Cyp1a1 Antibodies
Background
The Cyp1a1 gene encodes a metabolic enzyme belonging to the cytochrome P450 superfamily, which is mainly distributed in the liver and extrahepatic tissues of vertebrates. This enzyme participates in the metabolic clearance process of foreign substances such as drugs and toxins in the body by catalyzing the oxidation reactions of various exogenous compounds, especially playing a core role in the biotransformation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and other environmental pollutants. This gene was first identified in the 1970s. Its expression is transcriptionally regulated by the aromatic hydrocarbon receptor and is significantly activated when exposed to pollutants such as dioxins. As a classic model for drug metabolism research, Cyp1a1 has become a key biomarker for toxicological testing and environmental risk assessment due to its clear induction characteristics and repeatable dose-effect relationship, providing an important research basis for understanding the metabolic pathways and toxicity mechanisms of chemical substances in organisms.
Structure of Cyp1a1
Cyp1a1 is a membrane-bound protein with a molecular weight of approximately 58-60 kDa. Its precise molecular weight varies slightly due to differences in amino acid sequences among species.
| Species | Human | Rat | Mouse | Rabbit | Zebrafish |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 59.2 | 56.1 | 56.3 | 57.8 | 58.5 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Containing 503 amino acids, typical P450 structure domain | Sequence differences in the N-terminal transmembrane region | Similar to rats highly catalytic activity | Specificity exists for substrate binding pockets | Retain the core heme binding site |
This protein is composed of 503 amino acids, and its three-dimensional structure presents a typical P450 folding pattern. The active center of Cyp1a1 contains a heme cofactor, and this iron porphyrin structure is at the core of its catalytic function. The secondary structure of the protein alternates between α -helices and β -folds, forming hydrophobic channels to facilitate substrate binding. Conserved cysteine residues coordinate with heme iron, while adjacent threonine and glutamic acid residues jointly participate in electron transfer and REDOX reaction mechanisms.
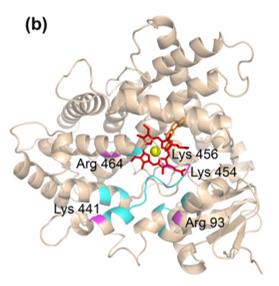 Fig. 1 Structural model of the proximal surface of human CYP1A1.1
Fig. 1 Structural model of the proximal surface of human CYP1A1.1
Key structural properties of Cyp1a1:
- Typical P450 folding conformation form hydrophobic pocket
- Conservative heme in combination with field is located in the core protein
- Iron porphyrin cogroups are responsible for catalyzing oxidation reactions
Functions of Cyp1a1
The main function of Cyp1a1 is to metabolize exogenous compounds and play a core role in drug detoxification. In addition, it is also involved in a variety of physiological and pathological processes, including pretoxin activation and oxidative stress responses.
| Function | Description |
| Metabolism of exogenous substances | Catalyze the first-stage oxidation reaction of exogenous compounds such as drugs and environmental pollutants, enhance their water solubility and facilitate their excretion. |
| Pre-toxin activation | Converting certain inert substances (such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons) into biologically active intermediate metabolites may cause cytotoxicity. |
| Regulation of oxidative stress | During the metabolic process, reactive oxygen species are produced and participate in the regulation of cellular REDOX balance. |
| Endocrine disturbance | Intervene in the metabolic process of steroid hormones and affect the homeostasis balance of endogenous hormones. |
| Application of Biomarkers | Its expression level is widely used as a molecular indicator for assessing the exposure of organisms to environmental pollutants. |
The substrate binding curve of Cyp1a1 shows typical type I spectral characteristics. The electron transport system composed of CYP1A1 and cytochrome P450 reductase endows it with broad-spectrum substrate recognition ability. However, its catalytic efficiency varies significantly among different species and tissues.
Applications of Cyp1a1 and Cyp1a1 Antibody in Literature
1. Kyoreva, Mariela, et al. "CYP1A1 enzymatic activity influences skin inflammation via regulation of the AHR pathway." Journal of Investigative Dermatology 141.6 (2021): 1553-1563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jid.2020.11.024
This study reveals that the activity of CYP1A1 enzyme is a key negative regulatory factor of the AHR signaling pathway in skin inflammation. Elevated CYP1A1 activity can exacerbate skin immunopathology, while inhibiting its activity can restore the protective effect of AHR. Inhibition of the AHR pathway and enhanced CYP1A1 activity can be observed in patients with psoriasis, suggesting that this axis may become a new therapeutic target.
2. Androutsopoulos, Vasilis P., Aristidis M. Tsatsakis, and Demetrios A. Spandidos. "Cytochrome P450 CYP1A1: wider roles in cancer progression and prevention." BMC cancer 9.1 (2009): 187. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-9-187
