SAT1 Antibodies
Background
SAT1 encodes a key enzyme called spermine/spermidine acetyltransferase, which is mainly found in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. This enzyme participates in maintaining the intracellular balance of polyamine metabolism by catalyzing the acetylation reaction of polyamines (such as spermidine and spermidine), thereby regulating the processes of cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis. It plays a significant role in immune responses and stress responses because polyamine metabolism is closely related to inflammation and oxidative stress. The SAT1 gene was first identified in the 1990s, and its functional studies have revealed the impact of polyamine homeostasis on pathological mechanisms such as cancer and neurodegenerative diseases. As a core regulatory factor of the polyamine metabolic pathway, SAT1 provides an important target for the development of therapeutic strategies for related diseases and continuously promotes in-depth exploration of the molecular mechanisms of cellular metabolic networks.
Structure of SAT1
SAT1 is a protein with a molecular weight of approximately 38 kDa. There are slight differences in this molecular weight among different species, mainly due to minor changes in the amino acid sequence.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Bovine |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 38.0 | 37.8 | 38.1 | 37.9 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Conservative catalytic domain | Have high homology with human | The amino acid sequences are slightly different | Homologous to mammals |
This protein is composed of approximately 170 amino acids and forms a typical acetyltransferase folding structure. The core structure of the SAT1 protein contains A highly conserved acetyl-CoA binding site, which fulfills its catalytic function through arginine and aspartic acid residues. Its tertiary structure forms a hydrophobic channel for binding polyamine substrates (such as spermidine and spermidine). The crucial histidine residue at position 136 serves as a catalytic base, directly participating in the acetyl group transfer reaction, while aspartic acid at position 100 is responsible for stabilizing the transition state intermediate.
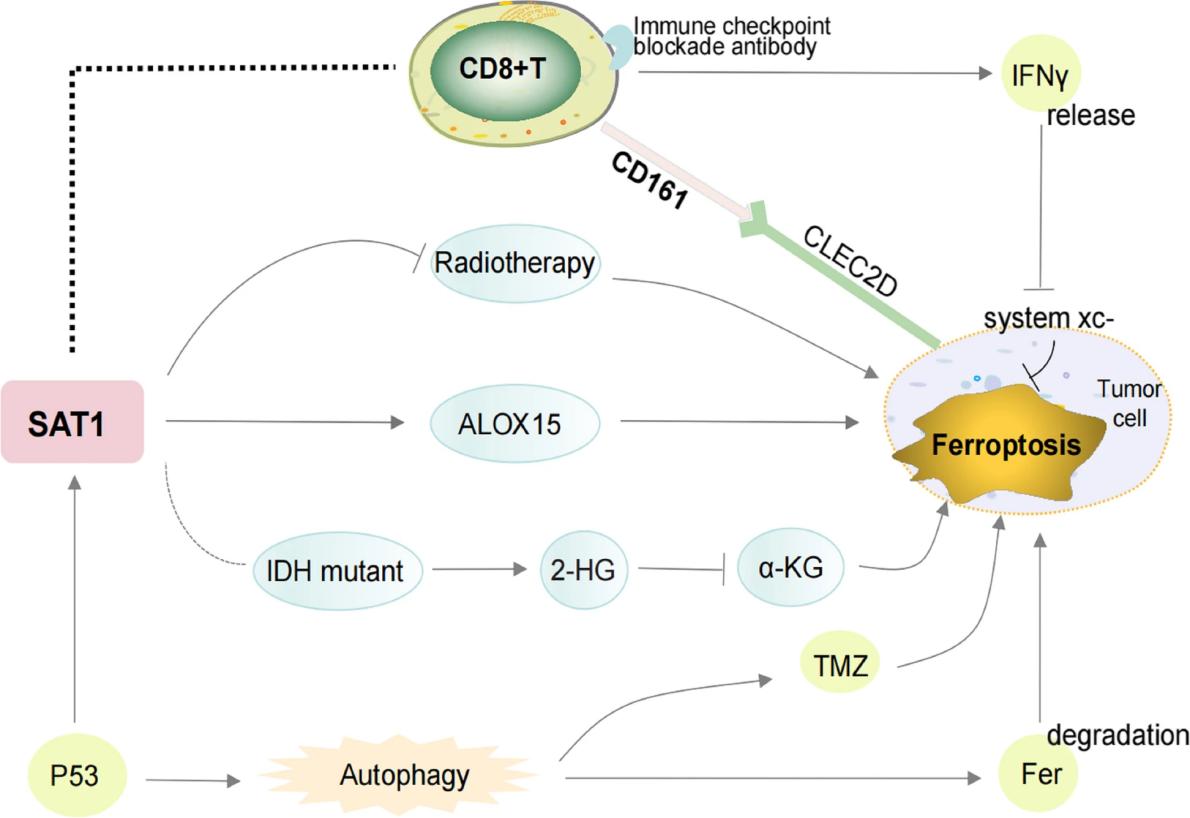 Fig. 1 Association of SAT1 with ferroptosis, immunotherapy, and chemoradiotherapy.1
Fig. 1 Association of SAT1 with ferroptosis, immunotherapy, and chemoradiotherapy.1
Key structural properties of SAT1:
- Typical folded structure of acetyltransferase
- Conserved acetyl-CoA binding pocket
