Antibody Structure & Isotypes
Creative Biolabs has more than ten years experience in antibody development, and is committed to providing customers all over the world with one-stop services including antigen production, custom antibody development, antibody detection and production, hybridoma antibody gene sequencing, recombinant antibody expression, antibody humanization, antibody affinity maturation, anti-idiotype antibody and bispecific antibody production services. We also provide a broad range of antibody validation products to meet your specific requirements.
Antibody Structure
Antibodies are immune system-related multifunctional proteins called immunoglobulins (Ig) that possess several functional domains, and each of which plays an important role in the overall functionality of the molecule. All classes of full antibodies are composed of Y-shaped monomeric subunits with a basic H2L2 structure. A pair of identical heavy chains have ~50-75 kDa in size, and two identical light chains have ~25 kDa in size. Based on the different sequence of the heavy chain defines the class of Ig, such that α, δ, ε, γ, and µ heavy chains define the IgA, IgD, IgE, IgG, and IgM classes, respectively. The light chains are divided into κ or λ isoforms paired with all classes.
For H2L2 structure, Igs have two major regions, named Fc (“fragment, crystallizable”) and Fabs (“fragment, antigen binding”), both of which are comprised of domains consisting of β-pleated sheets primarily. The Fc region of an IgG antibody has a pair of hinge, CH2 and CH3 constant domains involved in various key functions such as multiple cell killing mechanisms and extending the half-life of the antibody. The Fab portion functions in specifically recognizing antigen with high affinity and specificity. The heavy chain component of a FAb contains the CH1 and VH domains, and the light chain component has either κ or λ CL and VL domains. The variable region is the core region of Fab further subdivided into hypervariable (HV) and framework (FR) regions. The HV regions directly contact with the antigen, which are also referred to as complementarity determining regions (CDRs). The FR regions with a beta-sheet structure serve as a scaffold to hold the HV regions in position to recognize antigen. The constant domains of four human IgG subclasses (IgG1- IgG4) share approximately 95% overall similarity. The main differences between four IgG subclasses are the hinge region with different amino acid composition and structure, and the placement of the disulfide bond linking the heavy and light chains.
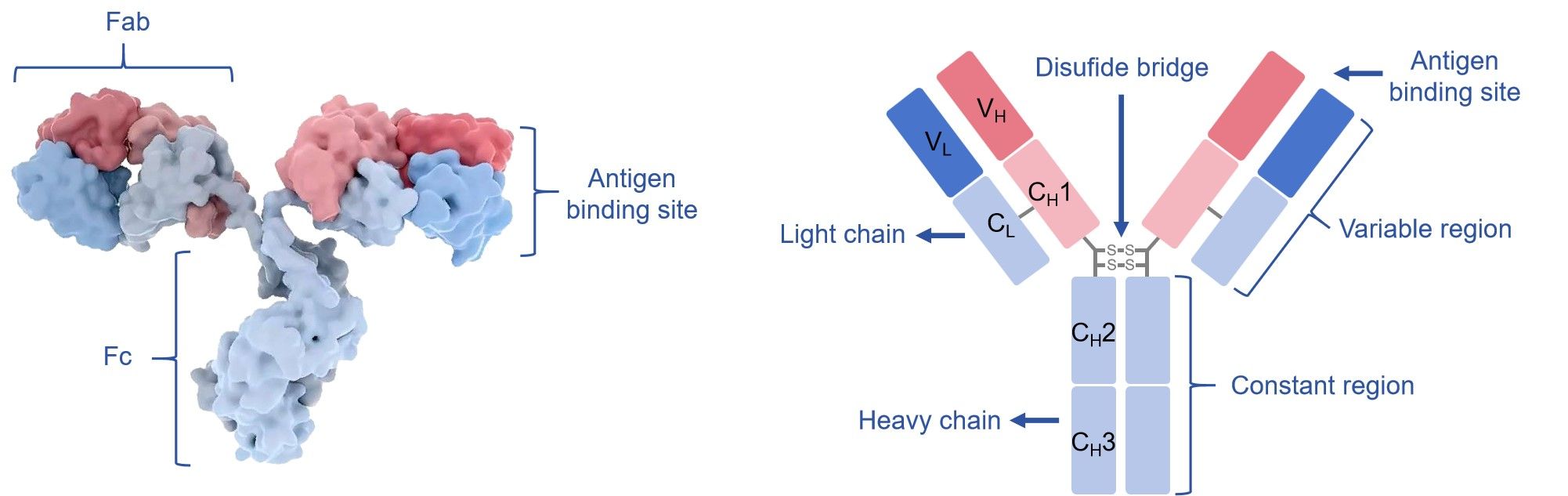 Fig.1 Schematic diagram of the immunoglobulin.
