PECAM1 Antibodies
Background
PECAM1 is a transmembrane glycoprotein mainly expressed in vascular endothelial cells, platelets and specific subsets of white blood cells. This protein mediates intercellular adhesion through homotypic interactions in its extracellular region and plays a key role in angiogenesis, inflammatory responses, and maintaining vascular integrity. After being first identified by Newman's team in 1990, research found that PECAM1 transmits inhibitory signals through the tyrosine inhibitory motif of the immune receptor, thereby regulating the activation threshold of immune cells. The precise spatial conformation of the six immunoglobulin-like domains in its extracellular region was clarified through crystal analysis in 1997. This discovery deepened people's understanding of the functional mechanisms of membrane proteins in intercellular recognition, signal transduction and vascular biology.
Structure of PECAM1
PECAM1 (CD31) is a transmembrane glycoprotein with a molecular weight of approximately 80-130 kDa. Its differences mainly stem from the degree of glycosylation modification and the presence of shear isomers. The extracellular region of this protein is composed of six highly conserved immunoglobulin-like domains (Ig-like domains), which mediate intercellular adhesion through isotype interactions. Its intracellular segment contains the immune receptor tyrosine inhibitory motif (ITIM), which forms a phosphorylation-dependent signaling platform at the junction of vascular endothelial cells. The ligand binding interface is mainly located in the distal Ig-like domain 1-2 of the membrane, while the proximal membrane domain (domain 6) is involved in maintaining the spatial orientation and stability of the molecule on the cell surface.
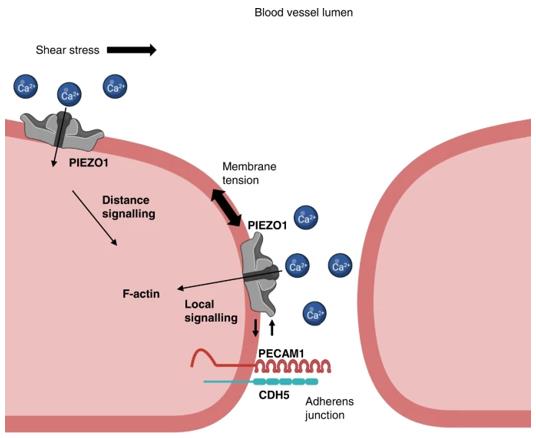 Fig. 1 Model for PIEZO1 and PECAM1 partnership.1
Fig. 1 Model for PIEZO1 and PECAM1 partnership.1
Key structural properties of PECAM1:
- Extended configuration of six immunoglobulin-like domains in extracellular region
- Proximal membrane structure domain and 6 anchored interface membrane formation
- Intracellular segments containing the immune receptor tyrosine inhibitory motif (ITIM)
Functions of PECAM1
The core function of PECAM1 (CD31) is to mediate intercellular recognition and signal transduction, and it also plays a regulatory role in various physiological and pathological processes.
| Function | Description |
| Intercellular adhesion | Through the Ig-like domain of the extracellular region, homotypic binding is mediated to promote vascular endothelial cell-to-cell junctions and leukocyte trans-endothelial migration. |
| Inflammatory regulation | In white blood cells - the interaction between endothelial cells and inhibitory signals regulate inflammation startup and strength. |
| Angiogenesis | Involved in the formation of new blood vessels lumen, its intracellular segment ITIM motif phosphorylation after recruiting - 2 phosphatase SHP promoting signaling. |
| Apoptosis regulation | By maintaining endothelial cell survival signals, it inhibits programmed cell death induced by growth factor deprivation. |
| Mechanical signal transduction | Sense blood flow shear stress, convert mechanical stimulation into intracellular biochemical signals, and regulate vascular tension and remodeling. |
Unlike the synergistic effect of adhesion molecules such as integrins, PECAM1 mainly transmits inhibitory signals through its immune receptor tyrosine inhibitory motif (ITIM), playing the role of a "molecular brake" in maintaining vascular homeostasis and immune balance.
Applications of PECAM1 and PECAM1 Antibody in Literature
1. Chuntharpursat-Bon, Eulashini, et al. "PIEZO1 and PECAM1 interact at cell-cell junctions and partner in endothelial force sensing." Communications biology 6.1 (2023): 358. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-023-04706-4
Research has found that PECAM1 can recruit the mechanical force-sensing ion channel PIEZO1 to the cell junction and interact with it, thereby linking the two major mechanical sensing mechanisms to jointly regulate vascular endothelial junctions.
2. Hu, Menglong, et al. "Structural basis for human PECAM-1-mediated trans-homophilic cell adhesion." Scientific Reports 6.1 (2016): 38655. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep38655
