GCK Antibodies
Background
The GCK gene encodes a metabolic regulatory enzyme that is mainly expressed in the liver and pancreas of vertebrates. This enzyme maintains blood glucose homeostasis by catalyzing glucose phosphorylation, a process directly involved in the regulation of insulin secretion and glycogen synthesis. As a core component of the glucose sensing system, mutations in the GCK gene can lead to various glucose metabolism diseases, including mature-onset diabetes in young adults (MODY). Since its discovery in the 1960s, GCK has become a key target in the development of diabetes drugs due to its unique kinetic properties, such as positive synergistic effects. Research on its structure and function has greatly advanced our understanding of metabolic regulatory mechanisms, enzyme kinetics, and the molecular basis of hereditary metabolic diseases.
Structure of GCK
GCK is a key metabolic enzyme with a molecular weight of approximately 50 kDa, and its precise weight varies slightly depending on the species and isomer form.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Bovine |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 50.0 | 49.8 | 50.2 | 50.1 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Containing 465 amino acids, the typical dual domain structure | High homology with human and conserved catalytic mechanism | Highly conserved structure, allosteric regulation area | Highly homologous catalytic core and mammals |
This protein is composed of 465 amino acids and adopts a typical double-domain spherical structure: a larger domain is responsible for binding glucose and ATP, while a smaller domain is involved in allosteric regulation. The active center of GCK contains a highly conserved catalytic motif, and its key residues (such as aspartic acid-204) directly participate in the phosphate transfer reaction. The allosteric regulatory region of this enzyme can sense glucose concentration and regulate enzyme activity through conformational changes. This characteristic is the core structural basis for maintaining glucose homeostasis.
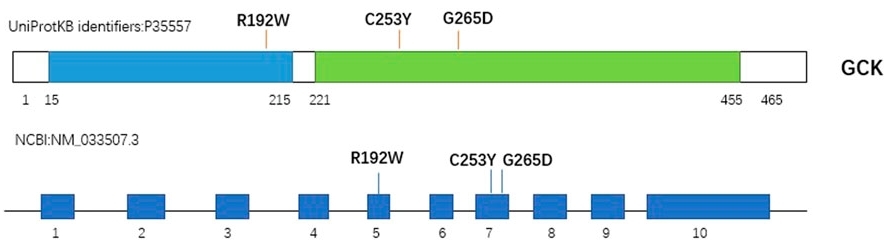 Fig. 1 Schematic view of human GCK protein and gene.1
Fig. 1 Schematic view of human GCK protein and gene.1
Key structural properties of GCK:
- Typical dual domain spheres, including large and small two function structure domain
- Large domains form glucose and ATP binding pockets, featuring highly conserved catalytic cores
- Small domains are involved in allosteric regulation and sense changes in glucose concentration
Functions of GCK
The main function of GCK is to act as a glucose sensor and a key enzyme for metabolic regulation. In addition, it is also involved in the regulation of insulin secretion and the initiation of liver glycogen synthesis.
| Function | Description |
| Glucose sensing | Sensing changes in blood glucose concentration in pancreatic β-cells regulates the rate of insulin secretion. |
| Catalytic phosphorylation of glucose | In the liver, it catalyzes the conversion of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate, which is the first rate-limiting reaction in glycolysis and glycogen synthesis. |
| Maintenance of blood glucose homeostasis | Through its unique dynamics features (low substrate affinity, positive synergies) physiological response to change blood sugar levels. |
| Metabolic signal conversion | Converting extracellular glucose concentration into intracellular metabolic signals affects gene expression and energy distribution pathways. |
| Association with diabetes | Loss or mutation of GCK function can lead to various types of diabetes, such as MODY2 (adult-onset diabetes). |
The kinetic curve of GCK is S-shaped (positive synergy effect) rather than the typical Mie hyperbola, which indicates that it can sensitively regulate catalytic activity within the physiological blood glucose range and play a core role as a "metabolic switch".
Applications of GCK and GCK Antibody in Literature
1. Mirshahi, Uyenlinh L., et al. "Reduced penetrance of MODY-associated HNF1A/HNF4A variants but not GCK variants in clinically unselected cohorts." The American Journal of Human Genetics 109.11 (2022): 2018-2028. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2022.09.014
The article indicates that the penetrance of GCK pathogenic gene variations in the population is extremely high (89%-97%), and they show consistent performance in different cohorts, which forms a sharp contrast with HNF1A/HNF4A. Its high penetrance and clear clinical significance make it suitable for inclusion in the secondary gene list of ACMG.
2. Abu Aqel, Yasmin, et al. "Glucokinase (GCK) in diabetes: from molecular mechanisms to disease pathogenesis." Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters 29.1 (2024): 120. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11658-024-00640-3