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of the immunoglobulin.
Antibody Isotypes
Based on the different sequence of the heavy chain of antibody (α, δ, ε, γ, and µ), there are five antibody isotypes in mammals including IgG, IgA, IgM, IgD and IgE.
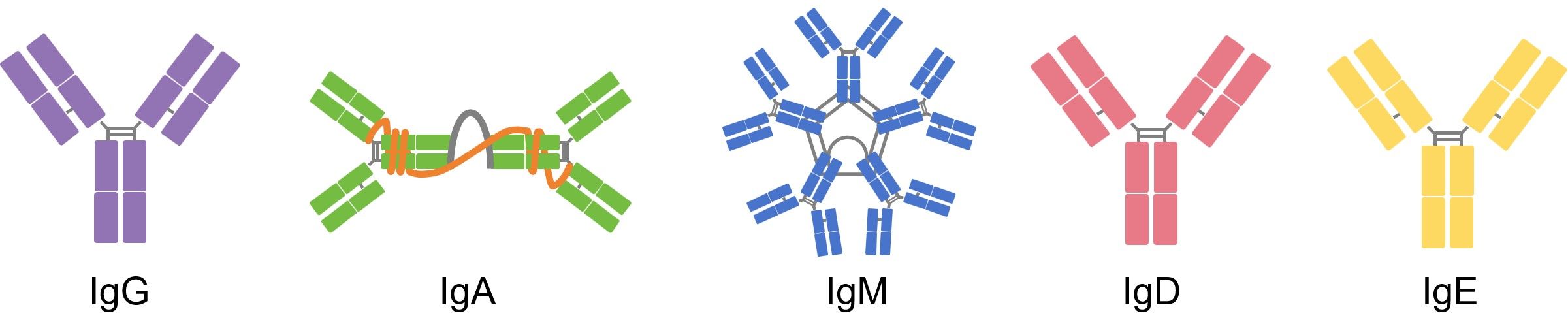 Fig.2 Antibody Isotypes.
Fig.2 Antibody Isotypes.
- IgG
IgG represents the most abundant circulating antibody, making up 80% of the total antibodies and 75% of that found in serum. IgG plays a major role in antibody-based immunity against pathogens. Besides, IgG can be further divided into 4 sub-isotypes (IgG1-IgG4), and each with its own effector function.
- IgA
IgA usually is a dimeric antibody produced locally in mucosal secretions of the respiratory, gastrointestinal and urogenital tracts, in saliva, tears, sweat, milk as well as in serum. IgA involves in protecting mucosal surfaces by neutralizing bacterial toxins and inhibiting adhesion to epithelial cells and maintain gut homeostasis.
- IgM
IgM is the largest antibody and an ancient immunoglobulin found in all jawed vertebrates, from sharks to mammals. It has five Y structures being joined by their Fc regions in a circular configuration. IgM is expressed on the surface of B cells that plays a significant role in B cell maturation in response to antigen stimulation. IgM presents in serum making up about 10 % of antibodies in the blood.
- IgD
IgD makes up about 1% of proteins in the plasma membranes of immature B-lymphocytes, which is monovalent and usually co-expressed with monomeric IgM, serves as antigen receptor for the activation of B cells. IgD is also produced in blood serum in a secreted, only representing 0.25% of immunoglobulins in serum.
- IgE
IgE is a monomeric antibody that has only been found in mammals. It accounts for only 0.002 % of the total serum antibodies. IgE binding to tissue cells, especially mast cells is associated with allergic reactions. IgE also functions in the immunity to parasites such as helminthes. IgE has been found it may severe as a last line of defense to protect against venoms.
What Can We Do For You?
Creative Biolabs has been providing comprehensive service for high quality rapid antibody development to customers for many years. Our antibody team strives to deliver successful projects to our customers at highly competitive prices with fast turnaround time for standard antibody production. We are confident enough to our personal service, cutting edge technology, speed, confidentiality, and delivering antibodies that work in our client’s intended assay. For more information, please contact us.


