EDAR Antibodies
Background
EDAR gene encodes a transmembrane protein belonging to the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, which is mainly expressed in ectodermal tissues during embryonic development. This protein regulates the formation and differentiation of skin accessory organs such as hair, teeth, and sweat glands by activating signaling pathways like NF-κB. Research on the function of EDAR has revealed its special position in the adaptive evolution of East Asian populations. Specific mutations in this gene (such as V370A) are associated with phenotypes such as hair thickness and sweat gland density, and were confirmed to be related to adaptation to cold environments through population genetic analysis around 2010. The research on its molecular mechanism has deepened people's understanding of the association among gene variation, phenotypic differences and natural selection, and has become a classic case in the field of evolutionary developmental biology.
Structure of EDAR
The protein encoded by the EDAR gene is a type I transmembrane receptor with a molecular weight of approximately 40 kDa. The molecular weight of this protein varies slightly among different mammals, mainly due to interspecific variations in the amino acid sequence of the cysteine-rich domain in its extracellular region. The following table shows the molecular weight and main structural characteristics of EDAR proteins in different species:
| Species | Human | Mouse | Dogs | Bovine |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 40 | 39.8 | 40.2 | 39.9 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Extracellular region contains nine characteristic cysteine residues, forming a typical structure of TNF receptor domain | Extracellular region sequence is highly conserved, more than 90% homology with humans | There are species-specific variations in the amino acid composition of the transmembrane region | Intracellular die structure domain sequence is highly conserved |
This protein is composed of 448 amino acids, and its primary structure includes a signal peptide sequence, an extracellular ligand-binding domain, a transmembrane domain, and an intracellular death domain. Its secondary structure is mainly composed of β -folds, which form specific spatial conformations in the extracellular region and are responsible for the recognition and binding to the ligand EDN. Intracellular death domains initiate cascade reactions of downstream NF-κB and other signaling pathways through specific protein-protein interactions.
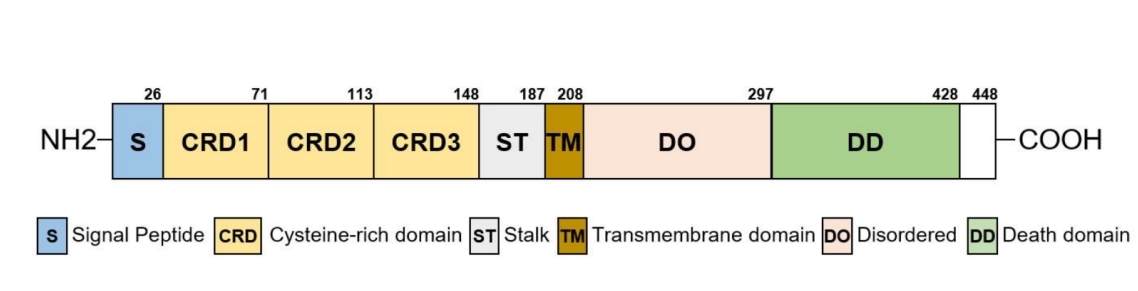 Fig. 1 Domain structure of EDAR.1
Fig. 1 Domain structure of EDAR.1
Key structural properties of EDAR:
- Extracellular ligand binding domains rich in cysteine
- Single transmembrane helical structure
- Intracellular death domains mediate signal transduction
Functions of EDAR
The core function of the EDAR gene is to regulate the development of ectodermal organs during the embryonic period. However, it also plays a role in various physiological and evolutionary processes.
| Function | Description |
| Hair/Tooth development | NF-κB is activated through the EDAR/EDARADD signaling pathway, directly regulating the occurrence and differentiation of hair follicles, sweat glands and tooth morphology. |
| Sweat gland formation | The function of determining the density and distribution of sweat glands is believed to be related to the adaptive evolution of ancient populations to hot climates. |
| Immune regulation | The NF-κB pathway it mediates plays an auxiliary role in the establishment and maintenance of the skin immune barrier. |
| Evolutionary adaptation | Specific mutation sites (such as V370A) are positively selected in East Asian populations and are associated with phenotypes such as thick and straight hair, serving as a classic example of natural selection. |
Unlike the extensive pleiotropic effects of most genes, the function of EDAR is highly concentrated in ectodermal derivatives, and the strength of its signaling pathway directly determines heritable physical characteristics such as hair thickness and tooth crown shape.
