IRAK4 Antibodies
Background
IRAK4 (interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4) is a serine/threonine protein kinase that mainly functions as a key signal transduction medium in the Toll-like/interleukin-1 receptor signaling pathway. This protein activates downstream transcription factors such as nuclear factor κB through the myeloid differentiation primary response protein 88-dependent pathway, thereby regulating inflammatory responses and innate immune processes. Research has found that individuals with IRAK4 gene defects will experience repeated suppurative infections, confirming its core position in anti-pathogen immunity. After three research teams simultaneously reported its molecular characteristics in 2002, this protein has become an important target for the development of drugs for autoimmune diseases and leukemia. Its unique kinase domain and allosteric regulatory mechanism continuously provide important models for immune signal transduction research, promoting the development of targeted therapeutic strategies.
Structure of IRAK4
IRAK4 is a serine/threonine protein kinase with a molecular weight of approximately 52 kDa. The molecular weight of this protein varies slightly among different mammals, mainly due to species-specific variations in the sequences of its kinase domain and death domain.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Rhesus monkey |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 52 | 51.8 | 51.9 | 52.1 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains the death domain and the kinase domain | Highly conservative kinase domain structure | The N-terminal sequence is slightly different | The sequence homology with human protein is extremely high |
IRAK4 is composed of 460 amino acid residues, and its polypeptide chain folds into two independent functional modules: the N-terminal death domain and the C-terminal kinase domain. The death domain is mainly composed of six amphoteric α -helices arranged in bundles, responsible for interacting with downstream signal-adaptor proteins. The kinase domain presents a typical bilayer structure and regulates phosphorylation activity through conformational changes in the ATP-binding pocket. Phosphorylation of the threonine residue (T345) on the activation loop is the key switch for kinase activation, while the "gated" residues located in the α -helical cluster maintain the structural basis of enzyme activity.
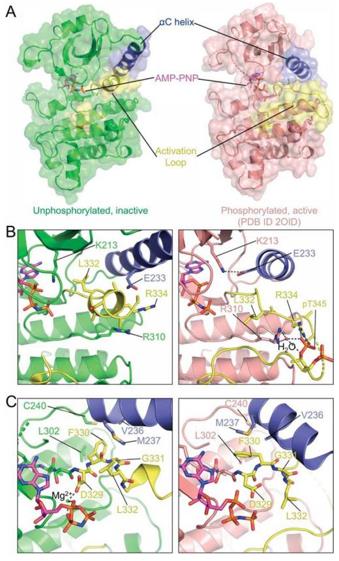 Fig. 1 Structure of AMP-PNP bound IRAK4 kinase domain.1
Fig. 1 Structure of AMP-PNP bound IRAK4 kinase domain.1
Key structural properties of IRAK4:
- Typical duplex kinase domain
- The N-terminal death domain mediates protein interactions
- Key threonine sites in the activation loop regulate phosphorylation activity
Functions of IRAK4
The main function of IRAK4 is to mediate the transduction and amplification of innate immune signals. However, it is also involved in regulating various pathophysiological processes such as apoptosis and metabolic reprogramming.
| Function | Description |
| Signal transduction | As the core kinase of the TLR/IL-1R signaling pathway, it receives upstream signals and activates the downstream NF-κB and MAPK pathways. |
| Inflammation initiation | By phosphorylating substrates such as IRAK1, the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines (such as TNF-α, IL-6) is triggered, initiating an inflammatory response. |
| Immune defense | In the body's first line of defense against pathogens infection play a key role, in particular against bacterial sepsis. |
| Pyroptosis regulation | Participate in the regulation of inflammatory corpuscle signal, jiao wu process affect the immune cells, which control the strength of the immune response. |
| Disease association | The dysfunction and autoimmune diseases, leukemia and chronic inflammatory disease development are closely related. |
The activation of IRAK4 depends on the phosphorylation of the key threonine residue on its activation loop (T-loop). This conformational change acts like a "molecular switch", transforming it from a self-inhibitory state to a fully catalytic active state, thereby efficiently amplifying immune signals.
