PAXX Antibodies
Background
PAXX is a non-homologous terminal join (NHEJ) factor that plays a key role in DNA damage repair and is mainly found in the nuclei of vertebrates. This protein maintains genomic integrity by interacting with the core components of the DNA repair complex, such as Ku protein and XLF, promoting the stability and connection of the ends of DNA double-strand breaks. Especially when cells respond to DNA damage caused by ionizing radiation or chemotherapy drugs, PAXX plays an important regulatory role in the repair efficiency. Its gene was simultaneously identified by multiple research teams in 2015. As a newly discovered auxiliary protein in the NHEJ pathway, it quickly became a research hotspot in the field of DNA repair. The structural and functional research of PAXX not only deepens the understanding of the molecular mechanism of NHEJ, but also provides a new molecular target perspective for DNA repair defects related to tumor treatment and genetic diseases.
Structure of PAXX
The molecular weight of the protein encoded by the PAXX gene is approximately 25 kDa. This protein is one of the core scaffold proteins in the non-homologous terminal junction (NHEJ) pathway. Its molecular weight is relatively conserved among different mammalian species, with the main differences reflected in the specific domain sequences involved in protein interactions.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Bovine |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 25.0 | 24.8 | 25.1 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains the typical SAP domain and coiled-coil domain | SAP domains are highly homologous with slightly different C-terminal sequences | Overall domain composition is highly similar to that of humans |
The PAXX protein is composed of approximately 230 amino acids, and its three-dimensional structure is shown as a compact spherical fold. The core feature of this protein is that its N-terminal contains an SAP (SAF-A/B, Acinus and PIAS) domain, which can specifically recognize and bind to DNA. The C-terminal of the protein forms a coiled-coil helical bundle, and this secondary structure is crucial for its specific interactions with other key proteins in the NHEJ repair complex, such as the Ku70/Ku80 heterodimer and XLF. This protein network formed through helical and helical interactions is the molecular basis for PAXX to stabilize repair complexes at DNA double-strand breaks and promote terminal joins.
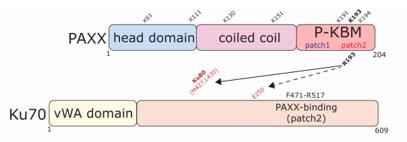 Fig. 1 PAXX and Ku70 schematics showing key functional regions and interactions.1
Fig. 1 PAXX and Ku70 schematics showing key functional regions and interactions.1
Key structural properties of PAXX:
- Contains conserved SAP (SAF-A/B, Acinus and PIAS) domains
- coiled-coil bundle domain with formation of homodimerization
- The C-terminal acid through its regional and NHEJ core complex (such as Ku70 / Ku80) specific interaction
Functions of PAXX
The main function of the protein encoded by the PAXX gene is to participate in the non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) process in DNA double-strand break repair. However, it also plays multiple roles in maintaining genomic stability and the response of cells to DNA damage.
| Function | Description |
| DNA terminal connection | As a molecular scaffold, it stabilizes the broken DNA ends and promotes the assembly of the NHEJ core complex, thereby connecting the broken DNA. |
| Repair complex stability | By interacting with core repair proteins such as Ku70/Ku80 heterodimers and XLF, the retention and function of the repair complex at the injury site are enhanced. |
| Maintenance of genomic stability | Ensure the efficient repair of DNA double-strand breaks, prevent harmful variations such as chromosomal translocations and deletions, and thereby maintain the integrity of the genome. |
| Cellular response to injury | Participate in cells from ionizing radiation or chemotherapy drugs such as genetic toxic stress after the survival of signaling pathways, decisions affect cell cycle checkpoint and apoptosis. |
| Development and immune support | Particularly important in lymphocyte development, its function defect can lead to abnormal V (D) J reprogramming, affect the normal form of the adaptive immune system. |
PAXX is not an absolutely essential core factor in the NHEJ pathway. Its function is more similar to that of an efficient "helper" or "enhancer". This enables it to dynamically adjust the fidelity and efficiency of repair in different scenarios such as basic repair and dealing with complex terminal or high-intensity genotoxic stress.
Applications of PAXX and PAXX Antibody in Literature
- Seif-El-Dahan, Murielle, et al. "PAXX binding to the NHEJ machinery explains functional redundancy with XLF." Science advances 9.22 (2023): eadg2834. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.adg2834
In this study, the structure of the PAXX protein and Ku70/80 complex was resolved by cryo-electron microscopy and crystallography, revealing that PAXX and XLF can simultaneously bind to Ku protein to form DNA-PK dimers of different conformations, synergically promoting the terminal connection of DNA.
- Arora, Mohit, et al. "PAXX, Not NHEJ1 is an independent prognosticator in colon cancer." Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences 7 (2020): 584053. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2020.584053
Research has found that in colon cancer, the expression of NHEJ pathway genes such as PAXX and XRCC5 is abnormal. High expression of PAXX is independently associated with poor prognosis in patients. Hypomethylation of its promoter may drive its overexpression and is related to changes in the tumor immune microenvironment.
- Gluza, Joanna, et al. "PAXX/Ku interaction is rate limiting for repair of double-strand DNA breaks requiring end processing." Journal of Biological Chemistry 301.8 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2025.110481
Research has found that a key amino acid mutation in the PAXX protein can significantly stabilize the DNA repair complex and accelerate the repair of DNA double-strand breaks requiring terminal treatment, revealing that the stability of the repair complex is a key rate-limiting step in regulating the repair speed of NHEJ.
- Liu, Xiangyu, et al. "PAXX promotes KU accumulation at DNA breaks and is essential for end-joining in XLF-deficient mice." Nature communications 8.1 (2017): 13816. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms13816
Research reveals that PAXX and XLF are functionally complementary in the DNA repair pathway NHEJ. Paxx-deficient mice rely on XLF, and vice versa. Double deletion leads to embryo death. Mechanistically, PAXX promotes the enrichment of KU protein at the fracture site, while XLF enhances LIG4 recruitment, jointly ensuring repair.
- Craxton, Andrew, et al. "PAXX and its paralogs synergistically direct DNA polymerase λ activity in DNA repair." Nature communications 9.1 (2018): 3877. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-06127-y
Research has found that PAXX and its homologous proteins XRCC4 and XLF can directly bind to and activate DNA polymerase λ (Pol λ), cooperatively promoting its recruitment to DNA damage sites and the connection of incompatible ends, and jointly regulating the function of polymerase in NHEJ repair.
Creative Biolabs: PAXX Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality PAXX antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom PAXX Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our PAXX antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Gluza, Joanna, et al. "PAXX/Ku interaction is rate limiting for repair of double-strand DNA breaks requiring end processing." Journal of Biological Chemistry 301.8 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2025.110481
Anti-PAXX antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-ALB Recombinant Antibody (V2-55272) (CBMAB-H0819-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL6 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0435) (CBMAB-0437-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CGAS Recombinant Antibody (CBFYM-0995) (CBMAB-M1146-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALB Recombinant Antibody (V2-180650) (CBMAB-A2186-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ARHGAP5 Recombinant Antibody (54/P190-B) (CBMAB-P0070-YC)

