FLNB Antibodies
Background
The FLNB gene encodes filamentin B, a large cytoskeletal protein that is mainly distributed in connective tissue and chondrocytes. This protein participates in cell morphology maintenance and movement regulation through cross-linked actin microfilaments, and plays a key role in integrin signal transduction and extracellular matrix interaction. Research has found that mutations in the FLNB gene can lead to various bone development disorders, such as Larson syndrome and Boitz-Jaeger syndrome-like diseases. In 2004, scientists first confirmed the association between FLNB mutations and human diseases. Its unique V-shaped dimer structure makes it an important model for studying the dynamics of the cytoskeleton. In-depth research on FLNB has greatly promoted our understanding of the molecular mechanisms of cell movement, bone development and mechanical signal transduction.
Structure of FLNB
Filamentin B encoded by the FLNB gene is a high-molecular-weight cytoskeletal protein with a molecular weight of approximately 280 kDa. There are certain structural differences among different species:
| Species | Human | Mouse | Zebra fish | Chicken |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 280 | 278 | 275 | 282 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Containing 24 Ig domain structure | Highly conservative and functionally similar | Role in embryonic development | High homology with mammals |
The FLNB protein is composed of 2,647 amino acids and has a dimer structure, interacting with the cytoskeleton through its N-terminal actin binding domain. This protein contains 24 repetitive immunoglobulin (Ig) -like domains, forming a flexible V-shaped conformation that endows it with mechanical sensing capabilities.
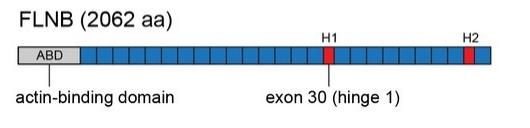 Fig. 1 Schematic of FLNB (Filamin B) protein domain structure.1
Fig. 1 Schematic of FLNB (Filamin B) protein domain structure.1
Key structural properties of FLNB:
- Multi-domain flexible configuration
- Mechanically sensitive hinge area
- Actin cross-linking site
- Signal molecule binding domain
Functions of FLNB
FLNB protein, as a key regulatory factor of the cytoskeleton, mainly participates in the maintenance of cell morphology and mechanical signal transduction, and also plays an important role in various physiological and pathological processes.
| Function | Description |
| Dynamic regulation of the cytoskeleton | Cell morphology and mechanical strength are maintained by forming a 3D network through cross-linking of actin microfilaments. |
| Mechanical signal transduction | Sensing mechanical force stimulation and activating integrin, Rho GTPase and other signaling pathways through conformational changes. |
| Regulation of bone development | Regulating the expression of SOX9 in chondrocytes affects the differentiation and mineralization processes of long bone growth plates. |
| Regulation of cell migration | By regulating the formation of filamentous pseudopodia and the turnover of adhesion spots, it affects embryonic development and wound healing. |
| Disease-related functions | Mutations lead to genetic diseases such as abnormal bone development (such as Larson syndrome), joint laxity and spinal deformities. |
Compared with other members of the filamentin family (FLNA/FLNC), FLNB has a unique developmental stage-specific expression pattern. The loss of its function can lead to more severe skeletal system defects. This protein forms a V-type dimer through the dimerization domain at the C-terminal. This special conformation enables it to simultaneously integrate mechanical stimuli and biochemical signals, playing an irreplaceable role in tissue development and homeostasis maintenance.
Applications of FLNB and FLNB Antibody in Literature
1. Fan, Guoyong, et al. "FLNB overexpression promotes tumor progression and associates with immune suppression, evasion and stemness in pancreatic cancer." American Journal of Cancer Research 14.2 (2024): 709. https://europepmc.org/article/med/38455418
This study, through bioinformatics analysis and experimental verification, found that filicin B (FLNB) is highly expressed in pancreatic cancer and is associated with a poor prognosis. FLNB promotes tumor progression by regulating the cell cycle, angiogenesis and immunosuppressive microenvironment (such as promoting Treg cell and TAMs infiltration and inhibiting CD8+ T cells), and may become a new target for the treatment of pancreatic cancer.
2. Fukushima, Kaya, et al. "Intragenic deletions in FLNB are part of the mutational spectrum causing spondylocarpotarsal synostosis syndrome." Genes 12.4 (2021): 528. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12040528
