RORC Antibodies
Background
RORC gene encodes retinoic acid-related orphan receptor γ, which is mainly expressed in immune cells (such as Th17 cells) and some metabolic tissues as a transcription factor. It participates in adaptive immune responses by regulating the generation of cytokines such as IL-17, and simultaneously affects the physiological processes of biological rhythms and bone metabolism. This gene has two isomers, RORγ and RORγt. Among them, RORγt is regarded as a key regulatory factor for Th17 cell differentiation, making it an important target for autoimmune disease research. Since its function was first clarified in 1998, drug development targeting the RORC structure has continuously advanced the treatment progress of diseases such as psoriasis and multiple sclerosis, and is of great value for understanding the immune regulatory mechanism.
Structure of RORC
The molecular weight of the protein encoded by the RORC gene is approximately 56 kDa, and its size varies among different splicing isomers.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Non-human primates |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 56.2 | 55.8 | 55.9 | 56.1 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Containing 584 amino acids, has the dna-binding domain and the ligand binding domain | Approximately 92% homology to human RORγ protein | In the ligand binding domain individual residues substitutions | Highly conserved to the human sequence |
The RORC protein contains typical zinc finger DNA-binding domains and ligand-binding domains, forming a compact tertiary structure. The ligand binding domain at its C-terminal forms a hydrophobic pocket, which can accommodate endogenous ligands such as cholesterol and its derivatives. The secondary structure of this protein is mainly composed of α -helices, which together form the complete transcriptional activation interface. Two zinc finger modules in the DNA binding domain directly bind to the RORE element in the promoter region of the target gene, while structural changes in the ligand binding domain regulate its transcriptional activity.
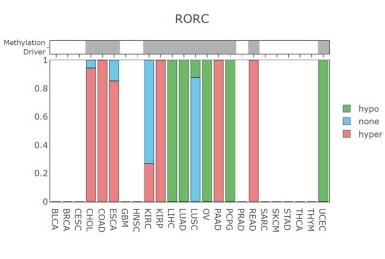 Fig. 1 RORC methylation type in various cancers.1
Fig. 1 RORC methylation type in various cancers.1
Key structural properties of RORC:
- Typical zinc refers to the DNA-binding domain
- The C-terminal ligand binding domain forms a hydrophobic pocket
- Endogenous ligand (such as cholesterol) binding lumen
Functions of RORC
The main function of the RORC gene is to act as a transcription factor to regulate the differentiation of immune cells and circadian rhythms. However, it is also involved in various pathophysiological processes, including the development of autoimmune diseases and metabolic regulation.
| Function | Description |
| Immune regulation | Dominant Th17 cell differentiation and regulation IL - 17, IL - 22, such as cytokines, plays a key role in host defense. |
| Rhythm regulation | Participate in the clock gene network regulation, affect circadian oscillation in the process of metabolism and immunity. |
| Inflammation promotion | Abnormally high expression in autoimmune diseases, inflammation and tissue damage. |
| Metabolic regulation | Involved in glucose homeostasis, lipid metabolism and connects the immune and metabolic pathways. |
| Tumor-related | In particular affect the immune cell function in tumor microenvironment, double potential has promote tumor or tumor suppression. |
Unlike widely expressed universal transcription factors, RORC achieves specific regulation by recognizing the RORE response element in the promoter region of the target gene, and its isomer RORγt has unique functional specificity in the immune system.
Applications of RORC and RORC Antibody in Literature
1. Croft, Carys A., et al. "Notch, RORC and IL-23 signals cooperate to promote multi-lineage human innate lymphoid cell differentiation." Nature communications 13.1 (2022): 4344. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-32089-3
This study reveals that Notch signaling promotes the effector function of human pluripotent and unipotent innate lymphoid progenitor cells (ILcps) in obtaining Group 1 and Group 3 by up-regulating the transcription factor RORγt. RORγt and its downstream IL-23R signaling are crucial for the differentiation of ILC3. The discovery of the Notch-ROR γ T-IL-23R pathway provides a basis for the in vitro amplification of functional ILC and the development of new therapies.
