EPCAM Antibodies
Background
The EPCAM gene encodes an epithelial cell adhesion molecule. This protein, as a type I transmembrane glycoprotein, is mainly expressed at the junction of the epithelial tissue basement membrane and cells. It maintains the integrity of the epithelial layer structure by mediating calcium-independent homologous affinity intercellular adhesion and participates in the regulation of signaling pathways such as cell proliferation, migration and differentiation. This gene was first identified on the surface of colon cancer cells by scientists in 1979. Its abnormal expression is closely related to the progression of various epithelial-derived tumors, such as colorectal cancer and ovarian cancer, and has become an important biomarker for targeted cancer therapy and circulating tumor cell detection. In-depth research on the molecular functions of EPCAM not only reveals the mechanism of maintaining epithelial tissue homeostasis but also provides a key theoretical basis for tumor diagnosis and treatment strategies.
Structure of EPCAM
EPCAM protein is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein with a molecular weight of approximately 30-40 kDa. The size difference mainly results from the varying degrees of glycosylation modification.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 30-40 | 32-38 | 33-39 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Extracellular domain containing EGF - like and TY structure | Extracellular structure highly conservative | Intracellular sequence is species specificity |
The primary structure of this protein is composed of 314 amino acids, forming typical extracellular regions, single transmembrane regions and short intracellular tail regions. Its extracellular segment contains epidermal growth factor-like repeat sequences and thyroglobulin-like repeat sequences, which jointly mediate homologous affinity cell adhesion. The secondary structure of EPCAM is mainly β -folding, constituting functional immunoglobulin-like domains. The physiological function of this protein is to act as a key adhesion molecule in epithelial tissues, and its abnormally high expression has become an important marker of various epithelial-derived tumors.
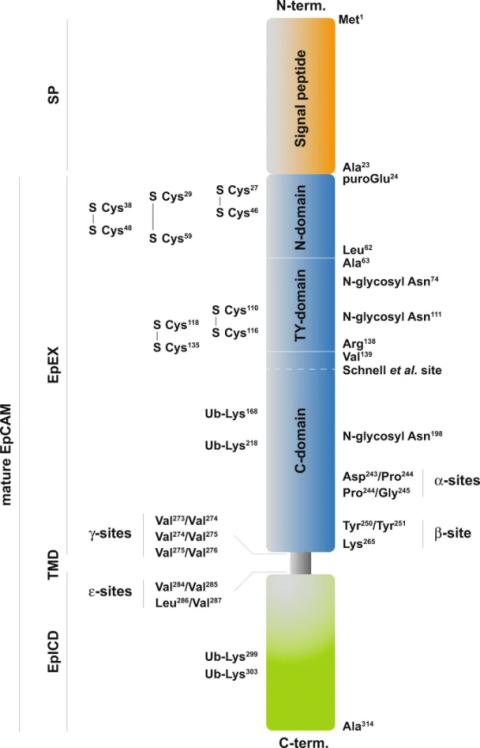 Fig. 1 Schematic representation of the EpCAM protein.1
Fig. 1 Schematic representation of the EpCAM protein.1
Key structural properties of EPCAM:
- Type I single transmembrane glycoprotein structure
- Extracellular sample containing epidermal growth factor and thyroglobulin sample repeat domain
- Disulfide bonds formed by cysteine residues maintain the stability of the extracellular region
Functions of EPCAM
The main function of the EPCAM protein is to mediate calcium-independent adhesion between epithelial cells to maintain the integrity and polarity of tissue structure. In addition, it is also involved in the signal regulation of processes such as cell proliferation, differentiation and migration.
| Function | Description |
| Cell adhesion | Mediate the mutual recognition and adhesion between epithelial cells through homologous affinity interactions, forming a stable epithelial barrier. |
| Maintain organizational integrity | By connecting cytoskeletal proteins, it stabilizes the structure and polarity of the epithelial cell layer and prevents abnormal cell shedding. |
| Signal transduction | Its intracellular segment can be involved in regulating the cell cycle, differentiation and related signaling pathways, and affect the homeostasis of epithelial tissue. |
| Cancer markers | On a variety of original abnormal high expression in tumor, promote the proliferation and tumor, is an important diagnostic and therapeutic targets. |
| Stem cell maintenance | In some parts of the epithelial stem cell surface expression, participate in maintain self-renewal and differentiation potential of stem cells. |
The adhesion mediated by EPCAM does not rely on calcium ions, which is significantly different from the formation of the cadherin family and highlights its unique function in specific physiological and pathological environments.