Research has found that novel homozygous deletion mutations of the FLNB gene (c.1346-1372_1941+389del and c.3127-353_4223-1836del) can lead to spinal-carpal tarsal fusion syndrome (SCT), and for the first time confirmed that large fragment structural variations of FLNB are related to this disease. It is recommended to adopt copy number detection to improve the molecular diagnostic rate of SCT.
3. Veyssiere, Maëva, et al. "MYLK* FLNB and DOCK1* LAMA2 gene–gene interactions associated with rheumatoid arthritis in the focal adhesion pathway." Frontiers in genetics 15 (2024): 1375036.https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2024.1375036
Research has found that the rare interaction between the FLNB and MYLK genes can increase the risk of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Through whole exome sequencing and MB-MDR analysis, it was revealed for the first time that FLNB is involved in the plaque adhesion pathway and promotes the occurrence of RA through gene interaction (MYLK*FLNB), providing new insights into the genetic mechanism of RA.
4. Ni, Lina, et al. "The expression and prognostic value of disulfidptosis progress in lung adenocarcinoma." Aging (Albany NY) 15.15 (2023): 7741.https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.204938
Based on the TCGA and GEO databases, this study constructed a prognostic model for lung adenocarcinoma containing five disulfide bond death-related genes (ACTB, FLNB, NCKAP1, SLC3A2, SLC7A11), including FLNB. Single-cell sequencing revealed that FLNB and NCKAP1 were highly expressed in endothelial cells. This model has higher predictive efficacy than clinical parameters, providing a new tool for the prognosis assessment of lung adenocarcinoma.
5. Li, Ji, et al. "An alternative splicing switch in FLNB promotes the mesenchymal cell state in human breast cancer." Elife 7 (2018): e37184. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.37184
Research has found that RNA-binding proteins QKI and RBFOX1 induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) by regulating the alternative splicing of FLNB exon 30, which promotes the release of the FOXC1 transcription factor by FLNB splicing variants. Abnormal FLNB splicing is significantly associated with the EMT characteristics of basal-like breast cancer, revealing a new regulatory mechanism of tumor cell plasticity.
Creative Biolabs: FLNB Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality FLNB antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom FLNB Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our FLNB antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Li, Ji, et al. "An alternative splicing switch in FLNB promotes the mesenchymal cell state in human breast cancer." Elife 7 (2018): e37184. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.37184
Anti-FLNB antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-BLNK Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0623) (CBMAB-0626-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-AZGP1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJZ-007) (CBMAB-Z0012-WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0790) (CBMAB-0793-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-AMIGO2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0756) (CBMAB-C2192-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADAM29 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179787) (CBMAB-A1149-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC3 Recombinant Antibody (315304) (CBMAB-1214-CN)

-
Rabbit Anti-BAD (Phospho-Ser136) Recombinant Antibody (CAP219) (CBMAB-AP536LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP5F1A Recombinant Antibody (51) (CBMAB-A4043-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ARHGDIA Recombinant Antibody (CBCNA-009) (CBMAB-R0415-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-AQP2 Recombinant Antibody (E-2) (CBMAB-A3358-YC)

-
Rat Anti-C5AR1 Recombinant Antibody (8D6) (CBMAB-C9139-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AMH Recombinant Antibody (5/6) (CBMAB-A2527-YC)

-
Rat Anti-CCR2 Recombinant Antibody (475301) (CBMAB-C1338-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-8-oxoguanine Recombinant Antibody (V2-7719) (CBMAB-1898CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CD33 Recombinant Antibody (6C5/2) (CBMAB-C8126-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALB Recombinant Antibody (V2-55272) (CBMAB-H0819-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BSN Recombinant Antibody (219E1) (CBMAB-1228-CN)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S1 Monoclonal Antibody (CBFYR-0120) (CBMAB-R0120-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV-5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-503417) (CBMAB-V208-1369-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CIITA Recombinant Antibody (CBLC160-LY) (CBMAB-C10987-LY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






