SMURF2 Antibodies
Background
SMURF2 is a regulatory protein belonging to the HECT type E3 ubiquitin ligase, mainly existing in the cytoplasm and nucleus of eukaryotic cells. This protein participates in regulating key biological processes such as cell proliferation, apoptosis and cell polarity by specifically recognizing and ubiquitinating multiple substrates (such as SMAD proteins in the TGF-β signaling pathway). Due to its core role in maintaining tissue homeostasis, functional abnormalities of SMURF2 have been confirmed to be closely related to tumorigenesis and developmental defects. Since its first report by a team from Harvard Medical School in the United States in 2001, it has revealed a unique C2-WW-HECT domain synergy mechanism through crystal structure and functional domain analysis. This molecule, as a classic model for ubiquitination research, provides an important theoretical basis for understanding post-translational modifications of proteins, signal transduction regulation, and targeted treatment of diseases.
Structure of SMURF2
SMURF2 is a HECT type E3 ubiquitin ligase with a molecular weight of approximately 70-75 kDa. The exact molecular weight may vary depending on the different transcript splicing isomers.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Zebrafish | African clawed toad |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 73.2 | 72.8 | 73.1 | 71.5 | 72.3 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Includes C2, WW, HECT three functional areas | High homology with humans | The HECT domain is highly conserved | Functionally conserved during embryonic development | Functionally conserved during embryonic development |
This protein is composed of 748 amino acid residues, and its three-dimensional structure presents as a spherical catalytic core formed by the characteristic HECT domain. SMURF2 performs ubiquitin transfer through the C-terminal HECT domain, which contains a conserved cysteine residue as a catalytic center. The N-terminal of proteins is responsible for substrate recognition and subcellular localization, among which the WW domain can specifically bind to target proteins containing proline mods. After the HECT domain binds to E2, a conformational change occurs. By forming a ubiquitin thioester bond intermediate, the ubiquitin chain is ultimately transferred to the substrate protein, completing the ubiquitination process.
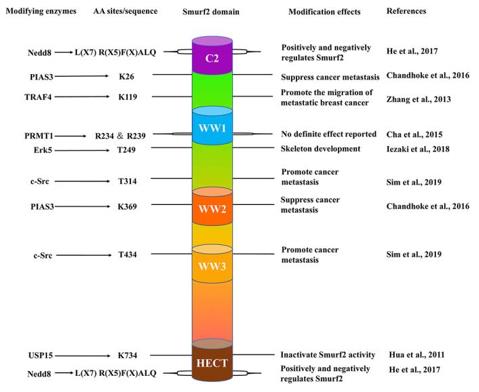 Fig. 1 The schematic structure of Smurf2.1
Fig. 1 The schematic structure of Smurf2.1
Key structural properties of SMURF2:
- Characteristic C2-WW-HECT multi-domain structure
- The HECT domain forms the catalytic center and contains the conserved cysteine active site
- The WW domain mediates protein interactions that recognize substrates containing proline motifs
- C2 domain is involved in cell membrane localization and functional regulation
Functions of SMURF2
The main function of the SMURF2 gene is to act as an E3 ubiquitin ligase to mediate the ubiquitination and degradation of substrate proteins. In addition, it is also widely involved in the regulation of various cellular physiological processes.
| Function | Description |
| Substrate targeted degradation | Specifically recognize and ubiquitinate transcription factors such as SMAD1/2 in the TGF-β signaling pathway, guiding their degradation through the proteasome pathway. |
| Cell cycle regulation | By regulating cell cycle-related proteins such as Cyclin D and p21, the process of G1/S phase transition is affected. |
| DNA damage response | Under the condition of DNA damage in regulating the BRCA1, TOP2A repair protein stability, etc. |
| Establishment of cell polarity | By ubiquitinating polar proteins such as PAR3, it affects the polarity of epithelial cells and the directional migration of cells. |
| Tumor suppression/promotion | According to the cellular context, it plays a dual role: it can not only degrade oncoproteins to inhibit tumors, but also may over-degrade tumor suppressor factors to promote tumor occurrence. |
The activity of SMURF2 is precisely regulated by its own phosphorylation state and subcellular localization. The catalytic efficiency of its HECT domain is significantly lower than that of the protein SMURF1 of the same family. This unique enzymatic kinetic characteristic is closely related to its biological functions in substrate selectivity and signal pathway specific regulation.
Applications of SMURF2 and SMURF2 Antibody in Literature
1. Pi, Yanan, et al. "Loss of SMURF2 expression enhances RACK1 stability and promotes ovarian cancer progression." Cell Death & Differentiation 30.11 (2023): 2382-2392. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-023-01226-w
This study reveals that SMURF2, as an E3 ubiquitin ligase of RACK1, inhibits the progression of ovarian cancer by promoting the ubiquitination and degradation of RACK1. Low expression of SMURF2 in ovarian cancer leads to increased stability of RACK1, thereby promoting tumorigenesis and is associated with a poor prognosis for patients. The SMURF2-RACK1 axis can serve as a potential therapeutic target.
