FOXP1 Antibodies
Background
The FOXP1 gene encodes a DNA-binding protein belonging to the Forkhead box transcription factor family, which is mainly expressed in the central nervous system, heart and immune system. This protein participates in key processes such as embryonic development, organ formation and cell differentiation by regulating the transcription of downstream target genes. Studies have shown that the loss or mutation of FOXP1 function is closely related to neurodevelopmental disorders, congenital heart disease, speech function disorders and the occurrence of various cancers. As a member of the FOXP protein family, the zinc finger domain and the fork head domain in its molecular structure jointly mediate protein dimerization and DNA-specific binding. Since its first identification in the early 2000s, FOXP1 has become an important model in developmental biology and disease mechanism research due to its core position in the transcriptional regulatory network, greatly promoting people's understanding of the mechanism of action of transcription factors in cell fate determination and pathological processes.
Structure of FOXP1
FOXP1 is a protein with a molecular weight of approximately 75-80 kDa. Its specific molecular weight varies among different splicing variants, which leads to subtle differences in protein size and function.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 78 | 77 | 77 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains polyglutamine and other flexible regions | The N-terminal sequence is highly homologous to that of humans | Species-specific variations exist in the central domain |
This protein is composed of approximately 680 amino acids. Its primary structure contains a characteristic FOX domain, which is made up of about 100 amino acids and forms a special three-dimensional conformation of a wing-like helix (winged-helix), enabling it to specifically recognize and bind to DNA sequences. In addition, the acidic amino acid region rich at the N-terminal and the zinc finger structure at the C-terminal jointly mediate the dimerization and transcriptional regulatory activity of the protein. The key residues located within the fork head domain, such as arginine and lysine, are directly involved in the interaction with the DNA groove, while the loops in the wing region are responsible for stabilizing the binding of proteins to the DNA skeleton.
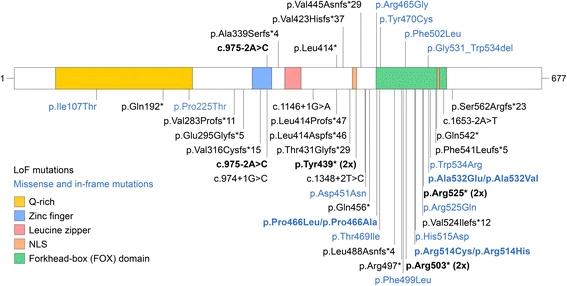 Fig. 1 FOXP1 mutations.1
Fig. 1 FOXP1 mutations.1
Key structural properties of FOXP1:
- Characteristic wing-shaped helical domain
- Functional dimerization interface
- Multi-domain collaborative regulation
- Key amino acid residue network
Functions of FOXP1
The core function of the FOXP1 protein is to act as a transcriptional regulatory factor in the regulation of gene expression. However, it also involves multiple physiological and pathological processes, including organ development and the maintenance of immune homeostasis.
| Function | Description |
| Transcriptional regulation | By binding to specific sequences of target gene promoters, histone modification complexes are recruited to inhibit or activate gene transcription. |
| Regulation of embryonic development | Dominate the morphogenesis and cell differentiation of multiple organs (such as the brain, lungs, and heart), and ensure the correct execution of tissue-specific gene expression programs. |
| Regulation of immune cell function | In control in the development of B cells, T cell receptor gene expression and signal response, balance the immune tolerance and reply. |
| Tumor suppression and promotion | On the basis of cell types play a dual role: in particular solid tumor of tumor suppressor genes, and may have a cancer gene function in the part of the lymphoma. |
| Regulation of synaptic plasticity | By regulating the neuron-specific gene network, it affects the formation of neural circuits and the development of cognitive behavior. |
FOXP1 achieves its regulatory function by forming homologous or heterodimers, and its DNA binding affinity is dynamically regulated by post-translational modifications (such as phosphorylation). This characteristic enables it to flexibly respond to developmental signals and microenvironmental changes, playing a core role in cell fate determination.
