NCAM1 Antibodies
Background
NCAM1 is a glycoprotein located on the cell surface and is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. It is widely distributed in neurons, neuromuscular junctions and immune cells. The protein encoded by this gene plays a core role in neural development, synaptic plasticity and axon orientation by mediating calcium-dependent homophilic and heterophilic cell adhesion. The multiple isomers produced by its alternative splicing can regulate cell signal transduction and cytoskeletal dynamics. This characteristic was first clarified by Stanley Hoffman's team in 1987. The multi-domain characteristics and glycosylation modification patterns of NCAM1 have become classic models for studying the mechanisms of cell recognition, neural regeneration and tumor metastasis, and are of great value for understanding the molecular basis of intercellular communication.
Structure of NCAM1
NCAM1 is a cell adhesion glycoprotein with a molecular weight of approximately 120-180 kDa, and its precise molecular weight varies by species and splicing isomers.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Chicken | Zebrafish |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 120-180 | 120-175 | 120-170 | 110-160 | 100-140 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Multiple splice variants containing PSA modifications | NCAM1 85% homology with people | 87% homology to human NCAM1 | Lack of certain splicing variants | Only basic adhesion function |
The extracellular region of this protein contains five immunoglobulin-like domains and two fibronectin III repeat sequences, forming the structural basis of its adhesion function. The transmembrane region connects intracellular domains, which participate in signal transduction by binding to cytoskeletal proteins such as spectrin. The degree of glycosylation modification, especially the length of the polysialic acid chain, directly regulates the intensity and specificity of intercellular interactions.
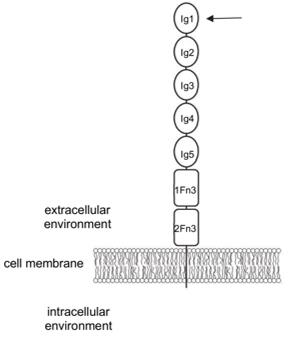 Fig. 1 Schematic of human NCAM1 structure.1
Fig. 1 Schematic of human NCAM1 structure.1
Key structural properties of NCAM1:
- The extracellular domain contains five immunoglobulin-like domains and two fibronectin III repeats
- Hydrophobic core to maintain the stability of immunoglobulin fold structure
- Calcium independent binding interface mediates homologous/allogenic cell recognition
Functions of NCAM1
The main function of NCAM1 is to mediate calcium-independent intercellular adhesion and signal transduction. In addition, it is also involved in a variety of physiological and pathological processes, including neurodevelopmental regulation and tumor metastasis.
| Function | Description |
| Cell adhesion | Mediated by with close sex and sexual affinity recognition and connections between cells, tissue morphogenesis. |
| Axon guidance | Guide the directional migration of growth cones and regulate cytoskeletal recombination through signal transduction. |
| Synaptic plasticity | Molecular mechanisms that regulate synaptic formation and function and influence learning and memory. |
| Tumor metastasis | In a variety of abnormal expression in cancer cells, and promote the process of invasion and metastasis. |
| Immune regulation | Participate in immune cell interactions, inflammation and autoimmune diseases. |
NCAM1 generates various isomers (such as NCAM-180, NCAM-140, NCAM-120) through alternative splicing. The functional differences mainly depend on the length of intracellular domains and the level of polysialic acid modification, which enables it to play a pleiotropic role in development and disease.
Applications of NCAM1 and NCAM1 Antibody in Literature
1. Shukrun, Rachel, et al. "NCAM1/FGF module serves as a putative pleuropulmonary blastoma therapeutic target." Oncogenesis 8.9 (2019): 48.https://doi.org/10.1038/s41389-019-0156-9
In this study, a patient-derived xenograft model of pleuropulmonary blastoma (PPB) was constructed, and it was found that the progenitor cells enriched in it highly expressed FGF signaling and NCAM1. Antibody-drug conjugates targeting NCAM1 can inhibit tumor progression, providing a new target for PPB treatment.
2. Yang, Yifeng, et al. "A functional SNP rs895819 on pre-miR-27a is associated with bipolar disorder by targeting NCAM1." Communications Biology 5.1 (2022): 309. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-022-03263-6
Studies have confirmed that the miR-27a gene polymorphism rs895819 is associated with bipolar disorder. Its C mutation affects the maturation of miR-27a, leading to the upregulation of the target gene NCAM1 expression, and inhibits cell migration and dopamine levels.
3. Xu, Dan-Hong, et al. "Upregulation of KLK8 contributes to CUMS-induced hippocampal neuronal apoptosis by cleaving NCAM1." Cell Death & Disease 14.4 (2023): 278. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-023-05800-5
Research has found that depressive behavior is associated with the upregulation of KLK8 protease in the hippocampus. KLK8 induces neuronal apoptosis by cleaving the nerve cell adhesion molecule NCAM1. Supplementation with NCAM1 can reverse this process, suggesting that KLK8 is a potential antidepressant target.
4. Nye, Jessica. "NCAM1: A Potential Biomarker for Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease Progression." Neurology Advisor (2022): NA-NA. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awac055
Studies have found that the nerve adhesion molecule NCAM1 is significantly elevated in the sera of various patients with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMT) and mouse models, and is positively correlated with the severity of neuropathy. It is expected to become a clinical biomarker for evaluating the course of CMT.
5. Mehrabian, Mohadeseh, Herbert Hildebrandt, and Gerold Schmitt-Ulms. "NCAM1 polysialylation: the prion protein's elusive reason for being?." ASN neuro 8.6 (2016): 1759091416679074. https://doi.org/10.1177/1759091416679074
Research has found that prion proteins (PrPC) can regulate the polymeric sialacidification level of the neural cell adhesion molecule NCAM1 during morphogenetic processes such as epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cells, thereby influencing multiple plasticity programs including cell migration and neurogenesis.
Creative Biolabs: NCAM1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality NCAM1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom NCAM1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our NCAM1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Cunningham, Claire, et al. "Isolation and characterisation of a recombinant antibody fragment that binds NCAM1-expressing intervertebral disc cells." PLoS one 8.12 (2013): e83678.https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0083678
Anti-NCAM1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Rabbit Anti-CAMK2A Recombinant Antibody (BA0032) (CBMAB-0137CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-14-3-3 Pan Recombinant Antibody (V2-9272) (CBMAB-1181-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-BAD (Phospho-Ser136) Recombinant Antibody (CAP219) (CBMAB-AP536LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AHCYL1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180270) (CBMAB-A1703-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CCT6A/B Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-0168) (CBMAB-C5570-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC5 Recombinant Antibody (6E4) (CBMAB-CP2646-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-COL1A2 Recombinant Antibody (CF108) (V2LY-1206-LY626)

-
Mouse Anti-APP Recombinant Antibody (5C2A1) (CBMAB-A3314-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BPGM Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-1806) (CBMAB-2155-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (HIS50) (CBMAB-C10123-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ARG1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYCL-103) (CBMAB-L0004-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-ALOX5AP Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-1219) (CBMAB-F0750-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ADGRL2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-58519) (CBMAB-L0166-YJ)

-
Mouse Anti-DLC1 Recombinant Antibody (D1009) (CBMAB-D1009-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CA9 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-2079) (CBMAB-C0131-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-dsRNA Recombinant Antibody (2) (CBMAB-D1807-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CRTAM Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2235) (CBMAB-C2305-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC7 Recombinant Antibody (88C570) (CBMAB-L0261-YJ)

-
Mouse Anti-BACE1 Recombinant Antibody (CBLNB-121) (CBMAB-1180-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-FOXL1 Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-0845) (CBMAB-F0462-CQ)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