- Arginine and aspartic acid residues constitute the catalytic center
- Hydrophobic channels are responsible for specifically recognizing polyamine substrates (such as spermidine and spermidine)
- Key histidine residues (such as His136) act as catalytic bases to participate in acetyl transfer
Functions of SAT1
The main function of the SAT1 gene-encoded protein (spermidine/spermidine acetyltransferase) is to regulate the balance of polyamine metabolism within cells. In addition, it is widely involved in key physiological and pathological processes such as cell proliferation, apoptosis, oxidative stress response and immune regulation.
| Function | Description |
| Regulation of polyamine metabolism | Catalyze the acetylation reaction of spermidine and spermidine, control the concentration of free polyamines in cells, and maintain polyamine homeostasis. |
| Cell proliferation and apoptosis | Acetylated polyamines affect DNA stability and cell cycle progression, inhibit excessive proliferation and induce apoptosis. |
| Oxidative stress response | Participate in adjusting reactive oxygen species (ROS) level, to protect cells from oxidative damage, and play an important role in the process of inflammation. |
| Immune regulation | In the polyamine mediated immune cell function and regulating role autoimmune disease development. |
| Cancer is associated with diseases | The abnormal expression and a wide variety of tumor, neurodegenerative diseases, and closely related to the occurrence and development of metabolic disease. |
The acetylation reaction catalyzed by SAT1 significantly reduces the positive charge carried by polyamines, affecting their interactions with nucleic acids and proteins. This mechanism plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular homeostasis and responding to internal and external stimuli.
Applications of SAT1 and SAT1 Antibody in Literature
1. Murthy, Divya, et al. "Cancer-associated fibroblast-derived acetate promotes pancreatic cancer development by altering polyamine metabolism via the ACSS2–SP1–SAT1 axis." Nature cell biology 26.4 (2024): 613-627. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-024-01372-4
The article indicates that pancreatic cancer-related fibroblasts regulate tumor metabolism by secreting acetic acid. Among them, ACSS2-mediated exogenous acetic acid promotes the acetylation of the K19 site of the SP1 protein, enhancing its stability and transcriptional activity, thereby upregulating SAT1 expression, maintaining polyamine homeostasis, and promoting the survival of cancer cells in an acidic microenvironment. Inhibiting the ACSS2-SP1-SAT1 axis can reduce tumor burden.
