Sandwich ELISA with Streptavidin-biotin Detection
Sandwich ELISAs are the most common type of ELISA. Sandwich ELISAs typically require the use of matched antibody pairs, where each antibody is specific for a different and non-overlapping region or epitope of the antigen molecule. It is important that matched antibody pairs are tested specifically in sandwich ELISA to ensure that they detect different epitopes, to achieve accurate results. The capture antibody, as its name implies, binds the antigen that can then be detected in a direct ELISA or in an indirect ELISA configuration.
The key advantage of a sandwich ELISA is its high sensitivity. It is 2-5 times more sensitive than direct or indirect ELISAs. Sandwich ELISA also delivers high specificity as two antibodies are used to detect the antigen. It offers flexibility since both direct and indirect methods can be used.
The advantages bring with sandwich ELISA a few disadvantages: if a standardized ELISA kit or tested antibody pair is not available, antibody optimization has to be worked out since it is important to reduce cross-reactivity between the capture and detection antibody pairs. Sandwich ELISAs are particularly suited to the analysis of complex samples, since the antigen does not need to be purified prior to the assay yet still delivers high sensitivity and specificity.
Click here for the Protocol of Sandwich ELISA with Streptavidin-biotin Detection.
Advantages
- High specificity: two antibodies are involved in antigen capture and detection.
- High sensitivity: 2-5 times more sensitive than direct or indirect ELISA.
- Flexibility and: both direct or indirect detection methods can be used.
Disadvantages
- Antibody pairs optimization or development can be challenging - cross-reactivity may occur between the capture and detection antibodies. Needs a standardized ELISA kit or tested antibody pair.
- Longer protocol.
Best for:
- Analysis of complex samples, since the antigen does not need to be purified prior to measurement.
Different Forms of Sandwich ELISA
The procedure for a sandwich ELISA firstly requires the well of an ELISA plate to be coated with a capture antibody. The analyte or sample is then added, followed by the detection antibody. According to the detection principle and whether to use the enzyme-labeled capture antibody, sandwich ELISA could be divided into three forms, direct sandwich ELISA, indirect sandwich ELISA, and sandwich ELISA with streptavidin-biotin detection.
- Form1: The detection antibody can be enzyme conjugated, in which case this is referred to as a direct sandwich ELISA.
- Form 2: If the detection antibody used is unlabeled, a secondary enzyme-conjugated detection antibody is required. This is known as an indirect sandwich ELISA.
- Form3: If the detection antibody used is biotin-labeled, the extra streptavidin-HRP is required for signal amplification. This is known as a sandwich ELISA with streptavidin-biotin detection.
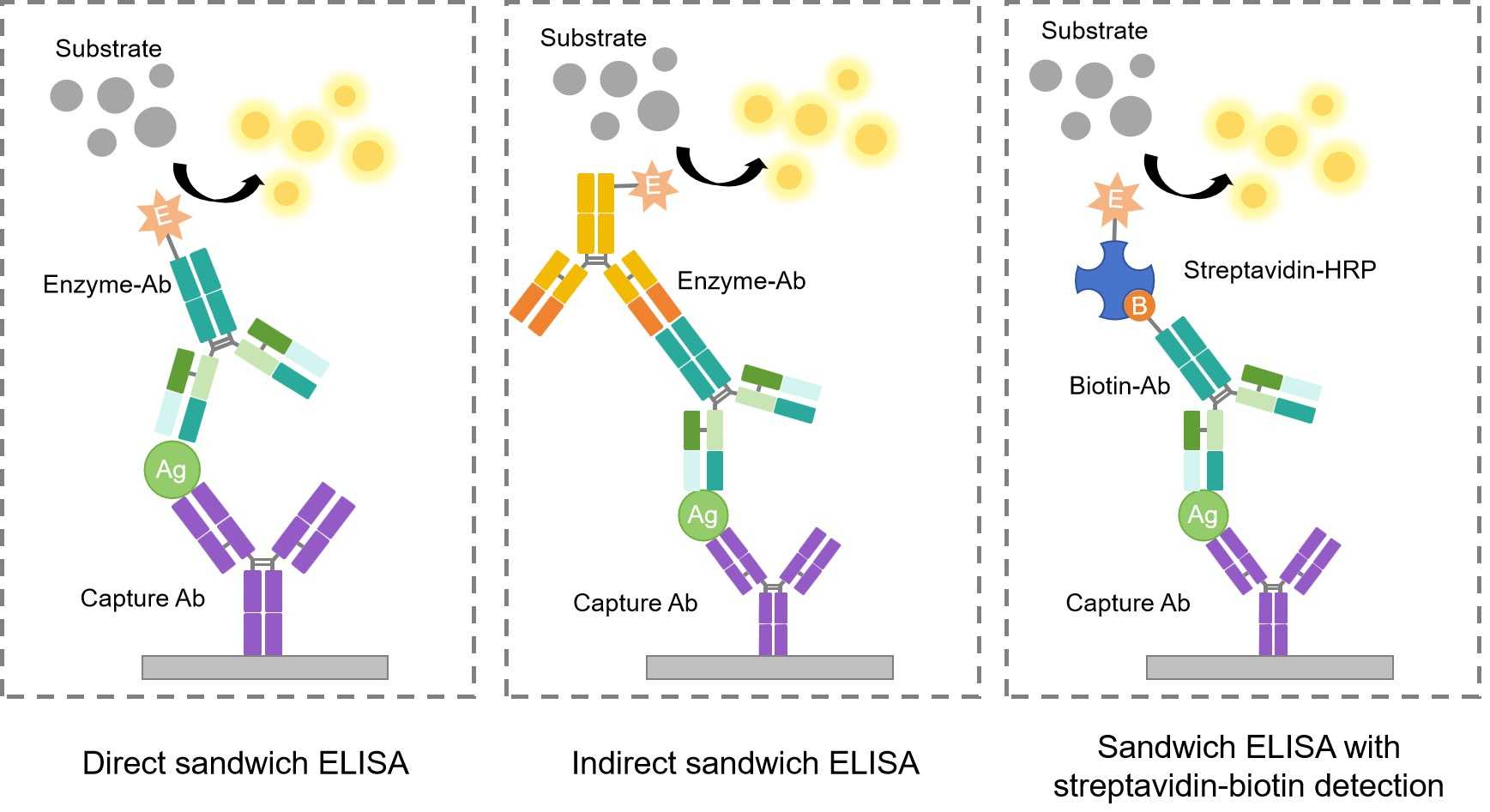 Fig.1 Normal modes and signal amplification mode of sandwich ELISA.
Fig.1 Normal modes and signal amplification mode of sandwich ELISA.
Streptavidin-biotin technology has been effectively used to improve ELISA detection due to the strong affinity between biotin and streptavidin because it has a dissociation constant (Kd) in the femtomolar range. Biotinylated probes are generally used to tag antibodies, antigens or peptides for subsequent detection using enzyme-conjugated streptavidin. Because biotin and streptavidin interact strongly, more analyte molecules can be captured on an ELISA plate.
Additionally, streptavidin conjugates are extremely popular in techniques such as Western Blot, ELISA and Flow Cytometry. Our Troubleshooting of Direct ELISA with Streptavidin-biotin Detection is designed to help you improve and troubleshoot the common problems.