The article indicates that GCK is a key enzyme in glucose metabolism, and its gene mutation can lead to single-gene diabetes such as MODY or congenital hyperinsulinemia. Studying the expression regulation, structure and function of GCK, as well as animal and stem cell models, is of great significance for understanding blood glucose homeostasis and targeted therapy.
3. Dai, Tongtong, et al. "GCK exonic mutations induce abnormal biochemical activities and result in GCK-MODY." Frontiers in Genetics 14 (2023): 1120153. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2023.1120153
The article indicates that GCK gene mutations (such as p.R192W, p.C253Y, p.G265D) can lead to a decrease in GCK enzyme activity, protein stability and expression level, enhanced ubiquitination degradation, and thereby cause GCK-Mody (MODY2) and abnormal glucose metabolism.
4. Crowley, Mairead T., et al. "Management of pregnancy in women with monogenic diabetes due to mutations in GCK, HNF1A and HNF4A genes." Frontiers in Genetics 15 (2024): 1362977. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2024.1362977
The article indicates the pregnancy management around GCK-MODY: Maternal carriers usually only present with mild fasting hyperglycemia, but the birth weight of the offspring mainly depends on the fetal genotype. The weight of fetuses with heterozygous mutations is mostly normal, while wild-type fetuses are often larger than the gestational age (about 600 grams). They need to be distinguished and monitored through ultrasound abdominal circumference or fetal DNA testing in maternal blood.
5. Fan, Junling Fu, and **nhua **ao. "Distinguishing the lipid profile of GCK-MODY patients and its correlation with hsCRP levels." Frontiers in Endocrinology 13 (2022): 1024431. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2022.1024431
The article indicates that patients with GCK-MODY have unique protective lipid characteristics: high HDL-C, low LDL-C and low TG/HDL ratio, and are associated with a lower hsCRP level. This anti-inflammatory lipid profile may be one of the important mechanisms for its relatively low risk of macrovascular complications.
Creative Biolabs: GCK Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality GCK antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom GCK Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our GCK antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Dai, Tongtong, et al. "GCK exonic mutations induce abnormal biochemical activities and result in GCK-MODY." Frontiers in Genetics 14 (2023): 1120153. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2023.1120153
Anti-GCK antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-ALX1 Recombinant Antibody (96k) (CBMAB-C0616-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BACE1 Recombinant Antibody (CBLNB-121) (CBMAB-1180-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-DES Monoclonal Antibody (440) (CBMAB-AP1857LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADRB2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180026) (CBMAB-A1420-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-EMP3 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYE-0100) (CBMAB-E0207-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACVR1C Recombinant Antibody (V2-179685) (CBMAB-A1041-YC)

-
Rat Anti-4-1BB Recombinant Antibody (V2-1558) (CBMAB-0953-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ARIH1 Recombinant Antibody (C-7) (CBMAB-A3563-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-ALOX5AP Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-1219) (CBMAB-F0750-CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-ADRA1A Recombinant Antibody (V2-12532) (CBMAB-1022-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL2L1 Recombinant Antibody (H5) (CBMAB-1025CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ALB Recombinant Antibody (V2-55272) (CBMAB-H0819-FY)

-
Rat Anti-ADGRE4 Recombinant Antibody (V2-160163) (CBMAB-F0011-CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-ALK (Phosphorylated Y1278) Recombinant Antibody (D59G10) (PTM-CBMAB-0035YC)

-
Mouse Anti-dsRNA Recombinant Antibody (2) (CBMAB-D1807-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BSN Recombinant Antibody (219E1) (CBMAB-1228-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-DMD Recombinant Antibody (D1190) (CBMAB-D1190-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ARSA Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A799) (CBMAB-A3679-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-FN1 Monoclonal Antibody (71) (CBMAB-1241CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-EIF4G1 Recombinant Antibody (2A9) (CBMAB-A2544-LY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








