SCIMP Antibodies
Background
SCIMP is a transmembrane adaptor protein mainly expressed in the plasma membrane of immune cells, such as dendritic cells and macrophages. This protein specifically binds to signal molecules (such as Syk and Lyn kinases) through its intracellular domain, participates in regulating immune receptor signal transduction pathways, and thereby regulates the intensity and duration of immune responses. As a key component of the immune synapse between T cells and antigen-presenting cells, SCIMP can promote the formation of signal microdomains and optimize intercellular communication. Its gene function was systematically analyzed in the early 2010s and it is the first transmembrane adaptor protein confirmed to directly participate in the MHC-II signaling pathway. The unique tyrosine motif and oligomerization ability of this protein provide an important model for the study of immune signal transduction and are of key significance for understanding the molecular mechanisms of autoimmune diseases and inflammatory responses.
Structure of SCIMP
SCIMP is a transmembrane adaptor protein with a molecular weight of approximately 26 kDa. There are certain differences in its molecular weight among different species, mainly due to the length polymorphism of intracellular domains.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Pig | Bovine |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 26.0 | 25.8 | 25.9 | 26.2 | 26.1 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Intracellular section contains multiple tyrosine phosphorylation site | The YxxI motif is highly conserved | The sequences of the transmembrane regions are consistent | Extracellular section has a single glycosylation sites | Helical structure highly homologous with humans |
This protein is composed of approximately 230 amino acids and has a typical type I transmembrane topological structure. Its intracellular domain contains a unique Tyr-XX-Ile (YxxI) signaling motif, which is a key site for binding to Syk kinase and initiating downstream signaling. The transmembrane region of SCIMP forms an α -helix, while the extracellular segment is a compact immunoglobulin-like domain responsible for mediating homologous or heterologous interactions between proteins.
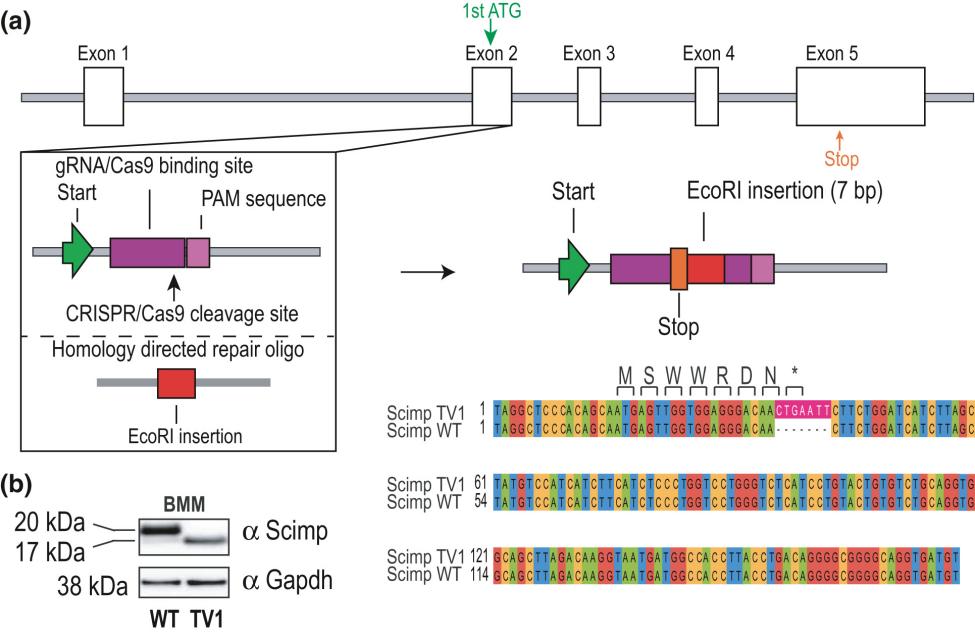 Fig. 1 Generation of a mouse line expressing a naturally occurring truncated form of Scimp.1
Fig. 1 Generation of a mouse line expressing a naturally occurring truncated form of Scimp.1
Key structural properties of SCIMP:
- Typical configuration of type I single transmembrane topology
- Intracellular signal modules rich in tyrosine (YxxI motifs)
- Conserved helical-helical interactions mediate oligomerization
- Extracellular immunoglobulin-like domains mediate specific recognition
Functions of SCIMP
The main function of SCIMP is to serve as a signal transduction hub in immune synapses. However, this protein is also involved in multiple immunomodulatory processes, including the regulation of cell activation and the balance of inflammatory responses.
| Function | Description |
| Signal transduction | The Syk and other kinases are recruited through the intracellular YxxI motif to initiate the downstream signaling pathway of MHC-II. |
| Immune synaptic assembly | Protein microdomains are formed at the T-cell -APC contact interface, promoting the spatial organization of signal molecules. |
| Activation threshold regulation | Set the threshold for immune cell activation by regulating the phosphorylation level to prevent overresponse. |
| Regulation of inflammatory factors | Affect the IL - 6, TNF alpha, causing inflammation factors such as negative control involved in the inflammatory response. |
| Cell migration assistance | Regulate the homing ability of dendritic cells to lymphoid tissue through integrin co-signaling. |
The signal dynamics of SCIMP are significantly different from those of typical adaptor proteins such as LAT - its activation curve shows the characteristics of rapid phosphorylation but slow dephosphorylation, indicating that it has a special function of continuous signal amplification in immune synapses.
