TRPV1 Antibodies
Background
TRPV1 is an important non-selective cation channel protein, mainly distributed in sensory neurons of mammals. As a member of the transient receptor potential (TRP) channel family, it can be activated by various stimuli, including high temperatures (>43℃), acidic protons (pH<6), and chemical ligands such as capsaicin, playing a key role in pain conduction and temperature perception. This channel was first discovered by David Julius' team through cloning technology in 1997. The analysis of its three-dimensional structure has provided an important breakthrough for understanding the molecular mechanism of noxious stimuli. The unique activation characteristics of TRPV1 have made it a key target in pain treatment and neuroscience research. Related studies have greatly advanced people's understanding of sensory signal transduction, ion channel gating mechanisms, and drug development.
Structure of TRPV1
TRPV1 is a non-selective cation channel protein with a molecular weight of approximately 95-100 kDa. There are certain differences in its molecular weight among different species:
| Species | Human | Rats | Mice | Guinea pigs |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | ~95 | ~97 | ~96 | ~95.5 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Six transmembrane domains (S1-S6), with the N-terminus and C-terminus located within the cell | With highly homologous in rats, but some key sites are different | Similar to rats, but with some different regulatory sites | Slightly higher sensitivity to capsaicin |
TRPV1 is composed of approximately 839 amino acids, and its structure includes six transmembrane helices (S1-S6), among which S5-S6 form pore regions responsible for the permeability of cations (such as Ca²⁺and Na⁺). Both the N-terminal and C-terminal are located intracellular and contain multiple regulatory sites, such as calmodulin binding domains and phosphorylation sites.
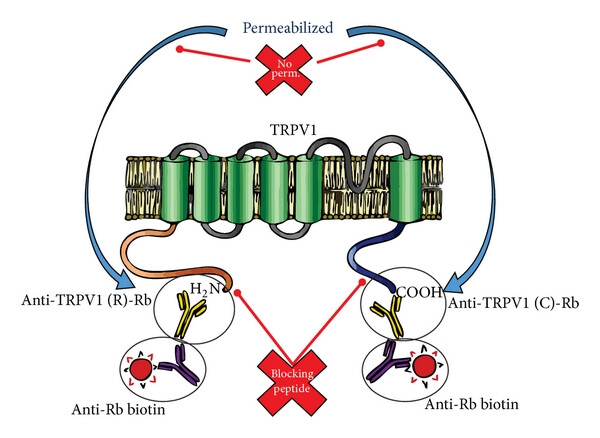 Fig. 1 TRPV1 detected by immunofluorescence.1
Fig. 1 TRPV1 detected by immunofluorescence.1
Key structural properties of TRPV1:
- Transmembrane helical structure
- Intracellular N-terminal and C-terminal regulatory domains
- Capsaicin binding site
- Heat/acid sensitive area
Functions of TRPV1
The main function of TRPV1 is to serve as a multimodal noxious stimulus sensor, simultaneously participating in multiple physiological and pathological processes:
| Function | Description |
| Noxious thermal perception | At temperature It is activated at 43℃ and mediates the transmission of thermal pain signals. |
| Chemical pain conduction | In response to chemical stimuli such as capsaicin and acidic protons (pH<6), it triggers a burning pain sensation. |
| Inflammatory pain sensitization | Upregulated in response to tissue inflammation, amplifying nociceptive signals (peripheral sensitization). |
| Body temperature regulation | Hypothalamic neurons are involved in core body temperature regulation. |
| Visceral sensory regulation | Mediates the perception of mechanical and chemical stimuli in internal organs such as the bladder and intestines. |
This channel triggers neuronal depolarization through calcium ion influx and promotes the release of pain-sensitive neuropeptides such as substance P and CGRP, playing a key role in chronic pain, heat injury defense and tissue protection. Abnormal functional regulation is closely related to the occurrence and development of neuropathic pain, inflammatory diseases and certain cancers.
Applications of TRPV1 and TRPV1 Antibody in Literature
1. Jin, Yuying, et al. "Antibody selection and automated quantification of TRPV1 immunofluorescence on human skin." Scientific Reports 14.1 (2024): 28496. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-79271-9
This study screened specific TRPV1 antibodies and optimized the immunofluorescence protocol. By combining rat DRG and human skin samples for verification, two automated image analysis methods (Python deep learning and Fiji machine learning) were developed, which can precisely quantify the TRPV1 signal of nerve fibers and provide new tools for the research of neuropathic pain.
2. Marrone, Maria Cristina, et al. "TRPV1 channels are critical brain inflammation detectors and neuropathic pain biomarkers in mice." Nature communications 8.1 (2017): 15292.https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15292
Research has found that TRPV1 is mainly expressed in microglia rather than neurons in brain regions such as the anterior cingulate cortex. After activation, it can regulate the activity of microglia and release through microvesicles to enhance the transmission of glutamate energy in neurons. In the neuropathic pain model, TRPV1 also appears in neurons and affects their electrophysiological characteristics, suggesting that it may be a key medium for detecting harmful stimuli and glial-neuron communication in the brain.
