THY1 Antibodies
Background
THY1 is a gene that encodes glycoproteins on the cell surface and is mainly expressed in vertebrate tissues such as neurons, thymocytes and fibroblasts. The protein encoded by this gene is anchored to the cell membrane through glycosylphosphatidylinositol, participating in intercellular recognition, adhesion and signal transduction processes, and plays an important role in neural development and immune regulation. THY1 was first identified in mouse thymocytes in the 1970s, and its human homologous gene was successfully cloned and located in 1985. As a classic cell marker in immunology and neurobiology research, the analysis of THY1 protein structure and the study of the transmembrane signaling pathways it mediates have greatly advanced the understanding of the interaction mechanism between cell surface receptor function and the cell microenvironment.
Structure of THY1
The protein encoded by the THY1 gene is a cell surface glycoprotein with a molecular weight of approximately 25-35 kDa. The fluctuation of this value mainly stems from the differences in its glycosylation modification. Its molecular weight varies to some extent among different species and tissue types
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | About 25-35 | About 25 | About 26-30 |
| Primary Structural Differences | THY1 is manifested as a highly glycosylated GPI-anchored protein | THY1 is a classic model for studying its functions and is also GPI-anchored | THY1 is highly conservative in structure and function |
The core polypeptide chain of THY1 protein is composed of 111 to 112 amino acids and is anchored to the cell membrane by glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI). Its structure belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily and contains an immunoglobulin variable region (IgV) -like domain. This characteristic spherical domain is responsible for mediating protein-protein interactions. This domain forms a typical immunoglobulin fold, mainly composed of reverse-parallel β -sheets. Its tertiary structure is stabilized by a conserved disulfide bond, which is crucial for maintaining its spatial conformation and functions such as cell adhesion and signal transduction.
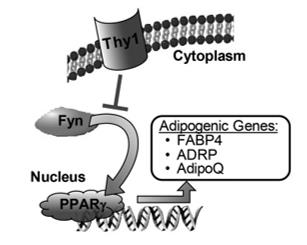 Fig. 1 Model describing the role of Thy1 in regulating adipogenesis.1
Fig. 1 Model describing the role of Thy1 in regulating adipogenesis.1
Key structural properties of THY1:
- Immunoglobulin folding structure
- Glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchoring
- Conserved disulfide bond
- N-glycosylation modification site
Functions of THY1
The glycoprotein encoded by the THY1 gene mainly performs the functions of signal transduction and cell adhesion on the cell surface, and is widely involved in physiological processes such as neural development, immune regulation and tissue repair.
| Function | Description |
| Cell signal transduction | As a cell surface receptor, it mediates intercellular recognition through its immunoglobulin domain, activates downstream signaling pathways such as tyrosine kinase, and regulates cell differentiation, proliferation and apoptosis. |
| Intercellular adhesion and recognition | Through homologous or heterologous interactions, it mediates the adhesion between neurons, between neurons and glial cells, as well as between immune cells and the matrix, influencing synaptic formation and immune cell migration. |
| Neural development and plasticity | Highly expressed in the nervous system, it participates in axon guidance, neuronal migration and synaptic stability, and is crucial for the correct establishment and plasticity of neural circuits. |
| Immune regulation | It is expressed on the surface of T cells, fibroblasts and other cells, regulating the activation threshold of T cells, the selection of thymocytes and inflammatory responses. |
| Tissue repair and fibrosis | Between activated fibroblasts and mesenchymal stem cells in the expression, involved in wound healing process, but its abnormal expression is associated with the pathological process of organ fibrosis. |
The interaction between THY1 and ligands (such as integrins) shows high specificity, and its signal output is highly dependent on cell type and microenvironment, which reflects its characteristic as a multifunctional "molecular switch" in complex biological systems.
Applications of THY1 and THY1 Antibody in Literature
1. Koren, Elle, et al. "Thy1 marks a distinct population of slow-cycling stem cells in the mouse epidermis." Nature Communications 13.1 (2022): 4628. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-31629-1
Research has found that Thy1+ keratinocytes in the basal layer of the epidermis have been confirmed as a stem cell population with unique transcriptional features and slow-cycle characteristics. Lineage tracing and cell clearance experiments have shown that this group can maintain skin homeostasis for a long time and promote wound repair, and it is a non-redundant skin stem cell population.
