IL10 Antibodies
Background
IL10 is a small molecule polypeptide cytokine secreted by various immune cells, mainly acting on targets such as macrophages and T cells. This factor exerts crucial anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory functions by inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and the antigen presentation process, maintaining immune homeostasis. In chronic infections and autoimmune diseases, the expression level of IL10 directly affects pathological progression, and its functional defect may lead to excessive inflammatory responses. This gene was first discovered by Fiorentino's team in 1989, and the construction of a gene knockout mouse model was completed in 1993. The related research was honored as an "Immunology Milestone Breakthrough" by Nature magazine in 2019. Its multi-level regulatory mechanism (including epigenetic modifications and post-transcriptional regulation) has become a research paradigm for immune tolerance, significantly promoting the development of therapeutic strategies for autoimmune diseases.
Structure of IL10
IL-10 is a small cytokine with a molecular weight of approximately 18.6 kDa. There are slight differences in its molecular weight among different species, mainly due to changes in amino acid sequences.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Bovine | Rhesus monkey |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 18.6 | 19.0 | 18.8 | 18.5 | 18.6 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Conserved sequence, highly homologous to primates | Several amino acid substitutions were present | Similar to the mouse variant | There are some sequence differences | Highly similar to human IL-10 |
This protein is composed of 178 amino acids and presents A typical four-helix bundle structure (A-D helix), belonging to the Class II cytokine family. Its tertiary structure is stabilized by two disulfide bonds, forming a compact homodimer or a complex bound to the receptor. IL-10 specifically binds to the receptor subunits of IL-10R1 and IL-10R2 through its receptor binding plane (mainly composed of partial residues of helical A, C, and D), thereby activating the JAK-STAT signaling pathway and exerting its immunosuppressive function.
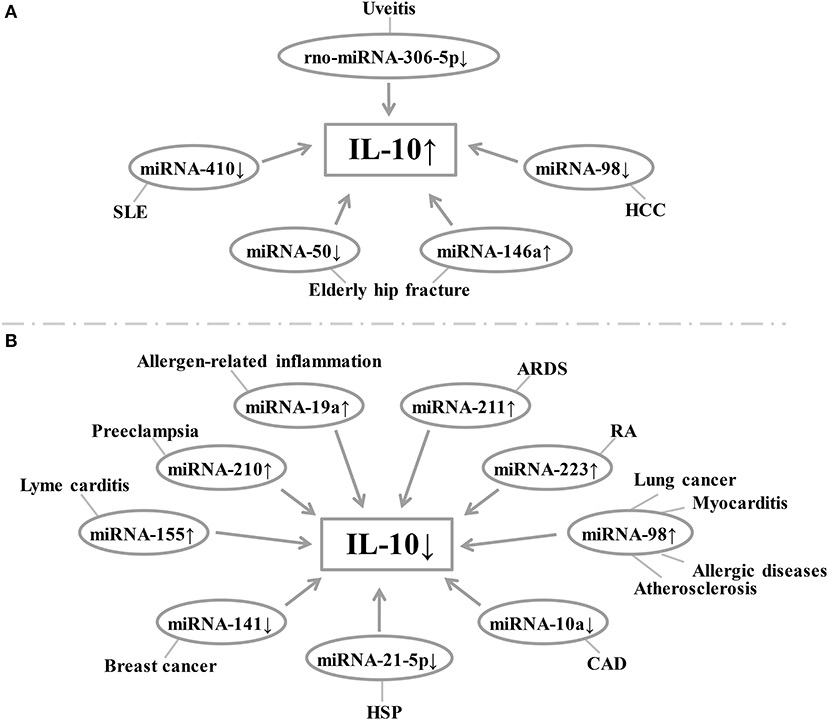 Fig. 1 Relationship between miRNA expression and IL-10 levels in each disease.1
Fig. 1 Relationship between miRNA expression and IL-10 levels in each disease.1
Key structural properties of IL-10:
- Conservative four-helix bundle topology (A-D helix)
- Hydrophobic cores maintain the stability of receptor binding interfaces
- Two disulfide bonds are crucial for maintaining the conformation and biological activity of proteins
- Specific receptor binding sites
Functions of IL10
The main function of IL-10 is to suppress excessive immune responses and maintain immune homeostasis. In addition, it is also involved in various pathophysiological processes such as tissue repair, cell proliferation and regulation of the tumor microenvironment.
| Function | Description |
| Immunosuppression | Inhibit the antigen presentation function of macrophages and dendritic cells, and reduce the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (such as TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6). |
| Regulate T-cell responses | Inhibit the immune response of Th1 cells, promote the differentiation and function of regulatory T cells (Treg), and maintain immune tolerance. |
| Anti-inflammatory effect | Downregulation of the transcription of inflammatory mediators through JAK-STAT signaling pathway can reduce tissue inflammatory damage. |
| Tissue repair support | In the late inflammation promote fibroblast proliferation and collagen synthesis, contribute to tissue damage repair and fibrosis process. |
| Regulation of the tumor microenvironment | Highly expressed in a variety of tumors, it can inhibit anti-tumor immune response, promote tumor immune escape and angiogenesis. |
IL-10 activates the downstream JAK1 and STAT3 signaling pathways through its receptor, and its dose-effect curve shows a steep inhibitory characteristic, indicating that it can efficiently inhibit the activation of immune cells at low concentrations, exerting a strong anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effect.
Applications of IL10 and IL10 Antibody in Literature
1. Crabtree, Elizabeth, et al. "Inhibition of experimental autoimmune uveitis by intravitreal AAV-Equine-IL10 gene therapy." PLoS One 17.8 (2022): e0270972. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0270972
This study evaluated the efficacy of AAV8-equine IL10 gene therapy on experimental autoimmune uveitis (EAU) in rats. A single intravitreal injection of AAV8-ma IL10 could significantly reduce the ocular inflammation score and the number of aqueous humor cells, and dose-dependent IL10 expression was detected in tissues such as the ciliary body and retina. The results show that the therapy is safe and effective, providing a new strategy for the treatment of recurrent uveitis in horses and humans.
