LGALS3 Antibodies
Background
The LGALS3 gene encodes a protein called galectin-3, which belongs to the animal lectin family and is widely expressed in various tissues and cells. This protein participates in key physiological processes such as cell adhesion, immune regulation and inflammatory response by specifically recognizing the structure of β -galactoside. Under pathological conditions, the abnormal expression of LGALS3 is closely related to organ fibrosis, tumor metastasis and the development of cardiovascular diseases. Since its first identification in 1985, its unique chimeric structure (including conserved sugar recognition domains and amino terminals of repetitive sequences) has become an important model for studying protein-carbohydrate interactions and holds significant scientific value in revealing cellular signal transduction and the molecular mechanisms of diseases.
Structure of LGALS3
Galectin-3 encoded by the LGALS3 gene is a relatively unique protein with a molecular weight of approximately 26-29 kDa. This molecular weight may fluctuate under different cell types or pathological conditions, mainly due to the degradation or truncation of protease sensitivity in the non-collagen sequence at the amino terminal.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Bovine |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | About 26-29 | About 28-29 | About 28-29 | About 27-28 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains a carbohydrate recognition domain and a long N-terminal tail | Highly homologous to humans and functionally conserved | The structure is similar to that of humans, and the research model is studied | Core structure domain highly conservative |
This protein is composed of approximately 250 amino acid residues, and its primary structure contains two characteristic regions: a long N-terminal domain rich in proline and glycine tandem repeats, and a highly conserved C-terminal carbohydrate recognition domain. Its secondary structure is mainly composed of β -folded sheets, which form a typical "β -sandwich" spherical conformation in space. The specific amino acid residues in this conformation (such as His-158, Arg-162, Asn-174, etc.) jointly form a hydrophilic sugar-binding pocket, which specifically recognizes and binds to β -galactoside carbohydrate ligands through direct coordination and hydrogen bond networks.
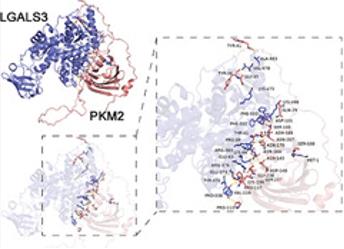 Fig. 1 The molecular docking of Lgals3 and PKM2.1
Fig. 1 The molecular docking of Lgals3 and PKM2.1
Key structural properties of LGALS3:
- Unique β -sandwich folding configuration
- Conservative carbohydrate recognition domain
- The N-terminal extension region rich in proline /glycine
Functions of LGALS3
Galectin-3 encoded by the LGALS3 gene is mainly involved in cell adhesion and signal transduction, but its functions are widely involved in immune regulation, cell cycle and various pathological processes.
| Function | Description |
| Immune regulation | Regulates the activation and function of immune cells (such as macrophages) at the site of inflammation and affects the balance of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory responses. |
| Cell adhesion | By cross-linking glycoproteins on the cell surface (such as integrins), it mediates cell-cell and cell-extracellular matrix interactions. |
| Cell cycle regulation | In the nucleus, it affects the function of splicing factors and regulates gene expression, thereby participating in the decision of cell proliferation and apoptosis. |
| Tissue fibrosis | Promote fibroblasts and collagen deposition activation, is the organ fibrosis (such as heart, liver, kidney), the key to promoting factors. |
| Pathogen defense | Recognize and bind to the sugar structures on the surface of specific pathogens, and participate in host defense as part of innate immunity. |
Unlike traditional lectins with a single structure, galectin-3 can form polymers through its N-terminus. This property enables it to build a wide molecular network, thereby initiating unique signaling complexes on the cell membrane. This explains why it is involved in such a diverse and sometimes functionally distinct physiological and pathological process.
Applications of LGALS3 and LGALS3 Antibody in Literature
1. Ye, Zehua, et al. "Lgals3 Promotes Calcium Oxalate Crystal Formation and Kidney Injury Through Histone Lactylation‐Mediated FGFR4 Activation." Advanced Science 12.12 (2025): 2413937. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202413937
Research has found that the Lgals3 protein stabilizes its expression by binding to PKM2, enhances the lactic acid modification of histone H3K18, and thereby promotes the deposition and fibrosis of calcium oxalate crystals in the kidneys, leading to the formation of kidney stones and kidney damage.
