascular diseases. The activity of this enzyme is strictly regulated by tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs), especially the specific inhibition of TIMP-1. In recent years, MMP-9 has become an important target for cancer treatment and fibrotic disease research. Inhibitors and antibodies developed against it (such as andecaliximab) have entered the clinical trial stage, demonstrating potential clinical application value.
Structure of MMP9
MMP-9 is a medium-sized protein with a molecular weight of approximately 92 kDa, and its molecular weight varies among different species.
| Species | Human | Mice | Rats | Bovine |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 92 | 95 | 94 | 91 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains signal peptide and hinge region | 85% homology to humans | One more glycosylation site | Catalytic structure domain more conservative |
MMP-9 maintains its proenzyme state through its cysteine switch (Cys99). When this region is proteolytic and excised, the enzyme active center is exposed, thereby acquiring the ability to degrade extracellular matrix components such as type IV collagen. This activation mechanism enables it to play a key role in tissue remodeling and pathological processes.
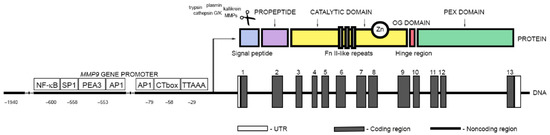 Fig. 1 A schematic representation of the MMP9 gene and protein organization.1
Fig. 1 A schematic representation of the MMP9 gene and protein organization.1
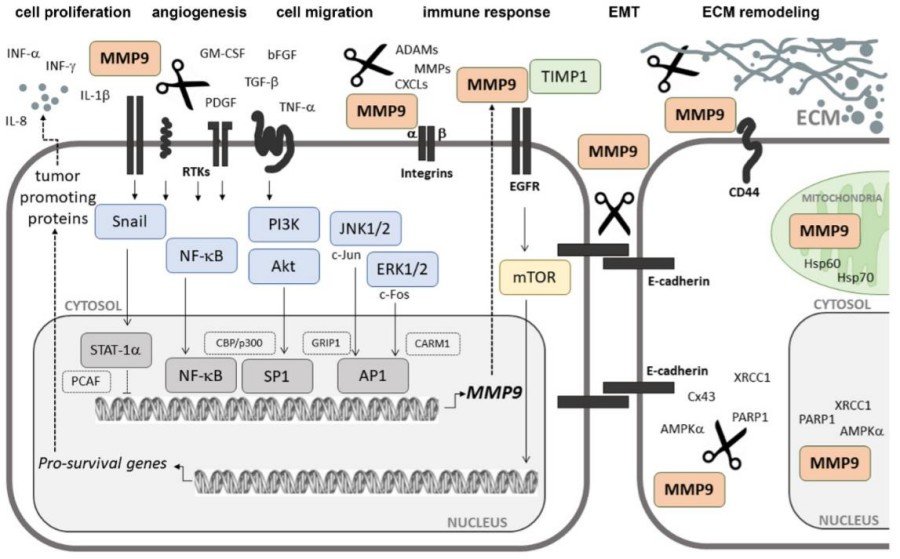 Fig. 2 Schematic representation of the signaling pathways involved in MMP9 expression.1
Fig. 2 Schematic representation of the signaling pathways involved in MMP9 expression.1
Key structural properties of MMP9:
- Amino-terminal signal peptide
- Propeptide domain
- Catalytic domain
- Hinge area
- Heme-binding protein-like domains
Functions of MMP9
The main function of MMP-9 is to degrade extracellular matrix and participate in various physiological and pathological processes.
| Function | Description |
| Extracellular matrix degradation | Specifically hydrolyze matrix components such as type IV collagen and gelatin to create space for cell migration. |
| Organizational Reshaping | Participate in normal tissue remodeling processes such as wound healing and embryonic development. |
| Angiogenesis | Promote the formation of new blood vessels through matrix degradation. |
| Inflammatory regulation | Influence of inflammatory cell migration and cytokine activation. |
| Tumor metastasis | Provide conditions for tumor cells to break through the basement membrane barrier, promote the invasion and metastasis. |
| Migration of immune cells | Assist white blood cells in crossing the vessel walls to reach the site of inflammation. |
The activity regulation of MMP-9 presents a typical "all or none" feature, and its proenzyme needs to be activated by proteolysis to exert its function. Compared with other matrix metalloproteinases, MMP-9 has higher specificity for gelatin substrates. This substrate selectivity enables it to play a unique role in pathological processes. The activity of this enzyme is specifically inhibited by TIMP-1, and this 1:1 inhibition ratio constitutes the key mechanism for in vivo balance regulation.
