EPRS is a bifunctional enzyme that mainly exists in the cytoplasm of eukaryotes. This enzyme can not only catalyze the synthesis of glutamyl-trNA but also participate in the γ -interferon mediated translation inhibition pathway as a component of the multi-protein complex, playing a dual role in protein synthesis and immune regulation. Mammalian cells rely on EPRS to precisely regulate protein translation, especially selectively inhibiting the translation of specific mRNAs when responding to inflammatory reactions. Initially identified as a member of the aminoacyl-trNA synthase family in 1978, EPRS has become one of the most deeply studied enzymes in this family due to its unique bifunctional characteristics. The analysis of its crystal structure provides an important basis for understanding the mechanism of enzymatic reactions.
EPRS is a bifunctional protein with a molecular weight of approximately 150-170 kDa, and its precise molecular weight varies by species and splicing variants.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Cattle | Zebrafish |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 170 | 168 | 172 | 155 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains a unique linked peptide domain | Lack of human-specific regulatory sequences | The catalytic domain is highly conserved | Simplified variant |
EPRS is composed of approximately 1,400 amino acids, and its structure contains two independent functional domains: the N-terminal glutamyl-trNA synthase catalytic domain and the C-terminal polypeptide linking domain. This protein achieves functional switching through precise conformational changes - the catalytic domain adopts a typical Rossmann folding structure to be responsible for tRNA aminoacylation, while the ligand domain forms a helical beam structure to participate in γ-interferon signaling. The key active sites are composed of the highly conserved HIS-Leu-Gley-His motif, and its spatial arrangement directly affects the ATP binding efficiency. The special dual-domain configuration enables EPRS to not only perform translation functions but also participate in cellular stress responses as a signaling molecule.
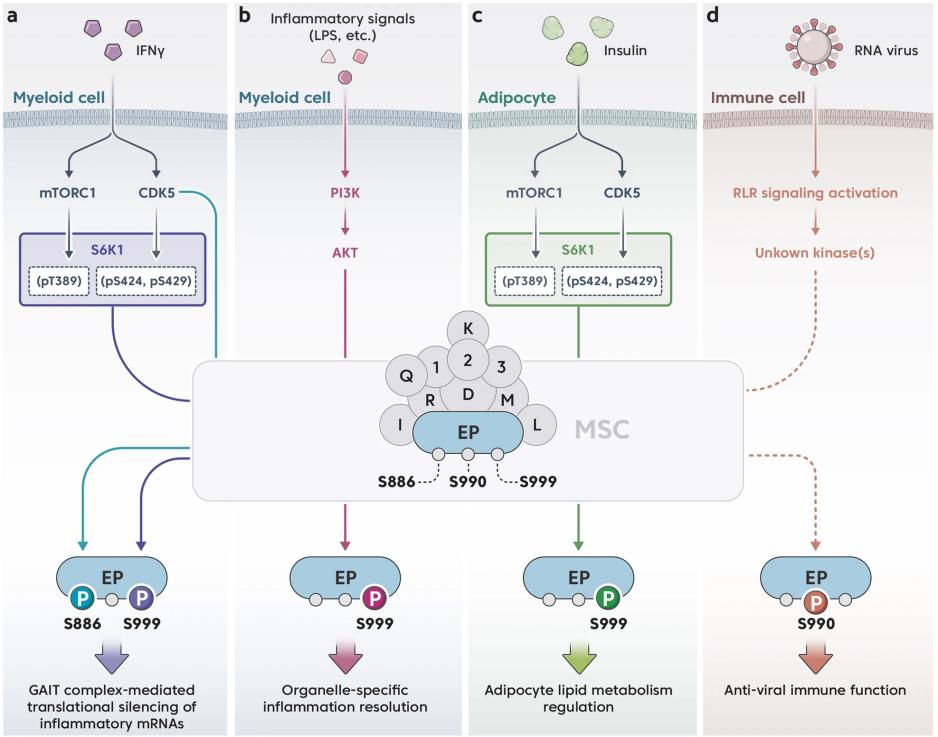 Fig. 1 Phosphocode-dependent EPRS1 signaling pathways are activated by different stimuli.1
Fig. 1 Phosphocode-dependent EPRS1 signaling pathways are activated by different stimuli.1
Key structural properties of EPRS:
The core function of EPRS is to catalyze the synthesis of glutamyl-trNA and participate in the immune regulatory pathway simultaneously. This enzyme plays a dual role in different physiological processes.
| Function | Description |
| Protein synthesis | Catalyze the combination of glutamic acid and tRNA^Glu to ensure the accurate translation of the genetic code. |
| Translation regulation | As a component of the multi-protein complex, it selectively inhibits the translation of specific mRNAs in response to interferon signals. |
| Regulation of inflammatory response | Change the conformation through phosphorylation modification and participate in the antiviral immune response. |
| Cellular stress response | Under the condition of the amino acids starvation is activated, regulating metabolism related gene expression. |
| Developmental regulation | The embryonic development process is affected through the quality control mechanism of tRNA synthesis. |
EPRS of dynamic performance for the typical double substrates orderly reaction mechanism: first, in combination with ATP, coupled with glutamic acid, finally combining with tRNA. Unlike most aminoacyl-trNA synthases, the activity of EPRS is regulated by both translation factors and signaling molecules. This unique regulatory mode makes it a key node connecting protein synthesis and cellular signal transduction.
