AK5 Antibodies
Background
AK5 is a small molecule phosphotransferase mainly present in the cytoplasm of vertebrates, especially in brain and testicular tissues, which regulates cellular energy metabolism by catalyzing the reversible phosphorylation reaction of AMP and ATP. As a member of the adenylate kinase family, AK5 supports the normal function of high-energy-consuming tissues by maintaining local ATP/ADP balance. The study of its crystal structure has revealed a typical adenylate kinase folding pattern, while the unique substrate selectivity and tissue distribution characteristics provide new insights into the cell-specific mechanisms of metabolic regulation. Recent studies have found that abnormal expression of AK5 is associated with neurodegenerative diseases and tumor metabolism, making it a potential therapeutic target. The functional research on AK5 not only deepens the understanding of the energy metabolism network but also lays a foundation for the development of related disease intervention strategies.
Structure of AK5
AK5 is a small phosphotransferase with a molecular weight of approximately 22kDa, and its precise molecular weight varies slightly among different species. The following are the comparative data of the main species:
| Species | Human | Mice | Rats | Bovine |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 22.1 | 21.9 | 22.0 | 22.2 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains characteristic N-terminal extension | A shorter N-terminal sequence | Conservative catalytic core | Highly conserved active sites |
AK5 is composed of 194 amino acids and has a typical adenylate kinase folding structure: the center is made up of 5 β -folded sheets, surrounded by 8 α -helicles. Its active center contains a conserved nucleotide binding motif (GXGDGKT sequence), which is responsible for catalyzing the reversible phosphorylation reaction between AMP and ATP. Unlike other members of the family, AK5 has a unique N-terminal domain, which may be related to its specific high expression in brain tissue. The key catalytic residues include Asp33 and Arg44, which are involved in the transfer of phosphate groups and substrate recognition. The three-dimensional structure of AK5 shows that it has a typical LID domain, which undergoes conformational changes when the substrate is bound.
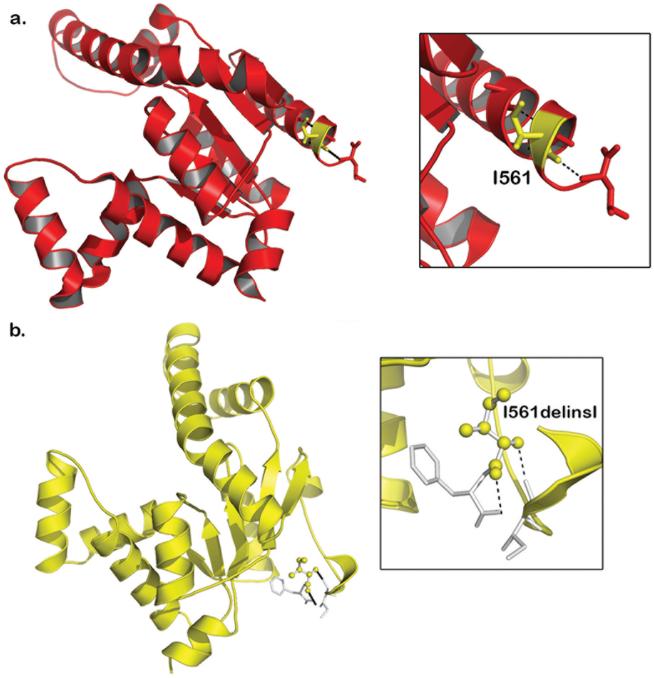 Fig. 1 Molecular view of wildtype (Red in color) and mutant (Yellow in color) AK5.1
Fig. 1 Molecular view of wildtype (Red in color) and mutant (Yellow in color) AK5.1
Key structural properties of AK5:
- Typical adenylate kinase folding structure
- Conserved nucleotide-binding pockets
- Unique N-terminal extended domain
- Key catalytic residues
- Dynamic LID domain
Functions of AK5
The enzymatic kinetic characteristics of AK5 indicate its high specificity for AMP, and its catalytic efficiency (kcat/Km) varies significantly among different tissues, which is in line with its tissue-specific function.
| Function | Description |
| Regulation of energy metabolism | Catalyze the reversible phosphorylation reaction between AMP and ATP to maintain intracellular energy homeostasis. |
| Nucleotide salvage synthesis | Participate in the purine nucleotide salvage synthesis pathway and reduce energy consumption. |
| Specific functions of brain tissue | High in neurons and glial cells, support energy intensive brain activity. |
| Metabolic stress response | Regulate the ATP/ADP ratio under energy stress conditions to maintain cell survival. |
| Signal transduction regulation | Influence energy sensing pathways such as AMPK by regulating the AMP/ATP ratio. |
Compared with other members of the AK family, AK5 shows a unique expression pattern in brain tissue, suggesting its special role in energy metabolism in the central nervous system.
Applications of AK5 and AK5 Antibody in Literature
1. Ahn, Bokyung, et al. "Identification of novel DNA hypermethylation of the adenylate kinase 5 promoter in colorectal adenocarcinoma." Scientific reports 11.1 (2021): 12626. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-92147-6
Research has found that the AK5 gene promoter in colorectal cancer (CRC) is highly methylated at high frequency (P<0.0001), leading to a down-regulation of its expression (P=0.0003). Demethylation treatment can restore the expression of AK5 and inhibit the migration and invasion of cancer cells by regulating the AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway. Low expression of AK5 is associated with poor tumor differentiation (P=0.014), suggesting that it may promote CRC metastasis through epigenetic silencing.
2. Al-Aama, Jumana Yousuf, et al. "Whole exome sequencing of a consanguineous family identifies the possible modifying effect of a globally rare AK5 allelic variant in celiac disease development among Saudi patients." PloS one 12.5 (2017): e0176664. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0176664
