Pharmacokinetic (PK) Bridging ELISA Measuring Free Drug
Bridging ELISA
Bridging enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a special case of a sandwich ELISA in which a dimeric or oligomeric antigen (most often an antibody in the sample) is detected by a capture and detection antibody. The antigen bridges the two specific antibodies. Bridging ELISAs are most frequently used for the detection of IgG in pharmacokinetic (PK) or anti-drug antibody (ADA) assays.
The bridging ELISA takes full advantage of the two antigen binding sites on each antibody that allows them to form a bridge between antibody immobilized on microtiter plate wells with another enzyme-labeled antibody that is added in the detection step. In bridging assay, the unlabeled antibody is first immobilized onto the microtiter plate wells, and optimally diluted antibody in a test sample (normally human serum) are allowed to bind, followed by the usual washing step to remove unbound antibody. Enzyme-labeled antibody is then added to complete the bridge, and the substrate is then added to detect the presence of specific antibody drug.
Advantages of the bridging ELISA
- The capability to detect antibodies regardless of their isotype or the species of origin.
- Reducing background readings by using fewer amplification steps.
- The requirement for two specific binding events for the target drug increases the specificity of the assay.
Anti-Idiotype Antibodies
Biotherapeutic proteins, such as monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), have proven to be highly effective as drug candidates. Antibodies against these drugs (anti-drug antibodies, anti-ID) can be utilized in bridging ELISA to detect the drugs in samples. Anti-ID antibody is specific to the unique antigen binding (variable) region of another antibody. In this case, the anti-ID antibody is specific to the monoclonal therapeutic and/or its biosimilar. Based on different properties and binding modes, anti-ID antibodies can be classified into the following three types.
- Type 1: Type 1 anti-ID antibody is antigen blocking specific which binds to the paratope of the therapeutic antibody and competes with its target antigen. Therefore, this format of anti-ID antibody will only detect free antibody drug. Click here for Protocol of Pharmacokinetic (PK) Bridging ELISA Measuring Free Drug and Troubleshooting of Pharmacokinetic (PK) Bridging ELISA Measuring Free Drug.
- Type 2: Type 2 anti-ID antibody is non-blocking specific which binds near the paratope but still allows the antibody to bind its target antigen. It can be used to measure total drug. Click here for Pharmacokinetic (PK) Bridging ELISA Measuring Total Drug.
- Type 3: Type 3 anti-ID antibody is complex specific anti-ID antibody which only binds specifically the antibody-target complex but not the unbound antibody or the unbound target. This type of anti-ID antibody is only able to measure target bound drug. Click here for Pharmacokinetic (PK) Antigen Capture ELISA Measuring Bound Drug Exclusively.
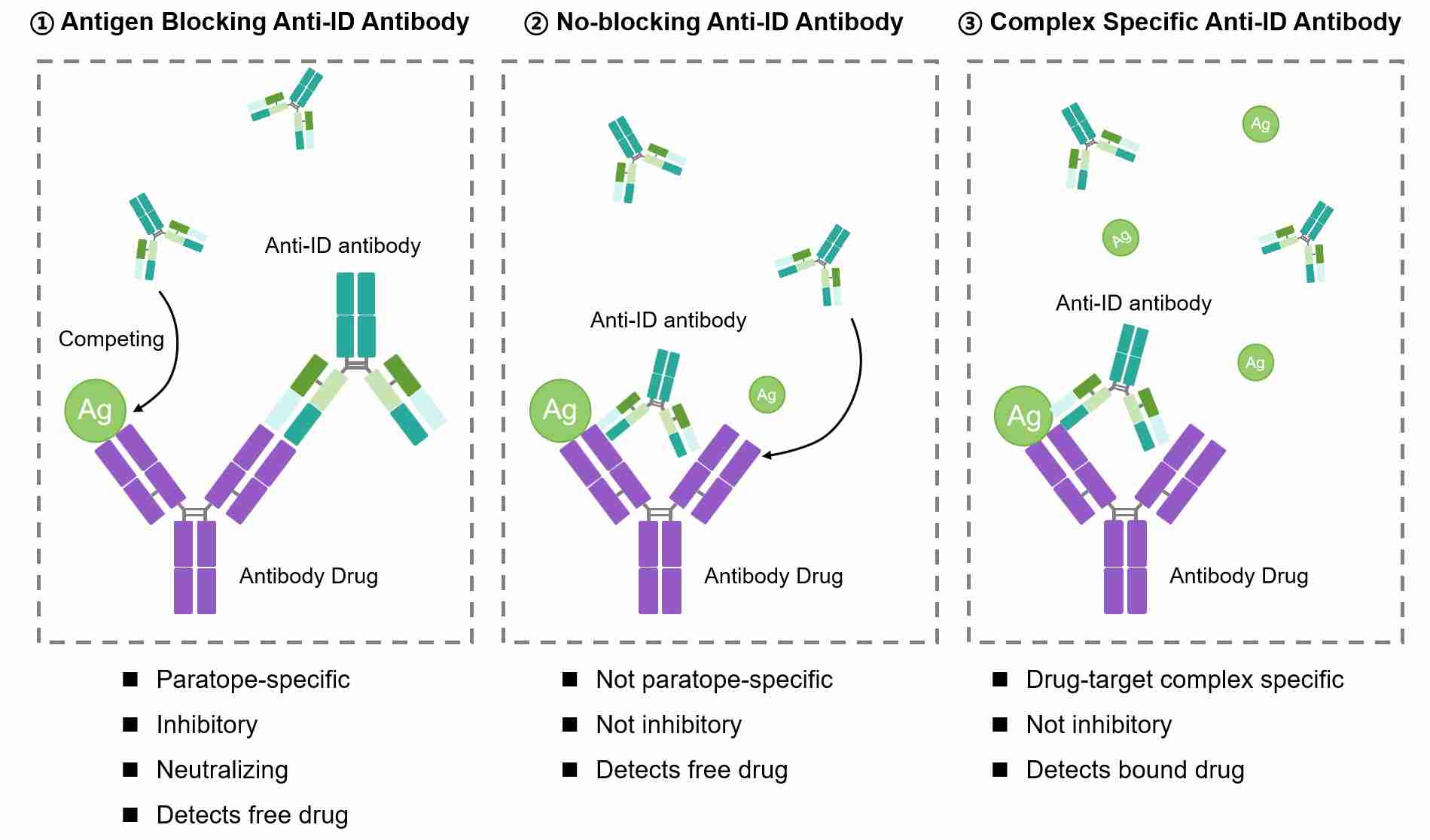 Fig.1 Types of anti-ID antibodies.