Applications of EPCAM and EPCAM Antibody in Literature
1. Fagotto, François. "EpCAM as modulator of tissue plasticity." Cells 9.9 (2020): 2128. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9092128
The article indicates that EpCAM is highly expressed in cancer tissues and is a sign of poor prognosis. Studies have shown that EpCAM does not promote cell migration and tissue plasticity by reducing myosin contractility through adhesion function but by inhibiting the PKC signaling pathway. This mechanism plays a key role in embryonic development and intestinal homeostasis, and may also be involved in the process of tumor invasion.
2. Gires, Olivier, et al. "Expression and function of epithelial cell adhesion molecule EpCAM: where are we after 40 years?." Cancer and Metastasis Reviews 39.3 (2020): 969-987. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-020-09898-3
The article indicates that EpCAM is a tumor antigen found in colorectal cancer and is highly expressed in various cancer tissues and circulating tumor cells. This transmembrane protein participates in multiple signaling pathways through intracellular and extracellular fragments, regulating processes such as cancer cell proliferation, migration, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Its expression level is closely related to tumor heterogeneity and patient prognosis, and it is an important prognostic marker and therapeutic target.
3. Gaber, Aljaž, Brigita Lenarčič, and Miha Pavšič. "Current view on EpCAM structural biology." Cells 9.6 (2020): 1361. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9061361
The article indicates that EpCAM is an important cancer marker, but the traditional understanding of it as a cell adhesion molecule is controversial. Based on structural biology evidence, this article points out that the cis-dimer formed by it is difficult to directly mediate intercellular adhesion, and focuses on analyzing its new function of participating in signal transduction through extracellular domain cleavable fragments, thereby regulating cell proliferation and differentiation.
4. Mohtar, M. Aiman, et al. "Revisiting the roles of pro-metastatic EpCAM in cancer." Biomolecules 10.2 (2020): 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020255
The article indicates that EpCAM is a cell surface protein that is highly expressed in epithelial tumors and stem cells. It is involved in regulating a variety of key biological processes such as cell adhesion, migration and proliferation, and can be present in the body fluids of cancer patients. Therefore, it is regarded as an important diagnostic marker and therapeutic target. This article focuses on reviewing the structural characteristics of EpCAM and its pathophysiological role in cancer.
5. Brown, Taylor C., Narendra V. Sankpal, and William E. Gillanders. "Functional implications of the dynamic regulation of EpCAM during epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition." Biomolecules 11.7 (2021): 956. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11070956
The article indicates that EpCAM is a transmembrane glycoprotein expressed in epithelial cells and cancer tissues. Its expression is dynamically regulated by the EMT process and participates in nuclear signal transduction through the intracellular domain (EpICD), influencing tumor growth, stem cell characteristics and metastasis. The functions of EpCAM are specific to cancer types, and its regulatory mechanism provides potential targets for tumor treatment.
Creative Biolabs: EPCAM Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality EPCAM antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom EPCAM Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our myoglobin antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Gires, Olivier, et al. "Expression and function of epithelial cell adhesion molecule EpCAM: where are we after 40 years?." Cancer and Metastasis Reviews 39.3 (2020): 969-987. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-020-09898-3
Anti-EPCAM antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-DDC Recombinant Antibody (8E8) (CBMAB-0992-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CCNH Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1054) (CBMAB-C1111-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADGRE5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-360335) (CBMAB-C2088-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-1728) (CBMAB-2077-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-dsRNA Recombinant Antibody (2) (CBMAB-D1807-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CDK7 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C1783) (CBMAB-C3221-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCS Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1093) (CBMAB-C1150-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CAT Recombinant Antibody (724810) (CBMAB-C8431-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-APP Recombinant Antibody (5C2A1) (CBMAB-A3314-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD247 Recombinant Antibody (6B10.2) (CBMAB-C1583-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-AKR1B1 Antibody (V2-2449) (CBMAB-1001CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CD83 Recombinant Antibody (HB15) (CBMAB-C1765-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-AKT1/AKT2/AKT3 (Phosphorylated T308, T309, T305) Recombinant Antibody (V2-443454) (PTM-CBMAB-0030YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BRD3 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0801) (CBMAB-0804-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-8-oxoguanine Recombinant Antibody (V2-7719) (CBMAB-1898CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC3 Recombinant Antibody (16E63) (CBMAB-C3367-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AMOT Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A564) (CBMAB-A2552-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ASH1L Monoclonal Antibody (ASH5H03) (CBMAB-1372-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ARID1B Recombinant Antibody (KMN1) (CBMAB-A3546-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ADGRL2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-58519) (CBMAB-L0166-YJ)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