2. Tian, Wenwen, et al. "Autophagy Deficiency Induced by SAT1 Potentiates Tumor Progression in Triple‐Negative Breast Cancer." Advanced Science 11.36 (2024): 2309903. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202309903
The article indicates that high expression of SAT1 in triple-negative breast cancer predicts a poor prognosis. JUN activates SAT1 through transcription. The SAT1 protein binds and stabilizes YBX1 through HERC5 deubiquitination. Subsequently, m5C modification is used to maintain the stability of mTOR and inhibit autophagy, promoting tumor progression. Targeting the SAT1/YBX1/mTOR axis may become a new therapeutic strategy.
3. Zheng, Cuimiao, et al. "A noncanonical role of SAT1 enables anchorage independence and peritoneal metastasis in ovarian cancer." Nature Communications 16.1 (2025): 3174. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-58525-8
The article indicates that SAT1 promotes peritoneal metastasis of ovarian cancer through non-classical functions. SAT1 is highly expressed in ascites tumor cells. It acquires nuclear acetyl-CoA through reduction-carboxylation and acetylates H3K27 to enhance the transcription of mitose-related genes, maintaining anchor-independent survival and inhibiting mitotic death. Inhibiting SAT1 can reduce the transfer burden.
4. Dang, Yini, et al. "FTH1-and SAT1-induced astrocytic ferroptosis is involved in Alzheimer's disease: evidence from single-cell transcriptomic analysis." Pharmaceuticals 15.10 (2022): 1177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15101177
The article indicates that through scRNA-seq analysis, it was found that SAT1 and FTH1 jointly serve as the hub genes of ferroptosis in astrocytes. Changes in their expression affect ferroptosis activity and are associated with emotional cognitive function impairment and serum iron concentration in AD mice, suggesting that SAT1 may be involved in the pathological process of AD.
5. Yang, Huihuang, et al. "SAT1/ALOX15 signaling pathway is involved in ferroptosis after skeletal muscle contusion." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25.20 (2024): 11317. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252011317
The article indicates that SAT1 mediates ferroptosis by regulating the expression of ALOX15 after skeletal muscle contusion, promotes lipid peroxidation and affects the repair process. Inhibiting SAT1 can alleviate cell damage induced by iron overload and provide a new target for treatment.
Creative Biolabs: SAT1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality SAT1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom SAT1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our SAT1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Tian, Wenwen, et al. "Autophagy Deficiency Induced by SAT1 Potentiates Tumor Progression in Triple‐Negative Breast Cancer." Advanced Science 11.36 (2024): 2309903. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202309903
Anti-SAT1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-ARHGAP5 Recombinant Antibody (54/P190-B) (CBMAB-P0070-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ADAM12 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179752) (CBMAB-A1114-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AMIGO2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0756) (CBMAB-C2192-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCN2 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2383) (CBMAB-C2456-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-DES Monoclonal Antibody (440) (CBMAB-AP1857LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AMOT Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A564) (CBMAB-A2552-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CAT Recombinant Antibody (724810) (CBMAB-C8431-LY)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Recombinant Antibody (CBC05) (CBMAB-CR005LY)

-
Rat Anti-CD300A Recombinant Antibody (172224) (CBMAB-C0423-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BHMT Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0547) (CBMAB-0550-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALPL Antibody (B4-78) (CBMAB-1009CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-APP Recombinant Antibody (5C2A1) (CBMAB-A3314-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-APP Recombinant Antibody (DE2B4) (CBMAB-1122-CN)

-
Rabbit Anti-ENO2 Recombinant Antibody (BA0013) (CBMAB-0272CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO2 Recombinant Antibody (H14) (CBMAB-E1341-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CFL1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1771) (CBMAB-C1833-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CTCF Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2371) (CBMAB-C2443-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-8-oxoguanine Recombinant Antibody (V2-7719) (CBMAB-1898CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-AKT1 (Phosphorylated S473) Recombinant Antibody (V2-505430) (PTM-CBMAB-0067LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACVR1C Recombinant Antibody (V2-179685) (CBMAB-A1041-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