This study reveals that CYP1A1 is a key metabolic enzyme regulated by AhR and plays a dual role. It can not only activate environmental carcinogens, but also participate in detoxification and activate dietary compounds with anti-cancer activity. Its ultimate impact on cancer depends on the balance between this activation and detoxification.
3. Liu, Yanli, et al. "CYP1A1 methylation mediates the effect of smoking and occupational polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons co-exposure on oxidative DNA damage among Chinese coke-oven workers." Environmental Health 18.1 (2019): 69. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12940-019-0508-0
This study explores the effect of co-exposure to smoking and occupational PAH on oxidative DNA damage. Research has found that co-exposure of the two can cause hypomethylation of the CYP1A1 gene, and hypomethylation of CYP1A1, in turn, increases the risk of oxidative DNA damage, playing a partial mediating role in this process.
4. Ugartondo, Nerea, et al. "Functional analyses of four CYP1A1 missense mutations present in patients with atypical femoral fractures." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22.14 (2021): 7395. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147395
This study provides functional evidence that CYP1A1 gene mutations increase the risk of atypical femoral fractures. Research has found that two CYP1A1 variations, P. Arg98TRP and P. Arg136His, significantly reduce their enzymatic activity, and bisphosphonate drugs also generally inhibit this activity. The superimposed effect of the two may lead to an increased susceptibility to fractures in those who take the medicine for a long time.
5. Goh, Janice Jia Ni, et al. "Structure-based virtual screening of CYP1A1 inhibitors: towards rapid tier-one assessment of potential developmental toxicants." Archives of Toxicology 95.9 (2021): 3031-3048. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-021-03111-2
This study successfully constructed a virtual screening model for CYP1A1 inhibitors. This model can effectively identify known inhibitors and predict the inhibitory activity of new compounds (including various contraindicated drugs during pregnancy and environmental endocrine disruptors). Experiments have confirmed that most of the prediction results are accurate, indicating that this model can be used as a reliable tool for rapid initial screening of CYP1A1 inhibitors.
Creative Biolabs: Cyp1a1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality Cyp1a1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom Cyp1a1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our Cyp1a1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Goh, Janice Jia Ni, et al. "Structure-based virtual screening of CYP1A1 inhibitors: towards rapid tier-one assessment of potential developmental toxicants." Archives of Toxicology 95.9 (2021): 3031-3048. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-021-03111-2
Anti-Cyp1a1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-BrdU Recombinant Antibody (IIB5) (CBMAB-1038CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ACLY Recombinant Antibody (V2-179314) (CBMAB-A0610-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ACE2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179293) (CBMAB-A0566-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-BAD (Phospho-Ser136) Recombinant Antibody (CAP219) (CBMAB-AP536LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ARID3A Antibody (A4) (CBMAB-0128-YC)

-
Armenian hamster Anti-CD40 Recombinant Antibody (HM40-3) (CBMAB-C10365-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ALK (Phosphorylated Y1278) Recombinant Antibody (D59G10) (PTM-CBMAB-0035YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD83 Recombinant Antibody (HB15) (CBMAB-C1765-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-2C TCR Recombinant Antibody (V2-1556) (CBMAB-0951-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADRB2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180026) (CBMAB-A1420-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-AP2M1 (Phosphorylated T156) Recombinant Antibody (D4F3) (PTM-CBMAB-0610LY)

-
Mouse Anti-C5B-9 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYA-0216) (CBMAB-X0304-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-FOXA3 Recombinant Antibody (2A9) (CBMAB-0377-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-ALOX5AP Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-1219) (CBMAB-F0750-CQ)

-
Rat Anti-AChR Recombinant Antibody (V2-12500) (CBMAB-0990-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-CASP8 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0987) (CBMAB-C2424-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-DMPK Recombinant Antibody (CBYCD-324) (CBMAB-D1200-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-DMD Recombinant Antibody (D1190) (CBMAB-D1190-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-DLK1 Recombinant Antibody (9D8) (CBMAB-D1061-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CECR2 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJC-2465) (CBMAB-C3533WJ)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






