MR1 Antibodies
Background
MR1 gene encodes major histocompatibility complex class I related protein, which is widely present in various human cells as an antigen presentation molecule. This gene activates the innate immune response pathway by binding to microbial metabolites (such as vitamin B2 derivatives) and presenting them to mucosa-associated invariant T cells (MAIT cells). MR1 plays a core role in pathogen defense as it can identify the conserved metabolite characteristics of multiple pathogens, enabling rapid early warning of infections. This gene was first identified by a research team through genomic screening technology in 1995. Its unique antigen presentation mechanism was cracked by structural biology research in 2012, revealing the special evolutionary significance of the cross-population conservation of non-polymorphic MHC molecules. The discovery of the MR1 pathway not only revolutionizes the understanding of host-pathogen interactions but also provides precise targets for the development of novel vaccines and immunotherapy.
Structure of MR1
The MR1 gene encodes major histocompatibility complex Class I related proteins, with a molecular weight of approximately 42 kDa, and is highly conserved across different species. This protein is composed of three domains: α1, α2 and α3. It recognizes microbial metabolites (such as vitamin B2 derivatives) through the antigen-binding slots formed by the α1 and α2 domains. Its tertiary structure adopts a typical immunoglobulin folding pattern, relying on conserved disulfide bonds (Cys125-Cys191) and key amino acid residues (such as Tyr-84 and Arg-9) to maintain structural stability and antigen-presenting function. MR1 protein is widely expressed in various tissue cells and plays a role in pathogen monitoring by activating MAIT cells in mucosal immunity.
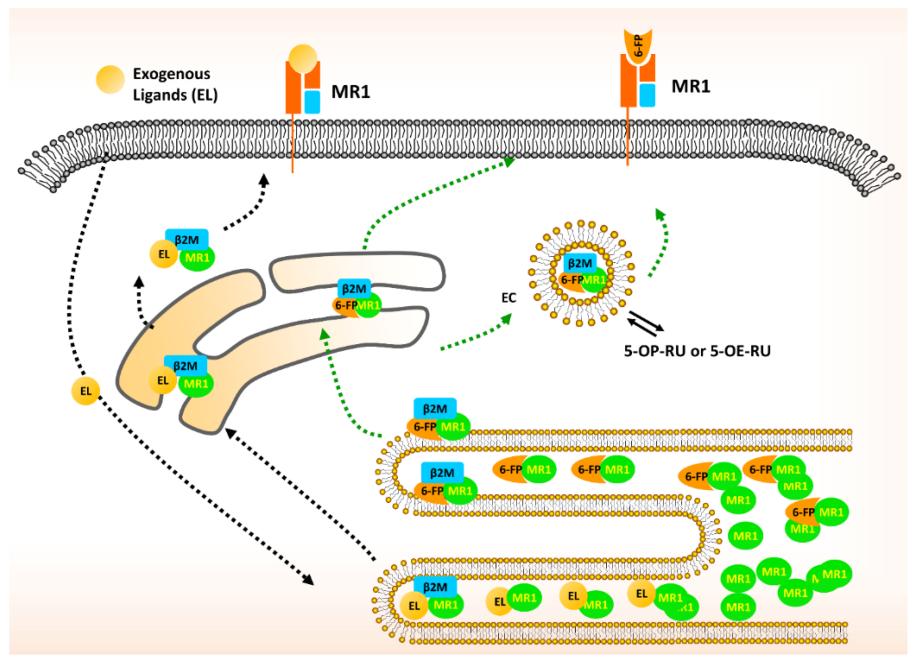 Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of MR1 trafficking and presentation.1
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of MR1 trafficking and presentation.1
Key structural properties of MR1:
- Conserved immunoglobulin folding domain
- Hydrophobic antigen-binding slots recognize microbial metabolites
- Nonpolymorphic α1/α2 domains enable broad-spectrum antigen presentation
- Key tyrosine and arginine residues maintain structural stability and are involved in T cell activation
Functions of MR1
The main function of the MR1 gene is to mediate antigen presentation and T cell activation in mucosal immunity. In addition, it is also involved in a variety of immune regulatory processes, including pathogen recognition, autoimmune regulation and inflammatory response.
| Function | Description |
| Antigen presentation | By binding to microbial metabolites (such as vitamin B₂ derivatives) and presenting them to mucosa-associated invariant T cells (MAIT cells), an immune response is initiated. |
| Immune surveillance | Extensively identify conserved metabolites of pathogens such as bacteria and fungi to achieve early warning and defense against various infections. |
| Autoimmune regulation | Participate in to maintain the immune balance, abnormal expression may be associated with autoimmune disease. |
| Inflammatory regulation | In the context of infection or tissue damage, the intensity of local inflammatory response is affected by regulating the activity of MAIT cells. |
| Immune memory formation | Support MAIT cells in forming memory-like responses under repeated antigen stimulation and enhance the adaptive defense of the mucosal barrier. |
The antigen recognition mechanism of MR1 is non-polymorphic and highly conserved, which is different from the pattern of classical MHC molecule presenting polypeptides, indicating that it may undertake a broad and fundamental immune surveillance function in evolution.
Applications of MR1 and MR1 Antibody in Literature
1. Vacchini, Alessandro, et al. "MR1-restricted T cells are unprecedented cancer fighters." Frontiers in immunology 11 (2020): 751. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.00751
The article indicates that the MR1 molecule can present bacterial antigens to MAIT cells and autoantigens to MR1T cells. MR1T cells can recognize and kill various tumor cells and have immunomodulatory functions, while MAIT cells may promote cancer progression. This article explores the regulatory role and therapeutic potential of MR1-restricted T cells in tumor immunity.
2. Flores-Villanueva, Pedro, et al. "MR1-restricted T cells in cancer immunotherapy." Cancers 12.8 (2020): 2145. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12082145