2. Jiang, Chen, et al. "FOXO1 regulates RUNX2 ubiquitination through SMURF2 in calcific aortic valve disease." Redox biology 73 (2024): 103215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2024.103215
This study reveals the key role of SMURF2 in calcific aortic valve disease (CAVD). FOXO1 inhibits valve calcification by recruiting the E3 ubiquitin ligase SMURF2, promoting the ubiquitination and degradation of the key osteogenic factor RUNX2. The down-regulation of the FOXO1/SMURF2 axis in CAVD leads to the accumulation of RUNX2 protein and drives disease progression, suggesting that this axis can serve as a potential therapeutic target.
3. Bai, Yangjinming, and Ying Ying. "The post-translational modifications of Smurf2 in TGF-β signaling." Frontiers in molecular biosciences 7 (2020): 128. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2020.00128
This study reveals that Smurf2 is a key negative regulatory factor for TGF-β signaling. Its own activity and stability are precisely regulated by various post-translational modifications (PTMs) such as ubiquitination, SUMOylation, and phosphorylation. These complex modification mechanisms jointly determine the role of Smurf2 under various pathophysiological conditions, providing a new perspective for targeting Smurf2 to treat related diseases.
4. Youssef, Emile, et al. "Targeting the SMURF2-HIF1α axis: a new frontier in cancer therapy." Frontiers in Oncology 14 (2024): 1484515. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2024.1484515
This study reveals that SMURF2, as a key E3 ubiquitin ligase, plays a core role in tumor metabolism, ferroptosis and drug resistance by promoting the ubiquitination and degradation of proteins such as HIF1α. This protein has dual functions of tumor suppression and promotion. Targeting the SMURF2-HIF1α axis is expected to become a novel and precise treatment strategy for overcoming tumor drug resistance.
5. Han, Mingwei, et al. "SMURF2 facilitates ubiquitin-mediated degradation of ID2 to attenuate lung cancer cell proliferation." International Journal of Biological Sciences 19.11 (2023): 3324. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.80979
This study reveals that in non-small cell lung cancer, SMURF2 promotes the ubiquitination and degradation of ID2 protein, relives its inhibition of the transcription factor E2A, thereby activating p21 expression, inducing G1/S phase cell cycle arrest, and ultimately inhibiting tumor progression. Low expression of SMURF2 is associated with poor prognosis in patients, suggesting it as a potential therapeutic target.
Creative Biolabs: SMURF2 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality SMURF2 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom SMURF2 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our SMURF2 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Bai, Yangjinming, and Ying Ying. "The post-translational modifications of Smurf2 in TGF-β signaling." Frontiers in molecular biosciences 7 (2020): 128. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2020.00128
Anti-SMURF2 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-ACO2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179329) (CBMAB-A0627-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CRTAM Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2235) (CBMAB-C2305-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-14-3-3 Pan Recombinant Antibody (V2-9272) (CBMAB-1181-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACLY Recombinant Antibody (V2-179314) (CBMAB-A0610-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ABCA3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-178911) (CBMAB-A0145-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CCL18 Recombinant Antibody (64507) (CBMAB-C7910-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BACE1 Recombinant Antibody (CBLNB-121) (CBMAB-1180-CN)

-
Rabbit Anti-ABL1 (Phosphorylated Y185) Recombinant Antibody (V2-443434) (PTM-CBMAB-0001YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ADV Recombinant Antibody (V2-503423) (CBMAB-V208-1364-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ARID3A Antibody (A4) (CBMAB-0128-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-DISP2 Monoclonal Antibody (F66A4B1) (CBMAB-1112CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-AHCYL1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180270) (CBMAB-A1703-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-B2M Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0050) (CBMAB-0050-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC3 Recombinant Antibody (315304) (CBMAB-1214-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-EIF4G1 Recombinant Antibody (2A9) (CBMAB-A2544-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD2AP Recombinant Antibody (BR083) (CBMAB-BR083LY)

-
Rat Anti-CCR2 Recombinant Antibody (475301) (CBMAB-C1338-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC7 Recombinant Antibody (88C570) (CBMAB-L0261-YJ)

-
Rabbit Anti-B2M Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0059) (CBMAB-0059-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD247 Recombinant Antibody (6B10.2) (CBMAB-C1583-YY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








