Glucocorticoid Receptor Antibodies
Background
Glucocorticoid receptors are transcription factors of the nuclear receptor superfamily, mainly distributed in the cytoplasm of vertebrates. After binding to glucocorticoids, this receptor forms an activated complex, which enters the cell nucleus to regulate the expression of target genes, thereby participating in key physiological processes such as stress response, immune regulation and metabolic homeostasis. The dysregulation of the GR signaling pathway under chronic stress is closely related to depression, autoimmune diseases and metabolic syndrome. Since its cloning and identification in 1985, GR has become a classic model for studying the mechanism of nuclear receptor signal transduction. The analysis of its structure and function not only reveals the molecular mechanism of ligand-dependent transcriptional activation but also provides key targets for the development of new anti-inflammatory drugs (such as selective glucocorticoid receptor modulators). Multi-level research on GR has greatly promoted the development of fields such as nuclear receptor pharmacological dynamics, epigenetic regulation, and spatio-temporal specificity of gene expression.
Structure of Glucocorticoid Receptor
The glucocorticoid receptor is a protein with a molecular weight of approximately 86 kDa. Its specific molecular weight varies slightly among different species, mainly due to differences in amino acid composition and post-translational modifications. The following table lists the molecular weight and structural characteristics of GR in several representative species:
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | African clawed toad | Chicken |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 86.7 | 85.2 | 86.5 | 87.1 | 84.8 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Containing 777 amino acids, the N-terminal transcriptional activation domain has frequent alternative splicing | Highly homologous to humans, the ligand binding domain is conserved | Highly conserved DNA binding domain, a similar response to glucocorticoids | Functionally conserved in amphibians and used in developmental studies | In poultry in GR response mechanisms and differences between mammals |
This protein is composed of approximately 700 to 800 amino acids and contains three main functional domains: the N-terminal transcriptional activation domain (NTD), the central DNA binding domain (DBD), and the C-terminal ligand binding domain (LBD). Its tertiary structure usually forms complexes with molecular chaperones such as Hsp90 when not bound to ligands and is located in the cytoplasm. After binding to glucocorticoids, conformational changes occur, exposing the nuclear localization sequence, which then enters the nucleus and binds to the glucocorticoid response element (GRE) in a dimer form, regulating the transcription of downstream genes. The precise conformation of the zinc finger structure in DBD and the hydrophobic environment of the ligand-binding pocket in LBD jointly determine its high-affinity ligand binding ability and specific transcriptional regulatory function.
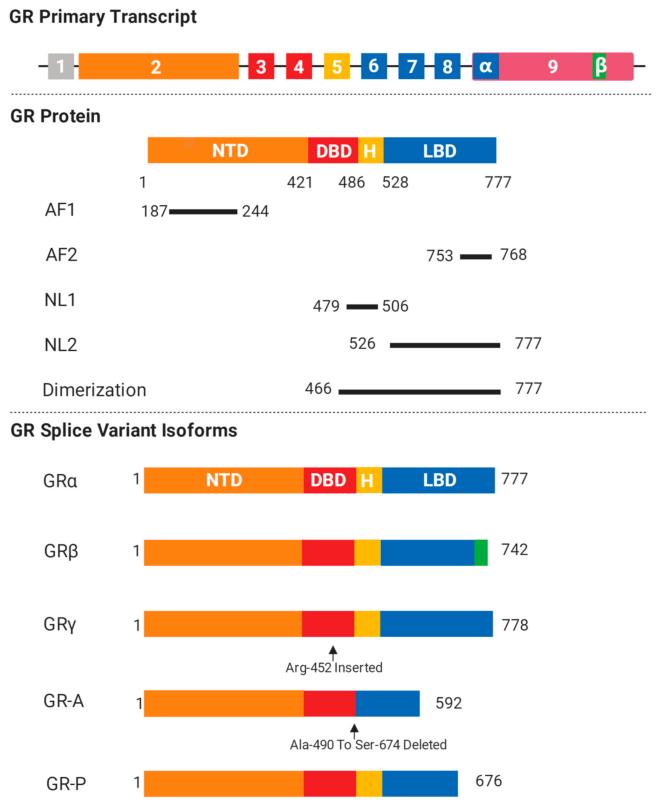 Fig. 1 Glucocorticoid receptor (GR) isoforms and structure.1
Fig. 1 Glucocorticoid receptor (GR) isoforms and structure.1
Key structural properties of Glucocorticoid receptor:
- Modular domain composition, including N-terminal transcription activation domain (NTD), DNA-binding domain (DBD) and ligand-binding domain (LBD)
- Ligand binding domain within a hydrophobic pocket, for specificity combined with glucocorticoid
- DNA binding domain contains two zinc finger protein, mediated with the target gene promoter on the components (GRE) combined with glucocorticoid reaction
- In an inactive state, it forms complexes with molecular chaperones (such as Hsp90), masking their nuclear localization signals
Functions of Glucocorticoid Receptor
The main function of glucocorticoid receptors is to act as ligand-activated transcription factors, regulating gene expression in response to stress. However, it is also widely involved in a variety of physiological and pathological processes, including metabolic regulation, immunosuppression and development.