Fig.1 Types of anti-ID antibodies.
Anti-ID Antibodies and PK Assays
Because most anti-ID antibodies are generated against a specific antibody drug, they are normally used in preclinical practices for PK analysis. PK is the study of drug metabolism throughout the body. Specifically, researchers will determine the rate of drug absorption, distribution, bioavailability, and excretion in various cohorts of patients. In order to accomplish this, scientists need to be able to track antibody drugs which are bound or unbound to their designated target at various time points. By using anti-IDs, various forms of antibody therapeutics can be easily tracked and quantified in patient urine, serum, blood or other bodily fluids. Four common ways of performing an ELISA based PK assays are shown in Figure 2. The schematic diagram of the experiment PK bridging ELISA measuring free drug is the second type shown in Figure 2- Anti-ID-Bridging.
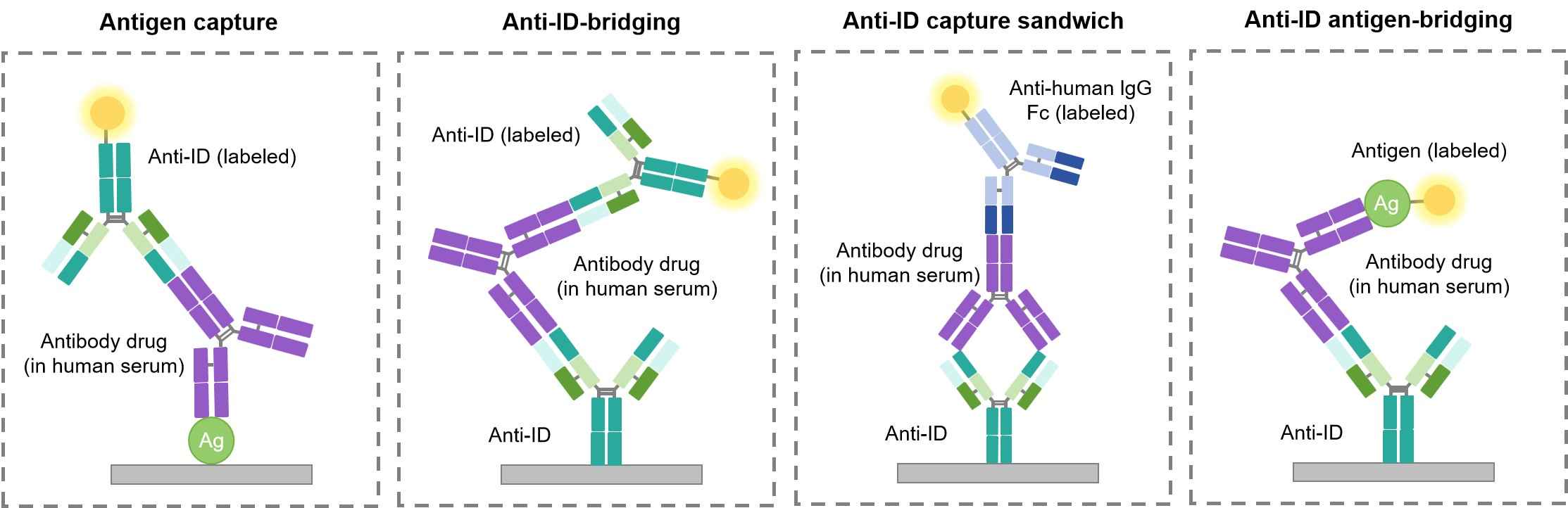 Fig.2 Types of ELISA-based PK assays.
Fig.2 Types of ELISA-based PK assays.
As a leading provider of anti-idiotypic antibody development, Creative Biolabs offers PK bridging ELISA services for measuring free drug to advance your drug development process. For more information, please feel free to contact us