This study analyzed the crystal structure of the IgL1-2 domain in the extracellular region of PECAM-1, revealed the molecular mechanism by which it forms a "trans-homodimer" through hydrophilic/hydrophobic interactions, and experimentally confirmed the key role of this structure in intercellular adhesion and communication.
3. Sun, Xiaogang, et al. "CD300A promotes tumor progression by PECAM1, ADCY7 and AKT pathway in acute myeloid leukemia." Oncotarget 9.44 (2018): 27574. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.24164
The study has for the first time revealed that the immune protein CD300A acts as an oncogene in acute myeloid leukemia. By up-regulating the expression of PECAM1 and ADCY7, it activates the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway, thereby promoting the proliferation and migration of cancer cells.
4. Etich, Julia, et al. "PECAM1+/Sca1+/CD38+ vascular cells transform into myofibroblast-like cells in skin wound repair." PLoS One 8.1 (2013): e53262. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0053262
Research has found that skin damage activates a group of PECAM1+/Sca1+/CD38+ vasogenic cells, which can proliferate and differentiate into myofibroblasts, promoting wound repair and angiogenesis. The CD38 signal regulates this process and may become a potential target for anti-vascular therapy of basal cell carcinoma.
5. Liu, Yonghong, et al. "PECAM1 combines with CXCR4 to trigger inflammatory cell infiltration and pulpitis progression through activating the NF-κB signaling pathway." Frontiers in cell and developmental biology 8 (2020): 593653. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.593653
This study reveals that MEF2C is a key regulatory factor for pulpitis. It can simultaneously upregulate the expression of PECAM1 and CXCR4, promote inflammation by activating the NF-κB pathway, and provide a new target for treatment.
Creative Biolabs: PECAM1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality PECAM1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom PECAM1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our PECAM1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Chuntharpursat-Bon, Eulashini, et al. "PIEZO1 and PECAM1 interact at cell-cell junctions and partner in endothelial force sensing." Communications biology 6.1 (2023): 358. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-023-04706-4
Anti-PECAM1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-ALB Recombinant Antibody (V2-363290) (CBMAB-S0173-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV-5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-503417) (CBMAB-V208-1369-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ARSA Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A799) (CBMAB-A3679-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC5 Recombinant Antibody (6E4) (CBMAB-CP2646-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALB Recombinant Antibody (V2-180650) (CBMAB-A2186-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-DDC Recombinant Antibody (8E8) (CBMAB-0992-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0790) (CBMAB-0793-YY)

-
Rabbit Anti-CBL Recombinant Antibody (D4E10) (CBMAB-CP0149-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCDC6 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-0106) (CBMAB-C5397-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ANXA7 Recombinant Antibody (A-1) (CBMAB-A2941-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ACTB Recombinant Antibody (V2-179553) (CBMAB-A0870-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-APOA1 Monoclonal Antibody (CBFYR0637) (CBMAB-R0637-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADGRE5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-360335) (CBMAB-C2088-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BrdU Recombinant Antibody (IIB5) (CBMAB-1038CQ)

-
Rat Anti-ABCC11 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179001) (CBMAB-A0236-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-dsDNA Recombinant Antibody (22) (CBMAB-AP1954LY)

-
Mouse Anti-C5AR1 Recombinant Antibody (R63) (CBMAB-C9553-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-CCL5 Recombinant Antibody (R0437) (CBMAB-R0437-CN)

-
Rabbit Anti-ENO2 Recombinant Antibody (BA0013) (CBMAB-0272CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ADRB2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180026) (CBMAB-A1420-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








