BMP1 Antibodies
Background
BMP1 is a secreted protein belonging to the transforming growth factor - β superfamily, mainly involved in the bone development and tissue repair processes of vertebrates. The protease encoded by this gene can cleave various extracellular matrix precursor proteins and plays a key role in the formation of collagen fibers and bone mineralization. BMP1 was first discovered in 1988 when studying the mechanism of bone repair. Its unique dual function - serving as both a morphogenetic signaling molecule and a matrix metalloproteinase - has made it an important research object in developmental biology. The discovery of this gene has greatly promoted people's understanding of the molecular mechanisms of skeletal system development and provided new targets for clinical research on osteoporosis and fracture repair, etc. Subsequent studies have also revealed the significant role of BMP1 in multiple physiological processes such as embryonic development, tooth formation, and wound healing.
Structure of BMP1
BMP1 is a metalloproteinase with a molecular weight of approximately 100-120kDa, and its precise molecular weight varies depending on different splicing variants. This protein has a relatively high structural conservation among different species, but there are certain differences in the composition of functional domains.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Zebrafish | Bovine |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 110-120 | 105-115 | 95-110 | 108-118 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contain more than one CUB structure domain and protease catalytic domain | Highly homologous to humans | Retain the core catalytic function | Existing species specificity |
BMP1 is composed of approximately 700 to 800 amino acids, and its tertiary structure contains a catalytic zinc ion binding site, which is the key to its proteolytic activity. This enzyme mediates substrate recognition through the CUB domain, while the metalloproteinase domain is responsible for cleecting matrix proteins such as procollagen. Its active center contains a conserved HEXXH motif, which maintains enzyme activity through the coordination of histidine residues with zinc ions. BMP1 is widely present in vertebrates, and its structural features reflect its core role in extracellular matrix remodeling.
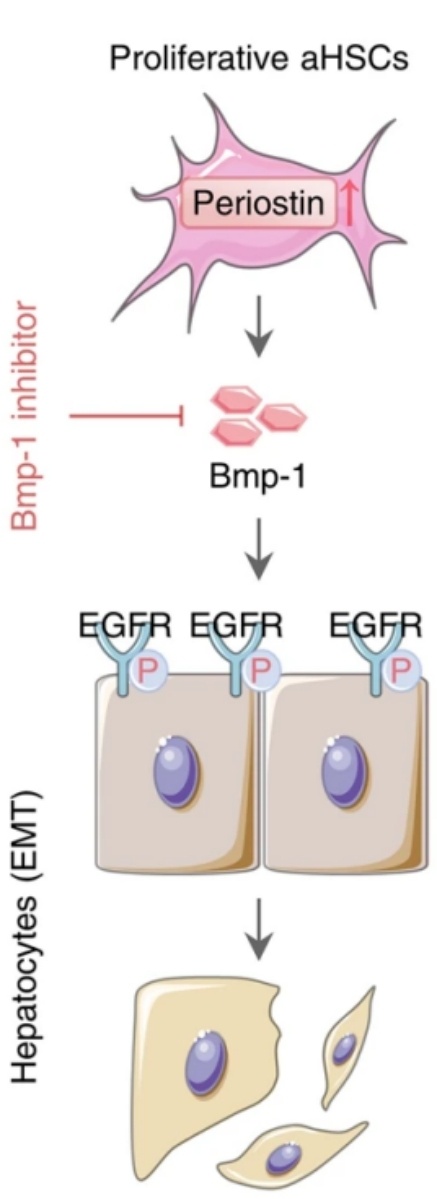 Fig. 1 BMP-1 promotes the occurrence of liver fibrosis driven by EMT in hepatocytes by activating the EGFR signaling pathway.1
Fig. 1 BMP-1 promotes the occurrence of liver fibrosis driven by EMT in hepatocytes by activating the EGFR signaling pathway.1
Key structural properties of BMP1:
- Multi-domain metalloproteinases
- Zinc ion-dependent active centers
- Substrate identification system
- Disulfide bonds stabilize the structure
- pH sensitivity
Functions of BMP1
The core function of the BMP1 gene is to participate in the maturation of extracellular matrix and the formation of bone tissue, and at the same time play a regulatory role in various physiological and pathological processes.
| Function | Description |
| Collagen processing | Specifically cleft the C-terminal propeptide of type I/III collagen to promote the correct assembly and cross-linking of collagen fibers. |
| Bone mineralization is initiated | By hydrolyzing matrix proteins such as osteocalcin, nucleation sites are provided for hydroxyapatite crystals. |
| Regulation of wound repair | Activate TGF-β superfamily growth factors (such as BMP2/4) to promote the migration and proliferation of fibroblasts. |
| Dentin formation | During the development of tooth germs, it cuts dentin matrix proteins and regulates the differentiation of odontoblasts. |
| Tumor microenvironment remodeling | Tumor metastasis by matrix metalloproteinases active effects, the hit show in breast cancer. |
The enzymatic digestion activity of BMP1 has strict substrate specificity, and its catalytic efficiency is triple regulated by pH value, zinc ion concentration and endogenous inhibitors (such as TIMP). Unlike most proteases, BMP1 can not only cleaving specific protein sequences (such as Asp-Xaa bonds), but also recognize spatially conformation-specific substrates through the CUB domain. This dual recognition mechanism ensures its precise regulation in complex physiological environments.