The article indicates that the MR1 molecule can present tumor-specific metabolites and activate non-MAIT-type MR1-restricted T cells. This type of cell can specifically kill various cancer cells without harming normal cells. Due to the monomorphism and wide expression of MR1, targeting MR1 may become a novel immunotherapy strategy for pan-cancer types.
3. Kim, Se-Jin, and Elham Karamooz. "MR1-and HLA-E-dependent antigen presentation of mycobacterium tuberculosis." International journal of molecular sciences 23.22 (2022): 14412.https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232214412
The article indicates that MR1 is a highly conserved non-classical antigen-presenting molecule that can present microbial metabolite antigens to MR1-restricted T cells. In Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection, the immune response mediated by MR1 plays a significant role in controlling the infection and provides a potential target for the development of new vaccines.
4. Wang, Zhiding, et al. "MR1-restricted T cells: the new dawn of cancer immunotherapy." Bioscience Reports 40.11 (2020): BSR20202962.https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20202962
The article indicates that MR1-restricted T cells can recognize broad-spectrum cancer cells in a non-HLA-dependent manner and are not subject to HLA-restricted constraints. It shows significant potential in cancer immunotherapy by recognizing the activation of metabolic antigens presented by MR1, providing a new direction for the development of novel pan-cancer therapies.
5. Corbett, Alexandra J., et al. "Antigen recognition by MR1-reactive T cells; MAIT cells, metabolites, and remaining mysteries." Frontiers in immunology 11 (2020): 1961.https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.01961
The article indicates that the MR1 molecule activates MAIT cells and a broader range of MR1-reactive T cells (MR1T cells) by presenting small molecule antigens such as vitamin B. These cells play a significant role in infections, autoimmune diseases and cancer, and their ligand recognition mechanisms and functions still require further research.
Creative Biolabs: MR1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality MR1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom MR1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our MR1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support,contact us at email.
Reference
- Flores-Villanueva, Pedro, et al. "MR1-restricted T cells in cancer immunotherapy." Cancers 12.8 (2020): 2145.https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12082145
Anti-MR1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-Acetyl-α-Tubulin (Lys40) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623485) (CBMAB-CP2897-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-EGR1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJZ-100) (CBMAB-Z0289-WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-CSPG4 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYM-1050) (CBMAB-M1203-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CTCF Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2371) (CBMAB-C2443-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-BAD (Phospho-Ser136) Recombinant Antibody (CAP219) (CBMAB-AP536LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL2L1 Recombinant Antibody (H5) (CBMAB-1025CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CD83 Recombinant Antibody (HB15) (CBMAB-C1765-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ARHGAP5 Recombinant Antibody (54/P190-B) (CBMAB-P0070-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CORO1A Recombinant Antibody (4G10) (V2LY-1206-LY806)

-
Mouse Anti-CASP8 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0987) (CBMAB-C2424-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD46 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0076) (CBMAB-C0085-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP1B1 Recombinant Antibody (E4) (CBMAB-0463-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-AP2M1 (Phosphorylated T156) Recombinant Antibody (D4F3) (PTM-CBMAB-0610LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ASH1L Monoclonal Antibody (ASH5H03) (CBMAB-1372-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CFL1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1771) (CBMAB-C1833-FY)

-
Rat Anti-4-1BB Recombinant Antibody (V2-1558) (CBMAB-0953-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CALR Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0763) (CBMAB-C0818-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACTB Recombinant Antibody (V2-179553) (CBMAB-A0870-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0790) (CBMAB-0793-YY)

-
Rabbit Anti-CCN1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJC-3580) (CBMAB-C4816WJ)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








