Ly6G Antibodies
Background
Ly6G gene encodes a highly specific glycosyl phosphatidylinositol anchored membrane protein, which is mainly expressed on the surface of neutrophils and is a key marker for the differentiation and maturation of myeloid cells. This protein effectively regulates the recruitment, activation and immune function of neutrophils at the inflammatory site by participating in the intercellular adhesion and signal transduction processes, and is crucial for the body's innate immune defense. First discovered on the surface of mouse granulocytes in the 1990s, Ly6G has become an important target in immunological research due to its unique cellular specificity. Monoclonal antibodies developed against this gene (such as 1A8) have been widely applied in the cutting-edge research of inflammatory diseases, tumor microenvironments, and immune cell differentiation, providing key molecular tools for exploring immune regulatory mechanisms.
Structure of Ly6G
Ly6G is a glycosylated protein with a molecular weight of approximately 20-25 kDa. Its specific molecular weight varies slightly among different species due to differences in glycosylation modifications and amino acid sequences.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 20-21 | 21-22 | 22-23 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Glycosylation pattern is different, belong to the same LY6 superfamily | Highly glycosylated, GPI anchored | Similar to mice, the sequence is highly conserved |
This protein belongs to the LY6/uPAR superfamily. Its structure is mainly composed of a highly conserved LU domain, forming a typical three-finged-like fold and stabilizing the spatial conformation through disulfide bonds. Its C-terminal is anchored to the cell membrane by glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI), responsible for binding to ligands and participating in membrane signal transduction. This structural feature contributes to its specific recognition and high-density expression on the surface of immune cells.
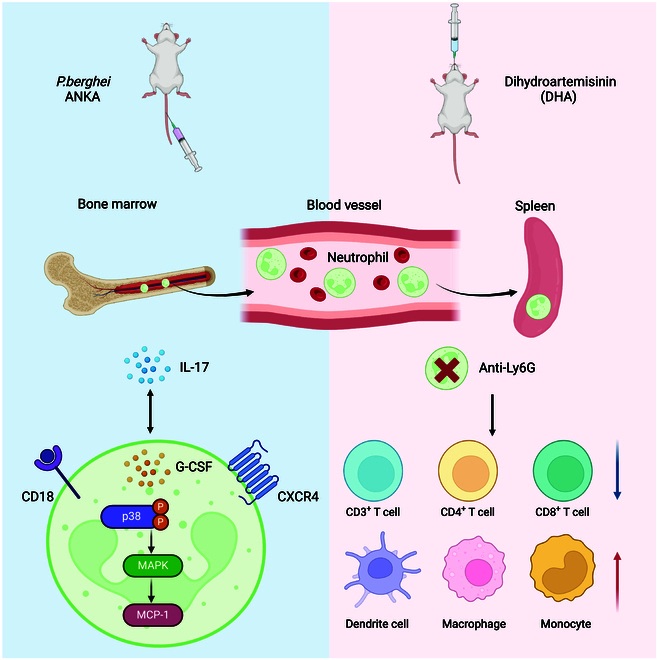 Fig. 1 Both Ly6G+ neutrophils and IL-17+ T cells are key cell subsets in resistance to Plasmodium infection.1
Fig. 1 Both Ly6G+ neutrophils and IL-17+ T cells are key cell subsets in resistance to Plasmodium infection.1
Key structural properties of Ly6G:
- Conservative three-fingered LU domain
- GPI anchor is due to the cell membrane surface
- Highly glycosylated carboxyl terminus
Functions of Ly6G
The main function of the Ly6G protein is to serve as a specific surface marker for neutrophils and participate in immune regulation. Its specific functions include:
| Function | Description |
| Cell recognition and adhesion | By recognizing specific ligands (such as P-selectin), it mediates the rolling and adhesion of neutrophils at the inflammatory site. |
| Regulation of immune cell activation | Participate in the transmembrane signal transduction, regulation of neutrophil activation, migration and phagocytosis. |
| Host defense | Plays a key role in innate immunity, promote neutrophils to remove pathogens and formation neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs). |
| Regulation of inflammatory response | By regulating the production of cytokines and the amplification of inflammatory signals, it affects the development process of acute and chronic inflammation. |
| Role in the tumor microenvironment | In some in pulp source inhibition in cancer cells (MDSC) immune suppression function, influence tumor progression. |
Ly6G has a high affinity for ligand binding and is specific. Its recognition process does not rely on the major histocompatibility complex (MHC), demonstrating its unique role in rapid innate immunity.
Applications of Ly6G and Ly6G Antibody in Literature
1. Ruscitti, Cecilia, et al. "Recruited atypical Ly6G+ macrophages license alveolar regeneration after lung injury." Science immunology 9.98 (2024): eado1227. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciimmunol.ado1227
The article indicates that after lung injury, mononuclear derived Ly6G+ macrophages aggregate around the lesion, clear immune cells, and mutually promote regeneration with alveolar type II epithelial cells. This cell population depends on the GM-CSF/IL-4 signaling and is crucial for epithelial repair, and can serve as a new target for the treatment of lung injury.
2. Deyhle, Michael R., et al. "Depleting Ly6G positive myeloid cells reduces pancreatic cancer-induced skeletal muscle atrophy." Cells 11.12 (2022): 1893. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11121893
The article indicates that in a mouse model of pancreatic cancer, treatment with anti-LY6G antibodies effectively eliminated Ly6G+ cells (including granulocytoid MDSCS and neutrophils) in tumors and skeletal muscles, significantly delaying weight loss, reducing muscle atrophy and the expression of atrophie-related genes, suggesting that Ly6G+ cells may promote skeletal muscle consumption in cancerous cachexia.
3. Wang, Heng, et al. "Highly sensitive magnetic particle imaging of abdominal aortic aneurysm NETosis with anti-Ly6G iron oxide nanoparticles." Cell death discovery 10.1 (2024): 395. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-024-02156-3
The article indicates that for neutrophil infiltration in abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA), multimodal imaging nanoparticles targeting Ly6G (Ly6G NPs) have been studied and developed. Precise localization and severity monitoring of AAA lesions are achieved through techniques such as magnetic particle imaging (MPI). It was confirmed that inhibiting NETosis could reduce the aggregation of Ly6G+ cells and aortic injury.
4. Kleinholz, Corinna L., et al. "Ly6G deficiency alters the dynamics of neutrophil recruitment and pathogen capture during Leishmania major skin infection." Scientific reports 11.1 (2021): 15071. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-94425-9
The article indicates that the absence of Ly6G can delay the early recruitment of neutrophils to the infection site, reduce the initial infection rate of Leishmania, but does not affect the uptake of neutrophil substances by monocytes. Studies have shown that Ly6G enhances the early control of intracellular pathogens by the immune system by promoting the timely entry of neutrophils into the infection site.
5. Su, Ziwei, et al. "Ly6G+ Neutrophils and Interleukin-17 Are Essential in Protection against Rodent Malaria Caused by Plasmodium berghei ANKA." Research 7 (2024): 0559. https://doi.org/10.34133/research.0559
The article indicates that in the face of Plasmodium bergii infection, Ly6G+ neutrophils significantly increase, and their absence enhances the susceptibility to infection. IL-17 exerts a protective effect by amplifying the Ly6G+ population, while dihydroartemisinin (DHA) can enhance the antimalarial function of this group of cells through the CD18/CXCR4 pathway.
Creative Biolabs: Ly6G Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality Ly6G antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom Ly6G Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our Ly6G antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Su, Ziwei, et al. "Ly6G+ Neutrophils and Interleukin-17 Are Essential in Protection against Rodent Malaria Caused by Plasmodium berghei ANKA." Research 7 (2024): 0559. https://doi.org/10.34133/research.0559
Anti-Ly6G antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-AGO2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-634169) (CBMAB-AP203LY)