Applications of SCIMP and SCIMP Antibody in Literature
1. Pei, Xiaolei, et al. "Exosomal secreted SCIMP regulates communication between macrophages and neutrophils in pneumonia." Nature Communications 15.1 (2024): 691. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-44714-4
The article indicates that in acute lung injury (ALI), macrophages secrete exosomes SCIMP (SCIMPexo), which mediate neutrophil chemotaxis and activation by activating the FPR1/2 receptor, enhancing pathogen clearance and thereby improving the survival rate of the ALI model. The SCIMP-FPRS-neutrophil axis plays a key role in innate immunity.
2. Sun, Xiaolei, et al. "SCIMP: A Novel Targeted Gene for Postmenopausal Osteoporosis Progression." Orthopaedic Surgery 15.5 (2023): 1375-1383. https://doi.org/10.1111/os.13715
This study reveals that the expression of the SCIMP gene is significantly reduced in postmenopausal osteoporosis (PMOP). SCIMP promotes osteoblast proliferation and inhibits apoptosis by activating the Akt signaling pathway, thereby regulating bone metabolic balance. In vivo experiments have confirmed that up-regulating SCIMP can improve bone structure and osteogenic activity.
3. Luo, Lin, et al. "SCIMP is a transmembrane non-TIR TLR adaptor that promotes proinflammatory cytokine production from macrophages." Nature Communications 8.1 (2017): 14133. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms14133
This study reveals that SCIMP is an immune-specific transmembrane aptamer protein. It drives tyrosine phosphorylation of TLR4 by directly binding to TLR4 and recruiting Lyn tyrosine kinase, thereby selectively promoting the production of key pro-inflammatory factors such as IL-6 and IL-12p40 by macrophages and precisely regulating the innate immune response.
4. Curson, James EB, et al. "An alternative downstream translation start site in the non‐TIR adaptor Scimp enables selective amplification of CpG DNA responses in mouse macrophages." Immunology and Cell Biology 100.4 (2022): 267-284. https://doi.org/10.1111/imcb.12540
The article indicates that SCIMP is an immune-specific transmembrane aptamer protein. It drives tyrosine phosphorylation of TLR4 by directly binding to TLR4 and recruiting Lyn tyrosine kinase, thereby selectively promoting the production of key pro-inflammatory factors such as IL-6 and IL-12p40 by macrophages and precisely regulating the innate immune response.
5. Kralova, Jarmila, et al. "The transmembrane adaptor protein SCIMP facilitates sustained dectin-1 signaling in dendritic cells." Journal of Biological Chemistry 291.32 (2016): 16530-16540. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M116.717157
The article indicates that SCIMP is a transmembrane aptamer protein expressed in antigen-presenting cells. Research has found that the absence of SCIMP has no significant effect on B cell function. However, in dendritic cells and macrophages, SCIMP is activated and phosphorylated by the Dectin-1 receptor, specifically maintaining the long-term signal transduction of MAP kinase and cytokine production.
Creative Biolabs: SCIMP Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality SCIMP antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom SCIMP Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our SCIMP antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Curson, James EB, et al. "An alternative downstream translation start site in the non‐TIR adaptor Scimp enables selective amplification of CpG DNA responses in mouse macrophages." Immunology and Cell Biology 100.4 (2022): 267-284. https://doi.org/10.1111/imcb.12540
Anti-SCIMP antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-DLL4 Recombinant Antibody (D1090) (CBMAB-D1090-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-DMD Recombinant Antibody (D1190) (CBMAB-D1190-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CDK7 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C1783) (CBMAB-C3221-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD33 Recombinant Antibody (6C5/2) (CBMAB-C8126-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD59 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-2097) (CBMAB-C4421-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ABL2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179121) (CBMAB-A0364-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ADAM12 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179752) (CBMAB-A1114-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP1B3 Recombinant Antibody (1E9) (CBMAB-A4021-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-AP2M1 (Phosphorylated T156) Recombinant Antibody (D4F3) (PTM-CBMAB-0610LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ASB9 Recombinant Antibody (1D8) (CBMAB-A0529-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BANF1 Recombinant Antibody (3F10-4G12) (CBMAB-A0707-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-8-oxoguanine Recombinant Antibody (V2-7697) (CBMAB-1869CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-AKT1/AKT2/AKT3 (Phosphorylated T308, T309, T305) Recombinant Antibody (V2-443454) (PTM-CBMAB-0030YC)

-
Mouse Anti-dsRNA Recombinant Antibody (2) (CBMAB-D1807-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ATG5 Recombinant Antibody (9H197) (CBMAB-A3945-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0216) (CBMAB-0217-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-B2M Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0050) (CBMAB-0050-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-C5b-9 Recombinant Antibody (aE11) (CBMAB-AO138LY)

-
Rat Anti-C5AR1 Recombinant Antibody (8D6) (CBMAB-C9139-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-AKT2 (Phosphorylated S474) Recombinant Antibody (V2-556130) (PTM-CBMAB-0605LY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