2. Zhao, Shulin, et al. "HDAC7 drives glioblastoma to a mesenchymal-like state via LGALS3-mediated crosstalk between cancer cells and macrophages." Theranostics 14.18 (2024): 7072. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.100939
Research reveals that HDAC7 promotes the secretion of LGALS3 by down-regulating SOX8. LGALS3 binds to ITGB1 on tumor cells and macrophages respectively, driving malignant transformation and M2 polarization, thus forming a positive feedback loop that promotes cancer. Targeting LGALS3 can enhance the therapeutic effect.
3. He, Xia, et al. "Increased LGALS3 expression independently predicts shorter overall survival in patients with the proneural subtype of glioblastoma." Cancer Medicine 8.5 (2019): 2031-2040. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.2075
Studies have found that LGALS3 is highly expressed in glioblastoma, especially in the proneural subtype. Its high expression is an independent prognostic factor for the shortened overall survival of patients, and its expression may be regulated by DNA methylation.
4. Scuderi, Grazia, et al. "Transcriptomic and Clinical Profiling Reveals LGALS3 as a Prognostic Oncogene in Pancreatic Cancer." Genes 16.10 (2025): 1170. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16101170
Studies have confirmed that Galectin-3 encoded by LGALS3 is highly expressed in various cancers and is associated with a poor prognosis for patients. Its absence affects key pathways such as cell division and stress, and can serve as a potential prognostic marker and therapeutic target.
5. Takashima, Yasuo, et al. "CD276 and the gene signature composed of GATA3 and LGALS3 enable prognosis prediction of glioblastoma multiforme." PloS one 14.5 (2019): e0216825. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0216825
Research has confirmed that in glioblastoma studies, CD276 (B7-H3) and the gene markers composed of GATA3 and LGALS3 can effectively predict the prognosis of patients, providing potential targets for immunotherapy.
Creative Biolabs: LGALS3 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality LGALS3 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom LGALS3 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our LGALS3 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Ye, Zehua, et al. "Lgals3 Promotes Calcium Oxalate Crystal Formation and Kidney Injury Through Histone Lactylation‐Mediated FGFR4 Activation." Advanced Science 12.12 (2025): 2413937. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202413937
Anti-LGALS3 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-CAT Recombinant Antibody (724810) (CBMAB-C8431-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV9 Recombinant Antibody (V2-634029) (CBMAB-AP023LY)

-
Mouse Anti-DMD Recombinant Antibody (D1190) (CBMAB-D1190-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ARHGAP5 Recombinant Antibody (54/P190-B) (CBMAB-P0070-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CCDC6 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-0106) (CBMAB-C5397-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BrdU Recombinant Antibody (IIB5) (CBMAB-1038CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ACTB Recombinant Antibody (V2-179553) (CBMAB-A0870-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AQP2 Recombinant Antibody (E-2) (CBMAB-A3358-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-ABL1 (Phosphorylated Y245) Recombinant Antibody (V2-505716) (PTM-CBMAB-0465LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD83 Recombinant Antibody (HB15) (CBMAB-C1765-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-EPO Recombinant Antibody (CBFYR0196) (CBMAB-R0196-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ARG1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYCL-103) (CBMAB-L0004-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-FOSB Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-3593) (CBMAB-F2522-CQ)

-
Rat Anti-ABCC11 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179001) (CBMAB-A0236-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV8 Recombinant Antibody (V2-634028) (CBMAB-AP022LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP5F1A Recombinant Antibody (51) (CBMAB-A4043-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ADGRL2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-58519) (CBMAB-L0166-YJ)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV-5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-503416) (CBMAB-V208-1402-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CFL1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1771) (CBMAB-C1833-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-APP Recombinant Antibody (DE2B4) (CBMAB-1122-CN)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








