PEAK1 Antibodies
Background
The PEAK1 gene (also known as pseudokinase 1) is a key gene encoding scaffold proteins and is mainly expressed in various tissue cells of vertebrates. This protein regulates key biological processes such as cell proliferation, migration and survival by participating in the intracellular signal transduction network, and plays a particularly important role in cancer occurrence and immune responses. PEAK1 was first identified in 2009, and its name is derived from its "peak" expression feature in the tyrosine kinase signaling pathway. As an atypical kinase domain protein, PEAK1, although lacking catalytic activity, can mediate the cross-dialogue of signaling pathways such as EGFR and Src through protein-protein interactions. Related research has provided an important model for understanding the complexity of cellular signaling networks and has continuously attracted attention in the field of tumor-targeted therapy.
Structure of PEAK1
PEAK1 (pseudo-kinase 1) is a large scaffold protein with a molecular weight of approximately 180 kDa. Its precise molecular weight may fluctuate slightly under different isomers or post-translational modifications.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | ~180 | ~178 | ~181 |
| Primary Structural Differences | As a signal hub, it regulates cell proliferation and migration | Similar effects in developmental and cancer models | Participate in tissue repair processes such as liver regeneration |
The PEAK1 protein contains multiple domains, with its core being a pseudo-kinase domain without catalytic activity. This domain is highly conserved during evolution and is mainly responsible for mediating protein-protein interactions. The overall conformation of the protein forms a flexible scaffold platform through its tertiary structure, which can integrate multiple upstream signaling pathways such as EGFR, Src, and focal adhesion kinase (FAK). The proline-rich region at its carboxyl terminus is crucial for recruiting downstream effector molecules such as CrkII and GIT1, thereby precisely regulating cytoskeletal rearrangement and growth factor signaling. This modular structure makes it a key node for coordinating the cell signal network.
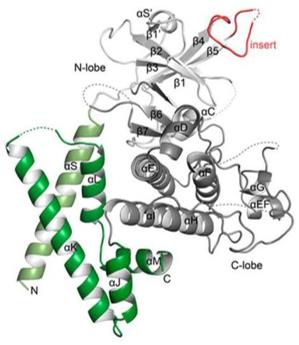 Fig. 1 Structure of PEAK1 pseudokinase domain.1
Fig. 1 Structure of PEAK1 pseudokinase domain.1
Key structural properties of PEAK1:
- Contains no catalytic activity of pseudo kinase domain structure as the core support
- Multiple protein interaction modules are available
- Carboxyl terminal structure domain is responsible for the specific recruit downstream signaling molecules
Functions of PEAK1
The main function of the PEAK1 gene is to serve as a signal transduction scaffold and regulatory hub within cells. However, it is also widely involved in a variety of pathophysiological processes, including cancer metastasis, tissue repair and immune cell activation.
| Function | Description |
| Signal transduction bracket | PEAK1 integrates and transduces key pathways from growth factor receptors (such as EGFR) and adhesion signals through its pseudokinase domain and multiple protein-protein interaction modules. |
| Regulation of cell migration | By recruiting adapter proteins such as CrkII/GIT, it dynamically regulates cytoskeletal rearrangement and adhesion spot turnover, directly driving the invasion and metastasis of cancer cells. |
| Proliferation and Survival | Under the stimulation of growth factors, PEAK1 can enhance the activity of downstream proliferation-promoting and anti-apoptotic signaling pathways such as ERK/MAPK. |
| Metabolic reprogramming | Recent studies have found that PEAK1 can affect the activity of glycolycle-related proteins and participate in the metabolic adaptation process of tumor cells. |
| Immune regulation | In immune cells such as T cells, PEAK1 is involved in regulating their activation and function, influencing the intensity and persistence of immune responses. |
Unlike classical kinases that directly transmit signals through phosphorylation, PEAK1, as a pseudo-kinase, its core function lies in serving as a dynamic and inducible platform for protein-protein interactions. It responds to upstream signals through conformational changes, thereby specifically altering the composition and flow direction of the downstream signal network. This regulation mode is more similar to a "signal switch" rather than a simple "signal amplifier".