3. Ramírez-Barrantes, R., et al. "Perspectives of TRPV1 function on the neurogenesis and neural plasticity." Neural plasticity 2016.1 (2016): 1568145. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/1568145
Studies have shown that TRPV1 calcium channels are expressed in neurogenic regions such as the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus and participate in neural differentiation and plasticity by regulating the dynamics, migration and survival of the cytoskeleton. As a molecular tool, it may control the fate of neural stem cells and provide a new target for neural regeneration therapy.
4. Facer, Paul, et al. "Differential expression of the capsaicin receptor TRPV1 and related novel receptors TRPV3, TRPV4 and TRPM8 in normal human tissues and changes in traumatic and diabetic neuropathy." BMC neurology 7 (2007): 1-12. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2377-7-11
Research has found that after nerve injury, the expression of TRPV1 and TRPV3 in peripheral nerves significantly increases, while the TRPV1-positive nerve fibers in the skin of diabetic neuropathy decrease. TRPV1 is expressed in the dorsal root ganglion and the posterior horn of the spinal cord, suggesting that it can serve as a specific therapeutic target for post-traumatic neuropathic pain.
5. Gao, Wen, et al. "Copper sulfide nanoparticles as a photothermal switch for TRPV1 signaling to attenuate atherosclerosis." Nature communications 9.1 (2018): 231. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-02657-z
This study developed TRPV1 antibody-conjugated copper sulfide nanoparticles (CuS-TRPV1), which activated the TRPV1 channel in vascular smooth muscle cells through near-infrared light control, induced calcium influx to promote autophagy, and inhibited foam cell formation. This technology can achieve photoacoustic imaging of cardiac vessels and effectively reduce atherosclerotic plaques in high-fat diet ApoE−/− mice without long-term toxicity, providing a new strategy for targeted therapy.
Creative Biolabs: TRPV1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality TRPV1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom TRPV1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our TRPV1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, please contact us.
Reference
- Ramírez-Barrantes, R., et al. "Perspectives of TRPV1 function on the neurogenesis and neural plasticity." Neural plasticity 2016.1 (2016): 1568145. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/1568145
Anti-TRPV1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-ATP1B3 Recombinant Antibody (1E9) (CBMAB-A4021-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ATG5 Recombinant Antibody (9H197) (CBMAB-A3945-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ALOX5 Recombinant Antibody (33) (CBMAB-1890CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-B2M Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0050) (CBMAB-0050-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-A2M Recombinant Antibody (V2-178822) (CBMAB-A0036-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-C1QC Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0600) (CBMAB-C0654-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BSN Recombinant Antibody (219E1) (CBMAB-1228-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-CD33 Recombinant Antibody (P67.6) (CBMAB-C10189-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-AKT2 (Phosphorylated S474) Recombinant Antibody (V2-556130) (PTM-CBMAB-0605LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0790) (CBMAB-0793-YY)

-
Rat Anti-CD300A Recombinant Antibody (172224) (CBMAB-C0423-LY)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S1 Monoclonal Antibody (CBFYR-0120) (CBMAB-R0120-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ATF4 Recombinant Antibody (D4B8) (CBMAB-A3872-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-COL1A2 Recombinant Antibody (CF108) (V2LY-1206-LY626)

-
Rat Anti-(1-5)-α-L-Arabinan Recombinant Antibody (V2-501861) (CBMAB-XB0003-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BZLF1 Recombinant Antibody (BZ.1) (CBMAB-AP705LY)

-
Rat Anti-ADAM10 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179741) (CBMAB-A1103-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-CCL5 Recombinant Antibody (R0437) (CBMAB-R0437-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-CTCF Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2371) (CBMAB-C2443-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATM Recombinant Antibody (2C1) (CBMAB-A3970-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