2. Chen, Luo, et al. "THY1 (CD90) maintains the adherens junctions in nasopharyngeal carcinoma via inhibition of SRC activation." Cancers 15.7 (2023): 2189. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15072189
Research has found that in nasopharyngeal carcinoma, THY1 exerts tumor suppressive effects by binding to PTPN22 and inhibiting the PDGF-Rβ/SRC signaling pathway. SRC inhibitors can effectively inhibit tumor metastasis in animal experiments, which provides a new potential target for treatment.
3. Noda, Seiji, et al. "CD34+ THY1+ synovial fibroblast subset in arthritic joints has high osteoblastic and chondrogenic potentials in vitro." Arthritis research & therapy 24.1 (2022): 45. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-022-02736-7
Research has found that among arthritis synovial fibroblasts, the CD34+THY1+ subset has the strongest osteogenic and chondrogenic differentiation capabilities. THY1 protein is crucial for the function of this stem cell. Targeting this subgroup may provide new strategies for joint repair.
4. Yi, Changsheng, et al. "THY1 is a prognostic-related biomarker via mediating immune infiltration in lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC)." Aging (Albany NY) 16.11 (2024): 9498. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.205880
Research has found that in lung squamous cell carcinoma, THY1 expression is significantly upregulated, which is associated with poor prognosis of patients and clinical features such as TP53 mutations and lymph node metastasis. Bioinformatics analysis suggests that it may exert its effect through the EMT pathway and by influencing immune infiltration.
5. Loui, Juliane, et al. "Neuronal THY1 Signaling Maintains Astrocytes in a Quiescent State." Glia 74.1 (2026): e70083. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.70083
Research has found that the THY1 protein on the surface of neurons communicates with astrocytes through the ITGB1 receptor, inhibiting their activation and proliferation, and promoting their apoptosis. Studies have shown that the absence of THY1 can lead to the continuous activation of astrocytes, thereby affecting the homeostasis of the brain.
Creative Biolabs: THY1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality THY1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom THY1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our THY1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Woeller, Collynn F., et al. "Thy1 (CD90) controls adipogenesis by regulating activity of the Src family kinase, Fyn." The FASEB Journal 29.3 (2014): 920. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.14-257121
Anti-THY1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-AZGP1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJZ-007) (CBMAB-Z0012-WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-AK4 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180419) (CBMAB-A1891-YC)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Recombinant Antibody (CBC05) (CBMAB-CR005LY)

-
Mouse Anti-FAS2 Monoclonal Antibody (1D4) (CBMAB-0071-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-AGK Recombinant Antibody (V2-258056) (CBMAB-M0989-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-EGR1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJZ-100) (CBMAB-Z0289-WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-CTCF Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2371) (CBMAB-C2443-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-CAMK2A Recombinant Antibody (BA0032) (CBMAB-0137CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CCN2 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2383) (CBMAB-C2456-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALB Recombinant Antibody (V2-55272) (CBMAB-H0819-FY)

-
Rat Anti-4-1BB Recombinant Antibody (V2-1558) (CBMAB-0953-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (ALB9) (CBMAB-0176CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-FOXA3 Recombinant Antibody (2A9) (CBMAB-0377-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BBS2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0253) (CBMAB-0254-YY)

-
Rat Anti-EMCN Recombinant Antibody (28) (CBMAB-E0280-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ASH1L Monoclonal Antibody (ASH5H03) (CBMAB-1372-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-CBL Recombinant Antibody (D4E10) (CBMAB-CP0149-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALX1 Recombinant Antibody (96k) (CBMAB-C0616-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BLNK Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0623) (CBMAB-0626-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-B2M Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0050) (CBMAB-0050-YY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






