INSM1 Antibodies
Background
The INSM1 gene encodes a zinc finger transcription factor that is specifically expressed in neuroendocrine tissues and various tumors. This protein plays a core role in neuroendocrine differentiation and cell cycle regulation by regulating the transcriptional activity of downstream target genes. Its expression characteristics make INMS1 an important diagnostic marker for neuroendocrine tumors (such as neuroblastoma and small cell lung cancer). This gene was first identified in 1992. Its promoter region contains characteristic E-box elements that can interact with basic helical-ring-helix transcription factors. In-depth research on the function of INMS1 not only reveals the molecular mechanism of neuroendocrine differentiation but also provides a theoretical basis for tumor pathological diagnosis and the development of therapeutic targets.
Structure of INSM1
INSM1 is a zinc finger transcription factor protein with a molecular weight of approximately 58 kDa. This protein contains 542 amino acids, and its core structure is composed of five consecutive C2H2-type zinc finger domains. These domains coordinate with zinc ions through specific amino acid residues to form modular units that can specifically recognize DNA palindromic sequences. The N-terminal of the protein contains an inhibitory domain, while the amino acid sequence at the C-terminal is involved in the regulation of transcriptional activation function. This special structural combination enables INSM1 to bind to the conserved sequences in the promoter regions of target genes through zinc finger structures, thereby regulating the expression programs of neuroendocrine differentiation-related genes.
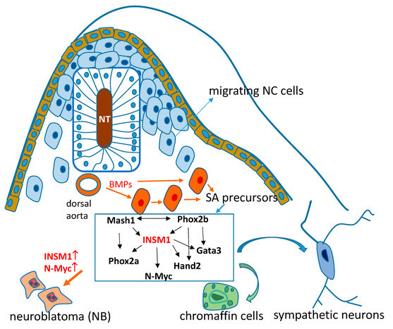 Fig. 1 Role of INSM1 in SA lineage differentiation.1
Fig. 1 Role of INSM1 in SA lineage differentiation.1
Key structural properties of INSM1:
- Contains five consecutive C2H2 -type zinc finger domains
- Each zinc finger structure coordinates with zinc ions through cysteine and histidine residues
- Form specific DNA-binding modules to recognize the promoter regions of target genes
Functions of INSM1
The core function of the INSM1 gene is to regulate neuroendocrine differentiation. However, this gene is also involved in various cellular processes, including cell cycle regulation and tumorigenesis.
| Function | Description |
| Regulation of neuroendocrine differentiation | As a key transcription factor, it activates the neuroendocrine-specific gene expression program and promotes the differentiation of cells into neuroendocrine phenotypes. |
| Cell cycle regulation | By inhibiting the activity of the Cyclin E/CDK2 complex, it prevents cells from entering the S phase from the G1 phase and maintains the quiescence of cells in the differentiated state. |
| Tumor suppressive function | Expressed in a variety of neuroendocrine tumor, its absence can lead to differentiation block and malignant proliferation. |
| Gene expression programming | By identifying conserved palindromic sequences in the promoters of target genes, cell-specific transcriptional networks are established and maintained. |
| The developmental pattern determines | Regulates the fate of certain cell lineages such as islet beta cells and nerve cells during embryonic development. |
INSM1 specifically binds to DNA through its zinc finger domain. This binding mode exhibits a high affinity feature, enabling it to precisely regulate the temporal expression of downstream genes and play a key role in development and disease.
Applications of INSM1 and INSM1 Antibody in Literature
1. Maleki, Zahra, et al. "INSM1, a novel biomarker for detection of neuroendocrine neoplasms: cytopathologists' view." Diagnostics 11.12 (2021): 2172. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11122172
The article indicates that INSM1 is a reliable novel biomarker for the diagnosis of neuroendocrine tumors. Its nuclear expression is clear in cytological specimens. Compared with traditional markers such as CGA and SYP, it usually shows higher sensitivity and specificity in the diagnosis of NETs in different sites and can effectively distinguish non-neuroendocrine tumors.
2. Lan, Michael S., and Chiachen Chen. "Small molecules targeting INSM1 for the treatment of high-risk neuroblastoma." Biology 12.8 (2023): 1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12081134
The article indicates that INSM1 is a key factor in neuroblastoma and interacts with the oncogenic protein N-Myc to promote tumor growth. Research has found that a variety of small molecule drugs can inhibit INSM1, providing a new potential strategy for the treatment of high-risk neuroblastoma.
3. Chen, Chiachen, and Michael S. Lan. "Interplay: the essential role between INSM1 and N-Myc in aggressive neuroblastoma." Biology 11.10 (2022): 1376. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11101376
The article indicates that INSM1 is a novel biomarker for neuroblastoma, which promotes each other with the oncogenic driver N-Myc and jointly drives tumor growth. Targeting the INSM1/N-Myc signaling axis is expected to become a new strategy for the treatment of high-risk neuroblastoma.
4. Zhang, Qian, et al. "INSM1 expression in mesenchymal tumors and its clinicopathological significance." BioMed Research International 2022.1 (2022): 1580410. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/1580410
Research has found that INSM1 is abnormally expressed in some mesenchymal tumors. Its expression characteristics in angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma and dedifferentiated liposarcoma may be helpful for the differential diagnosis of these tumors.
5. Metovic, Jasna, et al. "INSM1 expression in breast neoplasms with neuroedocrine features." Endocrine Pathology 32.4 (2021): 452-460. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12022-021-09682-1
Research has found that INSM1 has excellent sensitivity and specificity in the detection of neuroendocrine differentiation in breast cancer. However, like traditional markers, it cannot effectively distinguish neuroendocrine tumors from other subtypes of breast cancer with neuroendocrine differentiation.
Creative Biolabs: INSM1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality INSM1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom INSM1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our INSM1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Chen, Chiachen, and Michael S. Lan. "Interplay: the essential role between INSM1 and N-Myc in aggressive neuroblastoma." Biology 11.10 (2022): 1376. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11101376
Anti-INSM1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-BCL6 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0435) (CBMAB-0437-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CAPZB Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0944) (CBMAB-C2381-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CALR Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0763) (CBMAB-C0818-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-2C TCR Recombinant Antibody (V2-1556) (CBMAB-0951-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACO2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179329) (CBMAB-A0627-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-EMP3 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYE-0100) (CBMAB-E0207-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-APC Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A661) (CBMAB-A3036-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ADV Recombinant Antibody (V2-503423) (CBMAB-V208-1364-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AMIGO2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0756) (CBMAB-C2192-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCN2 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2383) (CBMAB-C2456-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ALK (Phosphorylated Y1278) Recombinant Antibody (D59G10) (PTM-CBMAB-0035YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BANF1 Recombinant Antibody (3F10-4G12) (CBMAB-A0707-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AQP2 Recombinant Antibody (G-3) (CBMAB-A3359-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ALB Recombinant Antibody (V2-55272) (CBMAB-H0819-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CARTPT Recombinant Antibody (113612) (CBMAB-C2450-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ARHGDIA Recombinant Antibody (CBCNA-009) (CBMAB-R0415-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-ANXA7 Recombinant Antibody (A-1) (CBMAB-A2941-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-8-oxoguanine Recombinant Antibody (V2-7719) (CBMAB-1898CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BrdU Recombinant Antibody (IIB5) (CBMAB-1038CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (D9S6V) (CBMAB-CP0017-LY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