Applications of EDAR and EDAR Antibody in Literature
1. Gao, Yanzi, et al. "The EDA/EDAR/NF-κB pathway in non-syndromic tooth agenesis: A genetic perspective." Frontiers in genetics 14 (2023): 1168538. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2023.1168538
The article indicates that non-syndromic tooth loss (NSTA) is a common dental developmental malformation, mainly caused by genetic factors. As a key member of the EDA/EDAR/NF-κB signaling pathway, mutations in the EDAR gene play a significant role in the pathogenesis of NSTA and ectodermal dysplasia. This article focuses on the tooth development defects caused by EDAR mutations.
2. Williams, Rebecca, et al. "Elevated EDAR signalling promotes mammary gland tumourigenesis with squamous metaplasia." Oncogene 41.7 (2022): 1040-1049. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-021-01902-6
Research has found that EDAR is a death receptor associated with certain types of breast cancer. In estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer with squamous differentiation, the expression of EDAR is significantly elevated. Animal experiments have confirmed that the enhanced EDAR signaling can drive the occurrence of breast tumors by activating the β-catenin pathway, thereby revealing that EDAR is a new oncogene for breast cancer.
3. Wegner, Kyle A., et al. "Edar is a downstream target of beta-catenin and drives collagen accumulation in the mouse prostate." Biology Open 8.3 (2019): bio037945. https://doi.org/10.1242/bio.037945
This study explored the role of EDAR in prostate development. It was found that β-catenin can transcriptionally activate the expression of Edar in the prostate. Functional experiments have shown that although Edar does not affect the morphogenesis of prostate branches, its overexpression can lead to abnormal thickening of the prostate matrix and collagen deposition in adult mice, revealing a new function of EDAR in endodermal organs.
4. Kim, Youn Jung, et al. "Critical Considerations in Calling Disease-Causing EDAR Mutations in Nonsyndromic Oligodontia." Journal of Clinical Medicine 13.23 (2024): 7328. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13237328
This study identified recessive inherited EDAR gene mutations in families with non-syndromic oligodontic malformations (NSO). The luciferase reporter gene assay confirmed that these novel missense mutations led to impaired function of the EDAR protein and reduced the transcriptional activity of the EDA signaling pathway, thereby clarifying the molecular mechanism of its pathogenicity.
5. Sadier, Alexa, et al. "Modeling Edar expression reveals the hidden dynamics of tooth signaling center patterning." PLoS biology 17.2 (2019): e3000064. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3000064
This study, by analyzing the expression dynamics of the Edar gene during the development of molars in mice, reveals that the formation of dental signal centers follows a "activation-inhibition" reaction-diffusion model. Research has found that the extensive activation of Edar precedes spatial constraints, and this process is malleable. Reducing the activity of Edar can actually "save" the R2 signal center that was about to disappear, indicating that the pattern formation is a dynamic adjustment rather than a predestined result.
Creative Biolabs: EDAR Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality EDAR antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom EDAR Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our myoglobin antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Kim, Youn Jung, et al. "Critical Considerations in Calling Disease-Causing EDAR Mutations in Nonsyndromic Oligodontia." Journal of Clinical Medicine 13.23 (2024): 7328. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13237328
Anti-EDAR antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-CARTPT Recombinant Antibody (113612) (CBMAB-C2450-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A950) (CBMAB-A4388-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AHCYL1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180270) (CBMAB-A1703-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-DDC Recombinant Antibody (8E8) (CBMAB-0992-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AKT1/AKT2/AKT3 (Phosphorylated T308, T309, T305) Recombinant Antibody (V2-443454) (PTM-CBMAB-0030YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CDK7 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C1783) (CBMAB-C3221-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ESR1 Recombinant Antibody (Y31) (CBMAB-1208-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AK4 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180419) (CBMAB-A1891-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-C4B Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C2996) (CBMAB-C4439-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-C5b-9 Recombinant Antibody (aE11) (CBMAB-AO138LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCS Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1093) (CBMAB-C1150-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AKR1C3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-12560) (CBMAB-1050-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-C1QC Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0600) (CBMAB-C0654-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-FeLV g27 Recombinant Antibody (1) (CBMAB-V208-1714-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-AKT2 (Phosphorylated S474) Recombinant Antibody (V2-556130) (PTM-CBMAB-0605LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0790) (CBMAB-0793-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-AGK Recombinant Antibody (V2-258056) (CBMAB-M0989-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-APC Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A661) (CBMAB-A3036-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-ATF4 Recombinant Antibody (D4B8) (CBMAB-A3872-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BACE1 Recombinant Antibody (61-3E7) (CBMAB-1183-CN)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