-
Rat Anti-C5AR1 Recombinant Antibody (8D6) (CBMAB-C9139-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BACE1 Recombinant Antibody (CBLNB-121) (CBMAB-1180-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-C4B Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C2996) (CBMAB-C4439-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV9 Recombinant Antibody (V2-634029) (CBMAB-AP023LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCND2 Recombinant Antibody (DCS-3) (CBMAB-G1318-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AFDN Recombinant Antibody (V2-58751) (CBMAB-L0408-YJ)

-
Mouse Anti-BrdU Recombinant Antibody (IIB5) (CBMAB-1038CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-CCL5 Recombinant Antibody (R0437) (CBMAB-R0437-CN)

-
Rabbit Anti-AP2M1 (Phosphorylated T156) Recombinant Antibody (D4F3) (PTM-CBMAB-0610LY)

-
Mouse Anti-A2M Recombinant Antibody (V2-178822) (CBMAB-A0036-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO2 Recombinant Antibody (85F11) (CBMAB-0276CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ACVR1C Recombinant Antibody (V2-179685) (CBMAB-A1041-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CARD11 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0811) (CBMAB-C0866-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BANF1 Recombinant Antibody (3F10-4G12) (CBMAB-A0707-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AKT1/AKT2/AKT3 (Phosphorylated T308, T309, T305) Recombinant Antibody (V2-443454) (PTM-CBMAB-0030YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