Applications of BMP1 and BMP1 Antibody in Literature
1. Ma, Hsiao-Yen, et al. "BMP1 is not required for lung fibrosis in mice." Scientific reports 12.1 (2022): 5466. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-09557-3
Research has found that the expression of BMP1 is elevated in pulmonary fibrosis tissues of humans and mice. However, through an induced conditional knockout mouse model, it has been confirmed that the absence of BMP1 has no protective effect on bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis and does not affect the production of type I procollagen C-terminal peptides. The results indicated that BMP1 was not a key factor in pulmonary fibrosis and might not be suitable as a therapeutic target for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
2. Zhuang, Mengmeng, et al. "LncRNA Bmp1 promotes the healing of intestinal mucosal lesions via the miR-128-3p/PHF6/PI3K/AKT pathway." Cell Death & Disease 12.6 (2021): 595. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-021-03879-2
Studies have found that the expression of lncRNA Bmp1 is elevated in intestinal mucosal injury tissues. Its overexpression can upregulate PHF6 by adsorbing miR-128-3p, activate the PI3K/AKT pathway, promote the proliferation and migration of intestinal epithelial cells, and thereby alleviate intestinal mucosal injury. This study revealed the mechanism of action of Bmp1 in intestinal mucosal repair.
3. Gong, Mancheng, et al. "Upregulation of BMP1 through ncRNAs correlates with adverse outcomes and immune infiltration in clear cell renal cell carcinoma." European journal of medical research 28.1 (2023): 440. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40001-023-01422-x
Research has found that BMP1 is highly expressed in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) and is associated with a poor prognosis for patients. Its regulatory mechanism may involve ncRNA pathways such as the LINC00685/hsa-miR-532-3p/BMP1 axis, and the expression of BMP1 is significantly correlated with tumor immune infiltration and immune checkpoint molecules, suggesting its role in the progression of ccRCC.
4. Zhou, Yiyi, et al. "An analysis of BMP1 associated with m6A modification and immune infiltration in pancancer." Disease Markers 2022.1 (2022): 7899961. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/7899961
Studies have shown that BMP1 is differentially expressed in 14 types of cancer and is associated with immunotherapy response, tumor microenvironment and m6A modification. Low BMP1 levels may enhance the efficacy of immunotherapy and be associated with sensitivity to specific anti-cancer drugs, suggesting its value as a potential target for cancer prognosis prediction and immunotherapy.
5. Kellett, Katherine AB, et al. "Proteolysis of the low‐density lipoprotein receptor in hepatocytes is mediated by BMP1 but not by other astacin proteases." FEBS letters 597.11 (2023): 1489-1502.https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.14667
Research has found that BMP1 is the only zinc metalloproteinase capable of cutting the ligand-binding domain of low-density lipoprotein receptors (LDLR). By altering the key sites of LDLR in mice, it can be cleaved by BMP1. This study revealed the specific mechanism of BMP1 in regulating LDLR function and cholesterol metabolism.
Creative Biolabs: BMP1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality BMP1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom BMP1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our BMP1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Wan, Sizhe, et al. "Activated hepatic stellate cell-derived Bmp-1 induces liver fibrosis via mediating hepatocyte epithelial-mesenchymal transition." Cell Death & Disease 15.1 (2024): 41.https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-024-06437-8
Anti-BMP1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-APCS Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A663) (CBMAB-A3054-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC7 Recombinant Antibody (88C570) (CBMAB-L0261-YJ)

-
Rabbit Anti-CCL5 Recombinant Antibody (R0437) (CBMAB-R0437-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-BRD3 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0801) (CBMAB-0804-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATG5 Recombinant Antibody (9H197) (CBMAB-A3945-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-AP2M1 (Phosphorylated T156) Recombinant Antibody (D4F3) (PTM-CBMAB-0610LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BrdU Recombinant Antibody (IIB5) (CBMAB-1038CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CASQ1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0863) (CBMAB-C0918-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CGAS Recombinant Antibody (CBFYM-0995) (CBMAB-M1146-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-C1QC Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0600) (CBMAB-C0654-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD33 Recombinant Antibody (P67.6) (CBMAB-C10189-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CDK7 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C1783) (CBMAB-C3221-YY)

-
Rabbit Anti-Acetyl-Histone H3 (Lys36) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623395) (CBMAB-CP0994-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ALDOA Recombinant Antibody (D73H4) (CBMAB-A2314-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC3 Recombinant Antibody (16E63) (CBMAB-C3367-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-EMP3 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYE-0100) (CBMAB-E0207-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ABL2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179121) (CBMAB-A0364-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BLNK Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0623) (CBMAB-0626-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CTNND1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2414) (CBMAB-C2487-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACTB Recombinant Antibody (V2-179553) (CBMAB-A0870-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