Applications of MMP9 and MMP9 Antibody in Literature
1. Augoff, Katarzyna, et al. "MMP9: a tough target for targeted therapy for cancer." Cancers 14.7 (2022): 1847. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14071847
The article indicates that MMP9 promotes tumor invasion and metastasis by degrading the extracellular matrix and is an important target for cancer treatment. Recently, selective MMP9 antibody inhibitors have made breakthroughs and are undergoing clinical trials, bringing new hope to targeted therapy. However, further exploration of their regulatory mechanisms is still needed to enhance therapeutic efficacy.
2. Ryu, Jina, et al. "Development of a CHO cell line for stable production of recombinant antibodies against human MMP9." BMC biotechnology 22.1 (2022): 8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12896-022-00738-6
In this study, a high-purity and high-sensitivity recombinant anti-HMMP9 antibody was successfully developed using the CHO cell expression system, and its efficient antigen binding ability was verified, providing a new antibody tool for the diagnosis and treatment of diseases such as cancer.
3. Juric, Vladi, et al. "MMP-9 inhibition promotes anti-tumor immunity through disruption of biochemical and physical barriers to T-cell trafficking to tumors." PLoS One 13.11 (2018): e0207255. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0207255
The mouse anti-MMP-9 monoclonal antibody developed in this study can inhibit the growth of HER2-positive breast cancer and enhance the immunotherapeutic effect of PD-L1 antibody by up-regulating T cell chemokines such as CXCL10. The combined treatment significantly increases the proportion of tumor-infiltrating memory/effector T cells and improves the immunosuppressive microenvironment.
4. Appleby, Todd C., et al. "Biochemical characterization and structure determination of a potent, selective antibody inhibitor of human MMP9." Journal of Biological Chemistry 292.16 (2017): 6810-6820. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M116.760579
This study resolved the crystal structure of the humanized monoclonal antibody GS-5745 complex with MMP9, revealing its dual inhibition mechanism by binding to the distal site of the enzyme: it not only prevents the activation of MMP9 but also allosterically inhibits its catalytic activity, providing a new targeted strategy for the treatment of inflammation and tumors.
5. Awasthi, Niranjan, et al. "Therapeutic efficacy of anti-MMP9 antibody in combination with nab-paclitaxel-based chemotherapy in pre-clinical models of pancreatic cancer." Journal of cellular and molecular medicine 23.6 (2019): 3878-3887. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14242
This study analyzed that the combination of anti-MMP9 antibody and nab- paclitaxel/gemcitabine significantly prolonged the survival period of pancreatic cancer models (with a maximum increase of 218%), exerting a specific targeting effect on the tumor microenvironment by reducing the expression of interstromal collagen and αSMA and increasing the level of IL-28, providing a new strategy for clinical combined treatment.
Creative Biolabs: MMP9 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality MMP9 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom MMP9 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our MMP9 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Augoff, Katarzyna, et al. "MMP9: a tough target for targeted therapy for cancer." Cancers 14.7 (2022): 1847. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14071847
Anti-MMP9 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-APOH Recombinant Antibody (4D9A4) (CBMAB-A3249-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BPGM Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-1806) (CBMAB-2155-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ARG1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYCL-103) (CBMAB-L0004-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD247 Recombinant Antibody (6B10.2) (CBMAB-C1583-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL6 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0442) (CBMAB-0445-YY)

-
Rabbit Anti-CBL Recombinant Antibody (D4E10) (CBMAB-CP0149-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-EIF4G1 Recombinant Antibody (2A9) (CBMAB-A2544-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AKT1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180546) (CBMAB-A2070-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV9 Recombinant Antibody (V2-634029) (CBMAB-AP023LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0216) (CBMAB-0217-YY)

-
Rat Anti-ABCC11 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179001) (CBMAB-A0236-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ACE2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179293) (CBMAB-A0566-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CEMIP Recombinant Antibody (3C12) (CBMAB-K0296-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CARTPT Recombinant Antibody (113612) (CBMAB-C2450-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BLNK Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0623) (CBMAB-0626-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATG5 Recombinant Antibody (9H197) (CBMAB-A3945-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ATM Recombinant Antibody (2C1) (CBMAB-A3970-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ACTN4 Recombinant Antibody (V2-6075) (CBMAB-0020CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BACE1 Recombinant Antibody (61-3E7) (CBMAB-1183-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-BRD3 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0801) (CBMAB-0804-YY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