Applications of PEAK1 and PEAK1 Antibody in Literature
- Zhang, Zaikuan, et al. "PEAK1 maintains tight junctions in intestinal epithelial cells and resists colitis by inhibiting autophagy-mediated ZO-1 degradation." Nature Communications 16.1 (2025): 6777. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-62107-z
Research reveals that PEAK1 blocks its LC3 interaction region by binding to ZO-1, preventing autophagic degradation and maintaining the integrity of tight junctions in intestinal epithelia. Src phosphorylates PEAK1 to promote this binding. The absence of PEAK1 will disrupt the connection and exacerbate colitis.
- Wang X, Zheng Y, Wang Y. "PEAK1 promotes invasion and metastasis and confers drug resistance in breast cancer." Clinical and Experimental Medicine 22.3 (2022): 393-402. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-021-00761-5
Studies have revealed that PEAK1 is highly expressed in breast cancer and is associated with tumor invasion, metastasis and chemotherapy resistance. Inhibiting PEAK1 can reduce the growth and metastasis of breast cancer cells and reverse drug resistance. Targeting PEAK1 may become a potential therapeutic strategy.
- Yang, Xue, et al. "Activation of CAMK2 by pseudokinase PEAK1 represents a targetable pathway in triple negative breast cancer." Nature Communications 16.1 (2025): 1871. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-57046-8
Research reveals that PEAK1 drives the invasion and metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer by activating CAMK2. Research has found that inhibiting CAMK2 (such as using RA306) can effectively block the carcinogenic signal of PEAK1, inhibit tumor growth and metastasis, and provide a new strategy for targeted therapy.
- Agajanian, Megan, et al. "PEAK1 acts as a molecular switch to regulate context-dependent TGFβ responses in breast cancer." PLoS One 10.8 (2015): e0135748. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0135748
Studies have revealed that high expression of PEAK1 shifts the TGFβ signaling from tumor suppressor to tumor promoter, promoting EMT, migration and metastasis of breast cancer by activating the non-classical Src/MAPK pathway, and is associated with drug resistance. Targeting PEAK1 or its pathways may inhibit tumor progression.
- Huang, Lanlan, et al. "PEAK1, acting as a tumor promoter in colorectal cancer, is regulated by the EGFR/KRas signaling axis and miR-181d." Cell death & disease 9.3 (2018): 271. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-0320-8
Studies have revealed that PEAK1 is overexpressed in colorectal cancer, especially in colon cancer, indicating a poor prognosis. It is induced by EGFR/KRas signaling and targeted inhibition by miR-181d. Inhibiting PEAK1 can prevent tumor growth and metastasis.
Creative Biolabs: PEAK1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality PEAK1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom PEAK1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our PEAK1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Ha, Byung Hak, and Titus J. Boggon. "The crystal structure of pseudokinase PEAK1 (Sugen kinase 269) reveals an unusual catalytic cleft and a novel mode of kinase fold dimerization." Journal of Biological Chemistry 293.5 (2018): 1642-1650. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA117.000751
Anti-PEAK1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-AHCYL1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180270) (CBMAB-A1703-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-A2M Recombinant Antibody (V2-178822) (CBMAB-A0036-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AZGP1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJZ-007) (CBMAB-Z0012-WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-AK4 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180419) (CBMAB-A1891-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-DLG1 Monolconal Antibody (4F3) (CBMAB-0225-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0790) (CBMAB-0793-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (2Q1282) (CBMAB-C1624-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-ARID1B Recombinant Antibody (KMN1) (CBMAB-A3546-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP1A2 Recombinant Antibody (M7-PB-E9) (CBMAB-A4013-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-APCS Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A663) (CBMAB-A3054-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CCDC6 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-0106) (CBMAB-C5397-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL6 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0435) (CBMAB-0437-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-BLK Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0618) (CBMAB-0621-YY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ABL1 (Phosphorylated Y185) Recombinant Antibody (V2-443434) (PTM-CBMAB-0001YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-ATF4 Recombinant Antibody (D4B8) (CBMAB-A3872-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-DISP2 Monoclonal Antibody (F66A4B1) (CBMAB-1112CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CD33 Recombinant Antibody (P67.6) (CBMAB-C10189-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-AP2M1 (Phosphorylated T156) Recombinant Antibody (D4F3) (PTM-CBMAB-0610LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATM Recombinant Antibody (2C1) (CBMAB-A3970-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CASP8 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0987) (CBMAB-C2424-YY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








