Anti-drug Antibody (ADA) Bridging ELISA
Anti-drug Antibody (ADA) Assays
Arising of ADAs against biotherapeutic drugs has been widely observed in preclinical and clinical research resulting in significant changes in toxicology, efficacy and pharmacokinetic (PK). These effects result from the generation of drug-induced (neutralizing) autoantibodies against e.g. insulin, erythropoietin and can be responsible for allergic reactions, and even anaphylactic shock. As a consequence, studies on ADA have become inevitable for bioengineered pharmaceuticals including biosimilars. Assays for the detection of ADAs facilitate understanding of potential immune responses to biologic drug candidates. Determining the presence of ADAs and evaluating their clinical implications are important for any antibody drug development program. A complete ADA determination entails the following steps:
- Screening Assays – bridging ELISA, direct ELISA or competitive ELISA
- Confirmation Assay - determination of specificity
-
Characterization Assay - isotypes identification, neutralizing ability
- IgM ADA may be an early marker of ADA formation.
- The presence of IgE ADA indicates an allergic reaction against the drug.
- The measurement of IgG subclasses may be supportive for the biological activities of ADA. For instance, in humans, IgG1 and IgG3 are mainly involved in complement activation and are more prone to natural killer (NK) cell recognition.
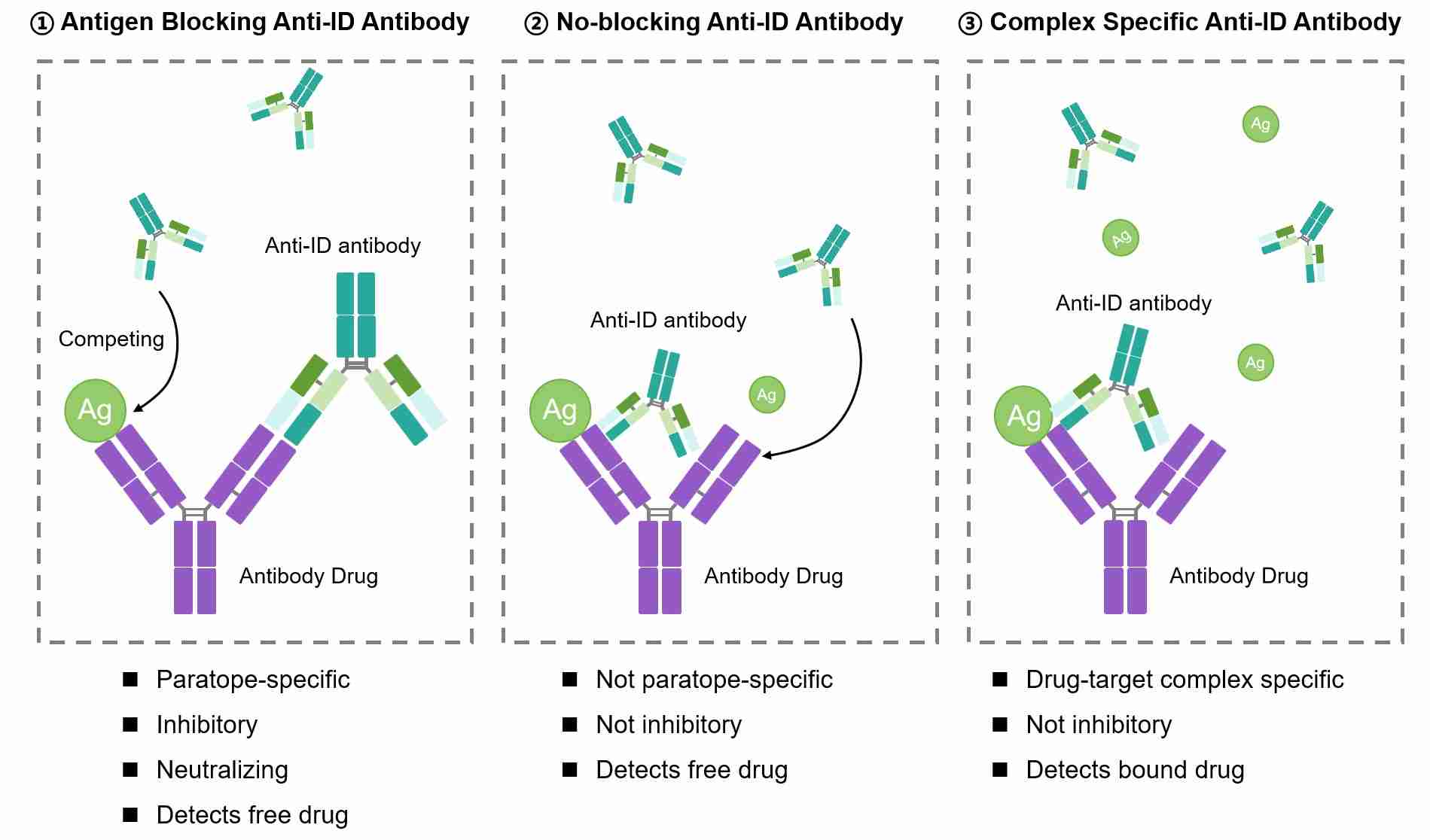 Fig.1 Types of anti-biotherapeutic antibody.