Applications of IRAK4 and IRAK4 Antibody in Literature
1. Kang, Chenglin, et al. "Tolerogenic dendritic cells and TLR4/IRAK4/NF-κB signaling pathway in allergic rhinitis." Frontiers in immunology 14 (2023): 1276512. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1276512
Studies have confirmed that in allergic rhinitis, tolerant dendritic cells promote immune tolerance and alleviate allergic inflammatory responses by inhibiting the TLR4/IRAK4/NF-κB signaling pathway, reducing the release of inflammatory factors and inducing regulatory T cells.
2. Ackerman, Lindsay, et al. "IRAK4 degrader in hidradenitis suppurativa and atopic dermatitis: a phase 1 trial." Nature Medicine 29.12 (2023): 3127-3136. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-023-02635-7
Studies have confirmed that the IRAK4 degrader KT-474 demonstrated in Phase 1 clinical trials that it can effectively degrade the IRAK4 protein in blood and skin lesions, reduce the inflammatory indicators of patients with moderate to severe hidrodermatitis suppurative and atopic dermatitis, improve symptoms, and has good safety.
3. Nishimura, Shiho, et al. "IRAK4 deficiency presenting with anti-NMDAR encephalitis and HHV6 reactivation." Journal of Clinical Immunology 41.1 (2021): 125-135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-020-00885-5
A study reported a rare case of a child with IRAK4 deficiency, who also suffered from anti-NMDAR encephalitis and HHV6 reactivation. The author developed a novel reporter gene detection method based on NF-κB, confirming that the compound heterozygous mutation of the IRAK4 gene is pathogenic, providing a simple and reliable analytical means for this genetic disease.
4. Ménoret, Antoine, et al. "IRAK4 is an immunological checkpoint in neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus." Scientific Reports 14.1 (2024): 16393. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-63567-x
Studies have shown that in lupus dementia models, inhibiting the activity of IRAK4 kinase can significantly reduce brain inflammation and improve memory impairment. The mechanism is related to the JAK/STAT pathway in the hippocampus, providing a new potential target for the treatment of dementia such as neuropsychiatric lupus.
5. Bothe, Ulrich, et al. "Discovery of IRAK4 inhibitors BAY1834845 (zabedosertib) and BAY1830839." Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 67.2 (2024): 1225-1242. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c01714
Research shows that based on high-throughput screening, researchers have successfully obtained two clinical candidate drugs of IRAK4 inhibitors (BAY1834845 and BAY1830839) through targeted design. They possess both good efficacy and selectivity, have demonstrated anti-inflammatory activity in animal models, and have entered the clinical development stage.
Creative Biolabs: IRAK4 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality IRAK4 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom IRAK4 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our IRAK4 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Wang, Li, et al. "Conformational flexibility and inhibitor binding to unphosphorylated interleukin-1 receptor–associated kinase 4 (IRAK4)." Journal of Biological Chemistry 294.12 (2019): 4511-4519. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA118.005428
Anti-IRAK4 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-CCDC25 Recombinant Antibody (CBLC132-LY) (CBMAB-C9786-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-FN1 Monoclonal Antibody (D6) (CBMAB-1240CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-DES Monoclonal Antibody (440) (CBMAB-AP1857LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL6 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0442) (CBMAB-0445-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-EMP3 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYE-0100) (CBMAB-E0207-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACVR1C Recombinant Antibody (V2-179685) (CBMAB-A1041-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD83 Recombinant Antibody (HB15) (CBMAB-C1765-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CASP8 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0987) (CBMAB-C2424-YY)

-
Rabbit Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (D9S6V) (CBMAB-CP0017-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO2 Recombinant Antibody (85F11) (CBMAB-0276CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-AKT1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180546) (CBMAB-A2070-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ALDOA Recombinant Antibody (A2) (CBMAB-A2316-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-F11R Recombinant Antibody (402) (CBMAB-0026-WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-CEMIP Recombinant Antibody (3C12) (CBMAB-K0296-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCL18 Recombinant Antibody (64507) (CBMAB-C7910-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-AKT2 (Phosphorylated S474) Recombinant Antibody (V2-556130) (PTM-CBMAB-0605LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ARHGDIA Recombinant Antibody (CBCNA-009) (CBMAB-R0415-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-FOXL1 Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-0845) (CBMAB-F0462-CQ)

-
Rat Anti-CCR2 Recombinant Antibody (475301) (CBMAB-C1338-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CARD11 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0811) (CBMAB-C0866-FY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