Research has found that the rare homozygous insertion mutation of the AK5 gene (c.1683_1684insATT) may reduce the risk of celiac disease by enhancing the activity of nucleoside phosphokinase and inhibiting the immune response of CD4+ T cells to gluten. This mutation was enriched in healthy people (MAF=0.62) and had a significant protective effect (p<0.002).
3. Liang, Xiangdong, et al. "Identification of prostate cancer risk genetics biomarkers based on intergraded bioinformatics analysis." Frontiers in Surgery 9 (2022): 856446. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsurg.2022.856446
This study, through bioinformatics analysis, found that AK5, KCNK3 and ARHGEF38 constitute a three-gene marker model, which is significantly associated with the prognosis of prostate cancer (P<0.05). AK5 may be involved in the progression of prostate cancer by influencing the infiltration of immune cells in the tumor microenvironment, providing a new target for immunotherapy.
4. Du, Qinglong, et al. "Establishing a Prognostic Model Correlates to Inflammatory Response Pathways for Prostate Cancer via Multiomic Analysis of Lactylation-Related Genes." International Journal of Genomics 2025.1 (2025): 6681711. https://doi.org/10.1155/ijog/6681711
This article develops a highly sensitive fluorescence-based biosensor using quantum dots conjugated with plastic antibodies to detect myoglobin at femtomolar concentrations, providing a cost-effective, selective, and stable alternative for early myocardial infarction diagnosis in human serum.
5. Khan, Muhammad Aaqil, et al. "Halotolerant rhizobacterial strains mitigate the adverse effects of NaCl stress in soybean seedlings." BioMed research international 2019.1 (2019): 9530963. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/9530963
Bacillus aryabhattai (AK5) isolated from the rhizosphere soil of salt-tolerant plants in this study can significantly alleviate salt stress in soybeans. It effectively enhances the salt tolerance of soybeans by promoting the secretion of growth hormone, regulating the activity of antioxidant enzymes, maintaining ionic balance and upregulating the expression of salt-tolerant genes, and has the potential for application as bio-fertilizer.
Creative Biolabs: AK5 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality AK5 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom AK5 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our AK5 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, please contact us.
Reference
- Al-Aama, Jumana Yousuf, et al. "Whole exome sequencing of a consanguineous family identifies the possible modifying effect of a globally rare AK5 allelic variant in celiac disease development among Saudi patients." PloS one 12.5 (2017): e0176664. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0176664
Anti-AK5 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-AZGP1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJZ-007) (CBMAB-Z0012-WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-BrdU Recombinant Antibody (IIB5) (CBMAB-1038CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-AKT1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180546) (CBMAB-A2070-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-C1QC Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0600) (CBMAB-C0654-FY)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Recombinant Antibody (CBC05) (CBMAB-CR005LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADGRL2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-58519) (CBMAB-L0166-YJ)

-
Mouse Anti-ASTN1 Recombinant Antibody (H-9) (CBMAB-1154-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-AFDN Recombinant Antibody (V2-58751) (CBMAB-L0408-YJ)

-
Mouse Anti-8-oxoguanine Recombinant Antibody (V2-7697) (CBMAB-1869CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL2L1 Recombinant Antibody (H5) (CBMAB-1025CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL6 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0442) (CBMAB-0445-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-BBS2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0253) (CBMAB-0254-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADIPOR1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179982) (CBMAB-A1368-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (HIS50) (CBMAB-C10123-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-EMP3 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYE-0100) (CBMAB-E0207-FY)

-
Rat Anti-C5AR1 Recombinant Antibody (8D6) (CBMAB-C9139-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-4-Hydroxynonenal Recombinant Antibody (V2-502280) (CBMAB-C1055-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-DES Monoclonal Antibody (440) (CBMAB-AP1857LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATG5 Recombinant Antibody (9H197) (CBMAB-A3945-YC)

-
Rat Anti-CD34 Recombinant Antibody (MEC 14.7) (CBMAB-C10196-LY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








