DNMT1 Antibodies
Background
DNMT1, as a maintenance DNA methyltransferase, mainly exists in the cell nuclei of vertebrates. This enzyme maintains the stable transmission of epigenetic patterns by recognizing semi-methylated DNA and catalyzing the methylation of cytosine residues after replication. This mechanism is crucial for embryonic development and cell differentiation. In 1998, scientist M. Okano first confirmed through gene knockout experiments that the deletion of DNMT1 would lead to embryo death and abnormal genomic imprinting. As the first DNA methylation regulatory factor to be clarified, its typical BAH domain and catalytic center have become a classic model for epigenetic research, and related studies have greatly advanced people's understanding of the mechanisms of tumorigenesis, stem cell differentiation and gene silencing.
Structure of DNMT1
DNMT1 is a large protein with a molecular weight of approximately 183 kDa. There are certain differences in its precise molecular weight among different species, mainly due to the variations in amino acid sequences in the regulatory domain.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Bovine | African clawed toad |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 183.2 | 162.5 | 181.8 | 182.1 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains PCNA binding domains and multiple BAH domains | The N-terminal regulation domain is relatively short | High homology with human | Highly conserved core catalytic domain |
This protein is composed of over 1,600 amino acids, and its multi-domain assembly forms a typical "letter clip" conformation. The core of DNMT1 is a C-terminal catalytic domain, which contains highly conserved SAM and substrate binding pockets, responsible for performing methyl transfer reactions. Its N-terminal large regulatory unit contains multiple BAH domains, which guide the targeting of enzyme activity by specifically recognizing hemimethylated DNA. In addition, a replication focal localization domain is responsible for recruiting DNMT1 to the DNA replication fork through interaction with PCNA, thereby precisely maintaining the methylation pattern of the genome after cell division.
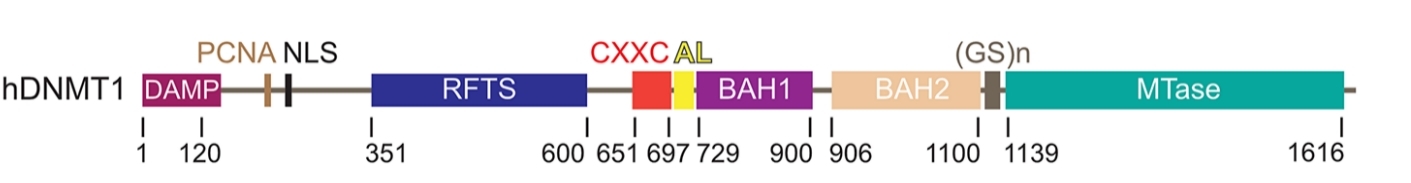 Fig. 1 Domain organization of human DNMT1.1
Fig. 1 Domain organization of human DNMT1.1
Key structural properties of DNMT1:
- Multi-domain "letter clip" shaped architecture
- N the control unit contains specific recognition half the BAH structure region of DNA methylation
- The C-terminal catalytic core contains conserved SAM and substrate binding sites
Functions of DNMT1
The core function of DNMT1 is to maintain the genetic stability of DNA methylation patterns during cell division. In addition, this enzyme is also involved in a variety of key biological processes, including transcriptional regulation, maintenance of genomic imprinting, and heterochromatin formation.
| Function | Description |
| Maintenance methylation | After DNA replication, the hemimethylation site is identified and the methyl group is precisely transferred to the corresponding cytosine of the sub-chain, achieving the copy of epigenetic information. |
| Regulation of transcriptional silencing | By maintaining the hypermethylation state of the promoter region, it participates in the long-term transcriptional inhibition of specific genes (such as tumor suppressor genes). |
| Maintenance of genomic imprinting | During embryonic development and cell differentiation, it is essential to ensure that specific methylation markers from parents are accurately inherited to maintain parental origin memory in the genome. |
| Heterochromatin stability | By stabilizing the methylation levels of repetitive sequence regions such as centromeres and telomeres, the integrity and functionality of chromosomal structures are protected. |
| Cell cycle coupling | Its activity peaks in the S phase and is precisely recruited into DNA replication forks through direct interaction with components of replication machines such as PCNA. |
Unlike the extensive substrate exploration characteristics of de novo methyltransferases (such as DNMT3A/B), DNMT1 exhibits high specificity for semi-methylated DNA substrates, which ensures both high fidelity and high efficiency in the replication process of epigenetic information.