Applications of FOXP1 and FOXP1 Antibody in Literature
1. Zhang, Yiyuan, et al. "Single-nucleus transcriptomics reveals a gatekeeper role for FOXP1 in primate cardiac aging." Protein & Cell 14.4 (2023): 279-293. https://doi.org/10.1093/procel/pwac038
The article indicates that through single-cell sequencing analysis of the left ventricle of aged macaques, this study found that the transcription factor FOXP1 was significantly downregulated in senescent cardiomyocytes, leading to disorders in the cardiac function-related genes it regulates. Experiments have confirmed that the deficiency of FOXP1 can cause myocardial cell hypertrophy and senescence phenotypes, suggesting that FOXP1 is a key regulatory factor for cardiac aging.
2. Jiang, Xuan, et al. "Pyruvate dehydrogenase B regulates myogenic differentiation via the FoxP1–Arih2 axis." Journal of cachexia, sarcopenia and muscle 14.1 (2023): 606-621. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcsm.13166
This study reveals that during the process of muscle aging, PDHB inhibits the expression of the transcription factor FOXP1, thereby down-regulating its target gene Arih2, and ultimately promoting myogenic differentiation and improving muscle atrophy. This indicates that targeting the FOXP1 pathway may be able to combat sarcopenia.
3. Lozano, Reymundo, et al. "FOXP1 syndrome: a review of the literature and practice parameters for medical assessment and monitoring." Journal of neurodevelopmental disorders 13.1 (2021): 18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11689-021-09358-1
This study reveals that FOXP1 syndrome is a neurodevelopmental disorder caused by mutations in the FOXP1 gene. The typical manifestations of the patient are intellectual disability, language deficiency, autism spectrum disorder and multiple congenital abnormalities. Based on clinical research, this article summarizes its core phenotypes and provides comprehensive assessment suggestions by a multidisciplinary expert team.
4. Kaminskiy, Yaroslav, et al. "Neglected, yet significant role of FOXP1 in T-cell quiescence, differentiation and exhaustion." Frontiers in Immunology 13 (2022): 971045. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.971045
The article indicates that FOXP1 is a key but underestimated regulatory factor for maintaining T cell homeostasis. It can prevent the spontaneous activation of T cells, maintain memory potential, and regulate the differentiation of follicular helper T cells and regulatory T cells as well as T cell exhaustion, which is crucial for immune homeostasis.
5. Wang, Le, et al. "FOXP1 inhibits pancreatic cancer growth by transcriptionally regulating IRF1 expression." PLoS One 18.3 (2023): e0280794. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0280794
The article indicates that FOXP1 significantly inhibits tumor growth in pancreatic cancer by directly binding to and activating the transcriptional activity of IRF1. Patients with high expression of FOXP1 have a higher survival rate, indicating that it can serve as a potential prognostic biomarker.
Creative Biolabs: FOXP1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality FOXP1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom FOXP1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our FOXP1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Siper, Paige M., et al. "Prospective investigation of FOXP1 syndrome." Molecular autism 8.1 (2017): 57. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13229-017-0172-6
Anti-FOXP1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-CGAS Recombinant Antibody (CBFYM-0995) (CBMAB-M1146-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AMACR Recombinant Antibody (CB34A) (CBMAB-CA034LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ABL1 (Phosphorylated Y245) Recombinant Antibody (V2-505716) (PTM-CBMAB-0465LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP5F1A Recombinant Antibody (51) (CBMAB-A4043-YC)

-
Rat Anti-ADAM10 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179741) (CBMAB-A1103-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD46 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0076) (CBMAB-C0085-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADRB2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180026) (CBMAB-A1420-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BrdU Recombinant Antibody (IIB5) (CBMAB-1038CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BHMT Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0547) (CBMAB-0550-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CALR Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0763) (CBMAB-C0818-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL6 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0442) (CBMAB-0445-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CASQ1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0863) (CBMAB-C0918-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACLY Recombinant Antibody (V2-179314) (CBMAB-A0610-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BACE1 Recombinant Antibody (CBLNB-121) (CBMAB-1180-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-CARD11 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0811) (CBMAB-C0866-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BLNK Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0623) (CBMAB-0626-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACO2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179329) (CBMAB-A0627-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CFL1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1771) (CBMAB-C1833-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CASP7 Recombinant Antibody (10-01-62) (CBMAB-C2005-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AMH Recombinant Antibody (5/6) (CBMAB-A2527-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