-
Mouse Anti-DISP2 Monoclonal Antibody (F66A4B1) (CBMAB-1112CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BRD3 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0801) (CBMAB-0804-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-DLL4 Recombinant Antibody (D1090) (CBMAB-D1090-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CDKL5 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1629) (CBMAB-C1689-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP1B1 Recombinant Antibody (E4) (CBMAB-0463-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD19 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-1224) (CBMAB-C1491-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CEMIP Recombinant Antibody (3C12) (CBMAB-K0296-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-APOH Recombinant Antibody (4D9A4) (CBMAB-A3249-YC)

-
Armenian hamster Anti-CD40 Recombinant Antibody (HM40-3) (CBMAB-C10365-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ENPP1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYE-0159) (CBMAB-E0375-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP1A2 Recombinant Antibody (M7-PB-E9) (CBMAB-A4013-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AMH Recombinant Antibody (5/6) (CBMAB-A2527-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BSN Recombinant Antibody (219E1) (CBMAB-1228-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-CD164 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0077) (CBMAB-C0086-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AOC3 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0014) (CBMAB-0014-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-DES Monoclonal Antibody (440) (CBMAB-AP1857LY)

-
Mouse Anti-Acetyl-α-Tubulin (Lys40) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623485) (CBMAB-CP2897-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-APC Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A661) (CBMAB-A3036-YC)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Recombinant Antibody (CBC05) (CBMAB-CR005LY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