Applications of DNMT1 and DNMT1 Antibody in Literature
1. Li, Hao, et al. "A meta‐analysis of the association between DNMT1 polymorphisms and cancer risk." BioMed Research International 2017.1 (2017): 3971259. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3971259
This article explores the relationship between three polymorphic loci of the DNMT1 gene (rs16999593, rs2228611, rs2228612) and cancer risk through meta-analysis. It is found that rs2228612 is significantly associated in the recessive model, while the other two loci may be respectively associated with gastric cancer and breast cancer.
2. Qin, Shuangkang, et al. "NS1-mediated DNMT1 degradation regulates human bocavirus 1 replication and RNA processing." PLoS Pathogens 20.11 (2024): e1012682. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1012682
This study reveals for the first time that in human bocavirus replication, host DNMT1-mediated viral DNA methylation is crucial for viral DNA synthesis. The viral NS1 protein regulates the splicing of viral RNA by degrading DNMT1, thereby influencing the expression of viral proteins.
3. De, Inessa, et al. "Structural insight into the DNMT1 reaction cycle by cryo-electron microscopy." Plos one 19.9 (2024): e0307850. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0307850
This study analyzed the entire conformational change process of DNMT1 from the self-inhibitory state to the non-productive state and finally to the productive DNA-binding state through cryo-electron microscopy, revealing the dynamic regulatory mechanism of its catalytic activity and providing key structural insights for understanding its reaction cycle.
4. Fangcao, et al. "DNMT1-mediated methylation inhibits microRNA-214-3p and promotes hair follicle stem cell differentiate into adipogenic lineages." Stem Cell Research & Therapy 11.1 (2020): 444. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-020-01864-8
This study reveals a novel mechanism by which DNMT1 positively regulates adipogenic differentiation of human hair follicle stem cells and skin trauma repair by promoting methylation of the miR-214-3p promoter and thereby regulating the MAPK1/ERK pathway.
5. Aghaei‐Zarch, Seyed Mohsen, Ali Esmaeili, and Saeid Bagheri‐Mohammadi. "A Comprehensive Review on LncRNAs/miRNAs‐DNMT1 Axis in Human Cancer: Mechanistic and Clinical Application." Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine 29.10 (2025): e70604. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.70604
This review focuses on DNMT1, systematically expounding its interaction mechanisms with various non-coding Rnas in cancer occurrence, stem cell characteristics, and therapeutic resistance, and exploring the potential of natural medicines and synthetic RNA therapies targeting this axis in cancer treatment.
Creative Biolabs: DNMT1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality DNMT1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom DNMT1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our DNMT1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- De, Inessa, et al. "Structural insight into the DNMT1 reaction cycle by cryo-electron microscopy." Plos one 19.9 (2024): e0307850. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0307850
Anti-DNMT1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-DMD Recombinant Antibody (D1190) (CBMAB-D1190-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-Acetyl-Histone H3 (Lys36) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623395) (CBMAB-CP0994-LY)

-
Rat Anti-FABP3 Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-2299) (CBMAB-F1612-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-EMP3 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYE-0100) (CBMAB-E0207-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-CCL5 Recombinant Antibody (R0437) (CBMAB-R0437-CN)

-
Rabbit Anti-Acetyl-Histone H4 (Lys16) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623415) (CBMAB-CP1021-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADIPOR1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179982) (CBMAB-A1368-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-C5B-9 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYA-0216) (CBMAB-X0304-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CRTAM Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2235) (CBMAB-C2305-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CDK7 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C1783) (CBMAB-C3221-YY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ALOX5AP Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-1219) (CBMAB-F0750-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ADAM12 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179752) (CBMAB-A1114-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ASTN1 Recombinant Antibody (H-9) (CBMAB-1154-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-CIITA Recombinant Antibody (CBLC160-LY) (CBMAB-C10987-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-AKT3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-12567) (CBMAB-1057-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-DMPK Recombinant Antibody (CBYCD-324) (CBMAB-D1200-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CEMIP Recombinant Antibody (3C12) (CBMAB-K0296-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALPL Antibody (B4-78) (CBMAB-1009CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-FeLV g27 Recombinant Antibody (1) (CBMAB-V208-1714-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AKR1C3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-12560) (CBMAB-1050-CN)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