2. Chang, Dehui, et al. "A cis-element at the Rorc locus regulates the development of type 3 innate lymphoid cells." Frontiers in Immunology 14 (2023): 1105145. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1105145
This study confirmed that the cis-regulatory element CNS9 of the Rorc gene controls the lineage stability of ILC3 by regulating the expression level of RORγt protein. The deletion of CNS9 reduces the expression of RORγt in ILC3, alters its gene expression characteristics, and promotes the generation of CD4+NKp46+ ILC3 subsets, revealing the key role of CNS9 in maintaining the function and identity of ILC3.
3. Pan, Banglun, et al. "N-glycosylated LTβR increases the Th17/Treg cell ratio in liver cancer by blocking RORC ubiquitination and FOXP3 transcription." Cell Death & Disease 16.1 (2025): 421. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-025-07738-2
This study reveals that LTβR competitionally inhibits the ubiquitination degradation of the transcription factor RORC by reducing the expression of PELI1, enabling TRAF3 to bind to SMURF1, thereby enhancing its stability and promoting the differentiation of Th17 cells. This mechanism increases the ratio of Th17/Treg cells and ultimately inhibits the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma.
4. He, Shengfu, et al. "A comprehensive pancancer analysis reveals the potential value of RAR-related orphan receptor C (RORC) for cancer immunotherapy." Frontiers in Genetics 13 (2022): 969476. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2022.969476
This study, through pan-cancer analysis, revealed that the expression of the transcription factor RORC was significantly correlated with patient prognosis, immune cell infiltration, and multiple immunomodulatory factors, suggesting its significant value in cancer immunity. However, in the existing cohorts, RORC expression has no significant association with the response to cancer immunotherapy, and its clinical application potential still needs further exploration.
5. van Tok, Melissa N., et al. "Paradoxical augmentation of experimental spondyloarthritis by RORC inhibition in HLA-B27 transgenic rats." Frontiers in Immunology 12 (2021): 699987. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.699987
In this study, it was found in the spinal arthritis model of HLA-B27 transgenic rats that although the use of RORC inhibitors could effectively inhibit the expression of cytokines such as IL-17, the treatment instead accelerated and aggravated the clinical symptoms and pathological damage of arthritis and spondylitis. This indicates that simply targeting RORC to inhibit the IL-17 axis may produce unexpected negative effects.
Creative Biolabs: RORC Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality RORC antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom RORC Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our RORC antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- He, Shengfu, et al. "A comprehensive pancancer analysis reveals the potential value of RAR-related orphan receptor C (RORC) for cancer immunotherapy." Frontiers in Genetics 13 (2022): 969476. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2022.969476
Anti-RORC antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-APP Recombinant Antibody (5C2A1) (CBMAB-A3314-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AMIGO2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0756) (CBMAB-C2192-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CAPZB Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0944) (CBMAB-C2381-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADRB2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180026) (CBMAB-A1420-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (HIS50) (CBMAB-C10123-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP1B3 Recombinant Antibody (1E9) (CBMAB-A4021-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-COL12A1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C3117) (CBMAB-C4560-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD63 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-1200) (CBMAB-C1467-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-AHCYL1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180270) (CBMAB-A1703-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CASP7 Recombinant Antibody (10-01-62) (CBMAB-C2005-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACTG1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179597) (CBMAB-A0916-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-APOA1 Monoclonal Antibody (CBFYR0637) (CBMAB-R0637-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ARSA Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A799) (CBMAB-A3679-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-DDC Recombinant Antibody (8E8) (CBMAB-0992-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ARID3A Antibody (A4) (CBMAB-0128-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CASP8 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0987) (CBMAB-C2424-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACLY Recombinant Antibody (V2-179314) (CBMAB-A0610-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP1B1 Recombinant Antibody (E4) (CBMAB-0463-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-F11R Recombinant Antibody (402) (CBMAB-0026-WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-BSN Recombinant Antibody (219E1) (CBMAB-1228-CN)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