1. Norcum, Mona Trempe, and J. David Dignam. "Immunoelectron microscopic localization of glutamyl-/prolyl-tRNA synthetase within the eukaryotic multisynthetase complex." Journal of Biological Chemistry 274.18 (1999): 12205-12208. https://www.jbc.org/article/S0021-9258(19)73339-0/fulltext
In this study, bifunctional EPRS in eukaryotic multi-synthase complexes was located for the first time through immunoelectron microscopy. This complex contains nine aminoacyl-trNA synthetases, and EPRS, as a key component, is located at the junction of the arm and base of the "Y" -shaped structure of the complex. In the study, anti-prolyl-trNA synthase antibody was used. In the negative staining electron microscope images of the rabbit reticulocytic complex, EPRS was observed to be located in the central region of the particles, verifying the existing structural model. In addition to participating in protein synthesis, EPRS also plays a role in cellular signal transduction.
2. Kurata, Keiji, et al. "Prolyl-tRNA synthetase as a novel therapeutic target in multiple myeloma." Blood cancer journal 13.1 (2023): 12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41408-023-00787-w
This study reveals that EPRS is a new therapeutic target for multiple myeloma. Inhibitor NCP26 disrupts the protein quality control of tumor cells and induces apoptosis by blocking proline aminoacylation, down-regulating key proteins such as CD138 and MYC. Experiments have confirmed that EPRS inhibition can overcome metabolic adaptation and show significant anti-tumor activity both in vivo and in vitro, providing a new strategy for clinical treatment.
3. Lee, Eun-Young, et al. "Glutamyl-prolyl-tRNA synthetase 1 coordinates early endosomal anti-inflammatory AKT signaling." Nature communications 13.1 (2022): 6455. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-34226-4
The study found that EPRS1 through regulating AKT signaling pathways play a role of anti-inflammatory. When the inflammation is activated, AKT phosphorylates serine at position 999 of EPRS1, promoting its release from the multi-synthase complex. EPRS1 localizes AKT to the early endosome by binding to the endosome membrane lipid PtdIns3P, forming a specific anti-inflammatory signal complex, enhancing the phosphorylation of GSK3β, and promoting the production of anti-inflammatory factors. The absence of EPRS1 can intensify the inflammatory response and affect the survival of mice with sepsis and colitis. This study reveals the new function of EPRS1 as a regulatory factor of inflammatory homeostasis.
4. Ting, Shu Mei, and J. D. Dignam. "Post-transcriptional regulation of glutamyl-prolyl-tRNA synthetase in rat salivary gland." Journal of Biological Chemistry 269.12 (1994): 8993-8998. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(17)37066-7
This article's research indicates that after isoproterenol treatment in rats, the EPRS activity significantly increased, accompanied by an increase in the synthesis of low-molecular-weight prolyl-trNA synthetase and proline-rich glycoprotein. After drug withdrawal, both enzyme activity and glycoprotein levels decreased. Northern blotting analysis showed that the level of EPRS mRNA changed little, indicating that its synthesis was mainly regulated at the post-transcriptional level and was related to the protein synthesis and utilization of proline and glutamic acid.
5. Lee, Eun-Young, Jungwon Hwang, and Myung Hee Kim. "Phosphocode-dependent glutamyl-prolyl-tRNA synthetase 1 signaling in immunity, metabolism, and disease." Experimental & Molecular Medicine 55.10 (2023): 2116-2126. https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-023-01094-x
This article indicates that EPRS1 is a key component of the mammalian polysynthase complex (MSC). Besides participating in protein translation, it also regulates immune responses and metabolic balance through phosphorylation. Studies have shown that EPRS1 plays a significant role in inflammation resolution and metabolic regulation, and is associated with the occurrence of diseases such as cancer. This review focuses on the non-classical functions of EPRS1 and its regulatory mechanisms in diseases.
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality EPRS antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies optimized for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western Blot, Immunohistochemistry (IHC), and other immunoassays.
For more details on our EPRS antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at info@creative-biolabs.com.
Reference