2. Fife, Mark S., et al. "Novel IL10 gene family associations with systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis." Arthritis research & therapy 8.5 (2006): R148. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar2041
This study analyzed the IL10 gene family polymorphisms in 473 controls and 172 children with systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (sJIA). It was found that the low-expression genotype of IL10-1082 and the polymorphism of IL20-468 were significantly associated with sJIA. The haplotype of IL10-1082A/IL20-468T increased the risk of disease by 2.24 times, suggesting that these cytokines play a key role in the pathogenesis of sJIA.
3. Zheng, Zhonghua, et al. "Epigenetic changes associated with interleukin-10." Frontiers in immunology 11 (2020): 1105. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.01105
The article indicates that IL-10, as a key anti-inflammatory factor, its expression is regulated by epigenetic modifications such as DNA methylation and histone acetylation. Studies have found that the abnormal expression of IL-10-related miRNA and lncRNA GAS5 in various diseases can affect the level of IL-10, suggesting that epigenetic mechanisms play an important role in IL-10-mediated inflammation and autoimmune diseases.
4. Thye, Thorsten, et al. "IL10 haplotype associated with tuberculin skin test response but not with pulmonary TB." PLoS One 4.5 (2009): e5420. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0005420
In this study, it was found in the tuberculosis population of Ghana that the low expression hahatype of IL10 (-2849A/-1082A/-819C/-592C) was significantly associated with negative individuals in the tuberculin skin test (OR=2.15). ELISA confirmed that the plasma IL-10 level of the haplotype carrier was low (p=0.016), suggesting that the high expression of IL-10 might lead to a long-term specific non-response state by inhibiting adaptive immunity.
5. Sziksz, Erna, et al. "Fibrosis related inflammatory mediators: role of the IL-10 cytokine family." Mediators of inflammation 2015.1 (2015): 764641. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/764641
This study indicates that chronic fibroproliferative disorders (FDs) are the main cause of approximately 45% of deaths in developed countries. Their common feature is the excessive activation of myofibroblasts and extracellular matrix deposition triggered by chronic inflammation. This review focuses on exploring the key roles of IL-10 cytokine family members (IL-10, IL-19, IL-20, etc.) in organ fibrosis. These newly discovered pro-tissue remodeling-related inflammatory factors provide new targets for the diagnosis and treatment of fibrosis.
Creative Biolabs: IL10 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality IL10 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom IL10 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our IL10 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Zheng, Zhonghua, et al. "Epigenetic changes associated with interleukin-10." Frontiers in immunology 11 (2020): 1105. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.01105
Anti-IL10 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-CD8 Recombinant Antibody (C1083) (CBMAB-C1083-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BACE1 Recombinant Antibody (CBLNB-121) (CBMAB-1180-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-CFL1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1771) (CBMAB-C1833-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-FOXA3 Recombinant Antibody (2A9) (CBMAB-0377-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BRD3 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0801) (CBMAB-0804-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-Acetyl-α-Tubulin (Lys40) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623485) (CBMAB-CP2897-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD19 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-1224) (CBMAB-C1491-CQ)

-
Rat Anti-CCR2 Recombinant Antibody (475301) (CBMAB-C1338-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP1B3 Recombinant Antibody (1E9) (CBMAB-A4021-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0216) (CBMAB-0217-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADAM12 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179752) (CBMAB-A1114-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-DDC Recombinant Antibody (8E8) (CBMAB-0992-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0790) (CBMAB-0793-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-C5AR1 Recombinant Antibody (R63) (CBMAB-C9553-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACTG1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179597) (CBMAB-A0916-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CCND2 Recombinant Antibody (DCS-3) (CBMAB-G1318-LY)

-
Rat Anti-4-1BB Recombinant Antibody (V2-1558) (CBMAB-0953-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-AP2M1 (Phosphorylated T156) Recombinant Antibody (D4F3) (PTM-CBMAB-0610LY)

-
Mouse Anti-APOA1 Monoclonal Antibody (CBFYR0637) (CBMAB-R0637-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AFDN Recombinant Antibody (V2-58751) (CBMAB-L0408-YJ)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