Fig.1 Types of anti-biotherapeutic antibody.
Using a combination of the different types of drug-specific antibodies offers the assay developer enhanced flexibility and better overall information about the availability and state of the drug antibody. As shown in Figure 1, type 1 anti-idiotypic antibodies are inhibitory for measuring free drug and are ideal for neutralizing assays and PK bridging ELISA. Type 1 anti-idiotypic antibodies could be used as a control or calibrator as a surrogate for human ADAs. Type 2 antibody is a non-inhibitory antibody that can be used to detect both free and bound drug in the sample. Type 3 antibodies are drug-target complex binders that can be used to quantify bound drug, as opposed to free drug levels.
Bridging ELISA
Bridging ELISA is a special case of a sandwich ELISA in which a dimeric or oligomeric antigen (most often an antibody in a sample) is detected by a capture and detection antibody. Bridging ELISAs are most frequently used for the detection of IgG in PK or ADA assays. High affinity, fully human ADAs are ideal for use in PK bridging ELISAs and as a reference standard in ADA assays.
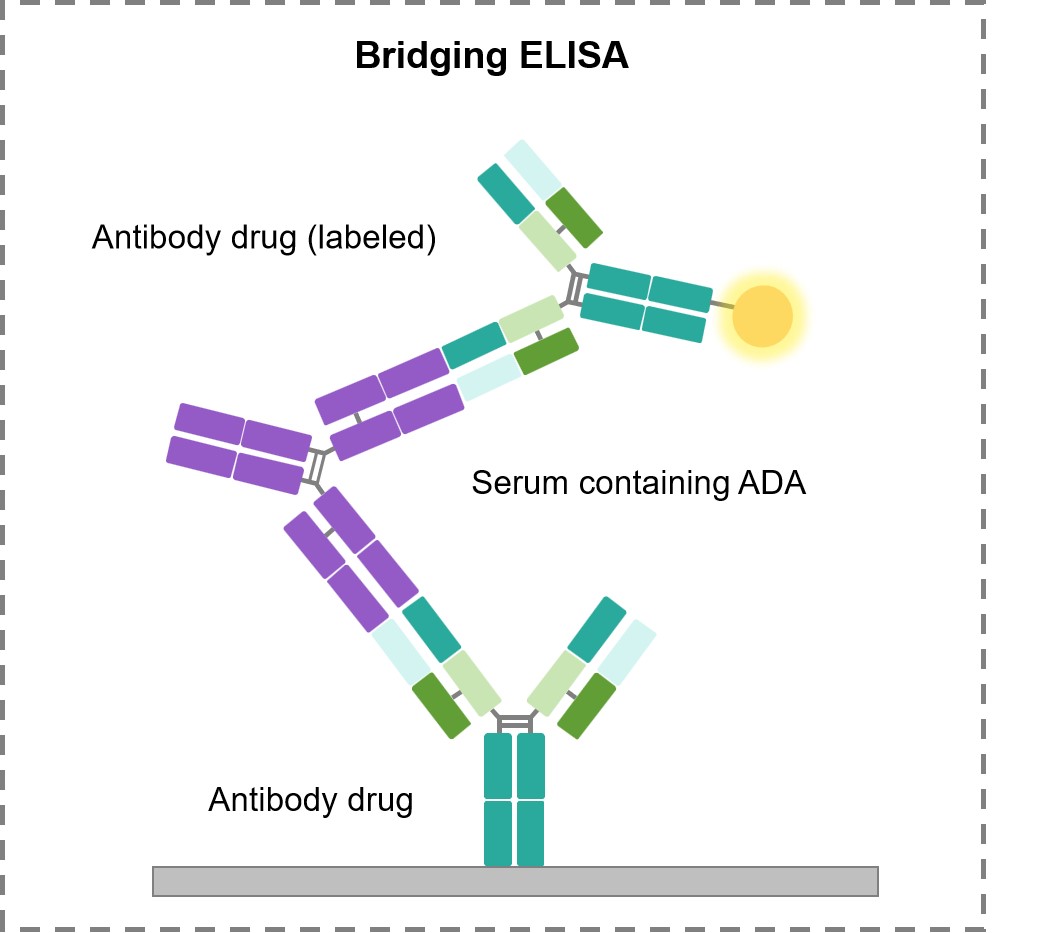 Fig.2 Bridging ELISA for ADA testing.
Fig.2 Bridging ELISA for ADA testing.
Advantages of the bridging ELISA
- The capability to detect antibodies regardless of their isotype or the species of origin.
- Reducing background readings by using fewer amplification steps.
- The requirement for two specific binding events for the target drug increases the specificity of the assay.
Click for Protocol of Anti-drug antibody (ADA) Bridging ELISA and Troubleshooting of Anti-drug antibody (ADA) Bridging ELISA.