| Function | Description |
| Gene transcriptional regulation | After binding to glucocorticoids, GR dimerizes and enters the nucleus, binding to the glucocorticoid response element (GRE) on the promoter of the target gene, activating or inhibiting its transcription. |
| Maintenance of metabolic homeostasis | Regulating hepatic gluconeogenesis, lipid metabolism and the utilization of glucose in skeletal muscle, it is a key molecule for maintaining blood glucose balance. |
| Immune inflammation suppression | By inhibiting the expression of various proinflammatory cytokines (such as TNF-α, IL-1) and inflammatory mediators through trans-inhibitory mechanism, it exerts powerful anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects. |
| Stress response coordination | As a core effector molecule of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis (HPA axis), it coordinates the overall adaptive response of the body to physiological and psychological stress. |
| Cell fate determination | In different cell types, the activation of GR can regulate cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis programs, which is crucial for processes such as brain development and bone density maintenance. |
The regulatory mechanisms of GR on different genes are diverse: for genes carrying positive GRE, GR directly binds to DNA in a dimer form and initiates transcription; For the inhibition of most inflammatory genes, it is mainly accomplished through the "transrepression" mechanism of protein-protein interactions (such as binding to NF-κB or AP-1), which is also the main target of anti-inflammatory drugs with fewer side effects.
Applications of Glucocorticoid Receptor and Glucocorticoid Receptor Antibody in Literature
1. Liu, Bing, et al. "The glucocorticoid receptor in cardiovascular health and disease." Cells 8.10 (2019): 1227. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101227
The article indicates that glucocorticoid receptors regulate the physiological and pathological processes of the cardiovascular system through genomic and non-genomic pathways, and their signaling mechanisms and receptor polymorphisms provide a new direction for targeted therapy.
2. Wang, Xinyue, et al. "Rescue RM/CS-AKI by blocking strategy with one-dose anti-myoglobin RabMAb." Nature Communications 16.1 (2025): 1044. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22073649
The article indicates that the glucocorticoid receptor GRβ not only negatively regulates GRα but also has intrinsic activity in independently regulating the expression of genes such as inflammation, cell migration, and malignant tumors. Its non-classical signaling pathways are associated with airway inflammatory diseases.
3. Spies, Lee-Maine L., Nicolette JD Verhoog, and Ann Louw. "Acquired glucocorticoid resistance due to homologous glucocorticoid receptor downregulation: a modern look at an age-old problem." Cells 10.10 (2021): 2529. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102529
The article indicates that long-term glucocorticoid therapy induces acquired drug resistance through ligande-mediated down-regulation of GRα, which is related to the dimerization state of the receptor. This article explores the influence of GRα expression regulation and conformation on drug resistance.
4. Kumar, Raj, and E. Brad Thompson. "Role of phosphorylation in the modulation of the glucocorticoid receptor's intrinsically disordered domain." Biomolecules 9.3 (2019): 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9030095
The article indicates that the N-terminal transcriptional activation domain AF1 of the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) undergoes a conformational transformation through site-specific phosphorylation, regulating its interaction with cofactors and gene expression activity, and influencing cell function.
5. Choi, Dabin, et al. "Identification of glucocorticoid receptor target genes that potentially inhibit collagen synthesis in human dermal fibroblasts." Biomolecules 13.6 (2023): 978. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13060978
The article indicates that glucocorticoids accelerate skin aging by activating GR receptors and upregulating multiple target genes (such as FKBP5, LOX, etc.), thereby inhibiting collagen synthesis in skin fibroblasts.
Creative Biolabs: Glucocorticoid Receptor Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality Glucocorticoid Receptor antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom Glucocorticoid Receptor Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our Glucocorticoid Receptor antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Liu, Bing, et al. "The glucocorticoid receptor in cardiovascular health and disease." Cells 8.10 (2019): 1227. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101227
Anti-Glucocorticoid Receptor antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-AMH Recombinant Antibody (5/6) (CBMAB-A2527-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ASH1L Monoclonal Antibody (ASH5H03) (CBMAB-1372-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD63 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-1200) (CBMAB-C1467-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ARID1B Recombinant Antibody (KMN1) (CBMAB-A3546-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-APP Recombinant Antibody (5C2A1) (CBMAB-A3314-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-4-Hydroxynonenal Recombinant Antibody (V2-502280) (CBMAB-C1055-CN)

-
Rabbit Anti-ABL1 (Phosphorylated Y185) Recombinant Antibody (V2-443434) (PTM-CBMAB-0001YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BLK Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0618) (CBMAB-0621-YY)

-
Rabbit Anti-CCL5 Recombinant Antibody (R0437) (CBMAB-R0437-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-DHFR Recombinant Antibody (D0821) (CBMAB-D0821-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BRD3 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0801) (CBMAB-0804-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALB Recombinant Antibody (V2-180650) (CBMAB-A2186-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ACTG1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179597) (CBMAB-A0916-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (SN3) (CBMAB-C1037-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CA9 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-2079) (CBMAB-C0131-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CDK7 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C1783) (CBMAB-C3221-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-8-oxoguanine Recombinant Antibody (V2-7697) (CBMAB-1869CQ)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S1 Monoclonal Antibody (CBFYR-0120) (CBMAB-R0120-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AQP2 Recombinant Antibody (G-3) (CBMAB-A3359-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AFDN Recombinant Antibody (V2-58751) (CBMAB-L0408-YJ)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






