SMAD3 Antibodies
Background
SMAD3 is a key central regulatory protein within cells and is a member of the SMAD protein family. This protein mainly mediates the conduction of the transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) signaling pathway, and is transported into the cell nucleus by forming a protein complex, directly regulating the transcriptional activity of target genes. It plays a core role in physiological processes such as embryonic development, cell cycle regulation and immune response. Research has found that SMAD3 gene mutations are closely related to a variety of human diseases, including cardiovascular abnormalities, tumorigenesis, and pathological processes such as tissue fibrosis. The research on its molecular mechanism not only reveals the basic laws of the signal transduction network, but also provides a theoretical basis for the targeted treatment of related diseases.
Structure of SMAD3
SMAD3 is an intracellular signal transduction protein with a molecular weight of approximately 48 kDa. Its precise molecular weight may vary slightly due to transcript subtypes and post-translational modification states. This protein is composed of 425 amino acids and has two highly conserved functional regions, MH1 (N-terminal domain) and MH2 (C-terminal domain), which form a stable three-dimensional structure through the intermediate junction region. The MH1 domain has sequence-specific DNA binding ability and can recognize gene regulatory elements such as the CAGA box. The MH2 domain mediates homologous/heterologous oligomerization and the recruitment of transcriptional co-activators. In the TGF-β signaling pathway, after the C-terminal SSXS motif of SMAD3 is phosphorylated, it forms a heterotrimer with SMAD4 and translocates into the nucleus. Through its MH1 domain, it is anchored to the promoter region of the target gene, thereby regulating the transcriptional process of related genes such as cell cycle, apoptosis, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. The activity of this protein is strictly regulated by E3 ubiquitin ligases (such as SMURF) and nuclear phosphatases. Its dysfunction is closely related to various pathological processes such as tumor metastasis, tissue fibrosis and immune disorders.
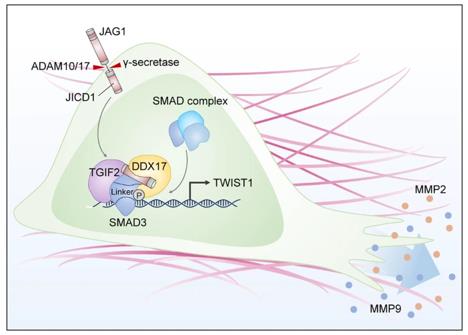 Fig. 1 JICD1/SMAD3-TWIST1 axis induces tumor invasion.1
Fig. 1 JICD1/SMAD3-TWIST1 axis induces tumor invasion.1
Key structural properties of SMAD3:
- Highly conserved MH1 and MH2 dual-domain architecture
- The β-hairpin ring unique to the MH1 domain enables DNA specific recognition
- The trimeric interface formed by the MH2 domain mediates protein complex assembly
- The C-terminal SSXS motif serves as a kinase phosphorylation switch
- Check and ratify a signal common regulation of gene expression and transcription activation area
Functions of SMAD3
The core function of the SMAD3 protein is to mediate the signal transduction of the TGF-β superfamily. Its main physiological functions include:
| Function | Description |
| Signal transduction | As a key mediator of the TGF-β pathway, it undergoes C-terminal phosphorylation after receptor activation, resulting in the translocation of the SMAD complex into the nucleus. |
| Gene regulation | By specifically identifying the CAGA motif in the promoter region of target genes through the MH1 domain, the transcription of cell cycle-related genes is directly regulated. |
| Cell cycle regulation | Induce the expression of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors such as p21 to achieve G1 phase cell cycle arrest. |
| Immune regulation | Regulate the differentiation and function of Treg cells and maintain the balance of immune tolerance. |
| Epithelial-mesenchymal transition | Drive epithelial phenotype transformation, play a key role in embryonic development and tumor metastasis. |
The signal activation of SMAD3 shows a typical "all or none" feature, and its phosphorylation level directly determines the intensity of transcriptional activity. This digital regulatory model, together with the context-dependent nature of the TGF-β pathway, constitutes an important molecular basis for determining cell fate.
Applications of SMAD3 and SMAD3 Antibody in Literature
1. Wu, Wenjing, et al. "Smad3 signatures in renal inflammation and fibrosis." International journal of biological sciences 18.7 (2022): 2795. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.71595
The article indicates that Smad3 is a key mediator in nephropathy, which can be activated by various stress signals and, in collaboration with other pathways, drive renal injury and fibrosis. Specific inhibition of Smad3 and its downstream targets represents a potential new therapeutic strategy.
2. Jeon, Hee-Young, et al. "SMAD3 promotes expression and activity of the androgen receptor in prostate cancer." Nucleic acids research 51.6 (2023): 2655-2670. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkad043
The article indicates that SMAD3 (rather than SMAD2/4) is a key upstream regulatory factor of androgen receptor (AR) in prostate cancer. It directly binds to the introns of the AR gene, promoting the transcription of AR and the expression of target genes, and works in synergy with the AR function. Targeting SMAD3 can effectively inhibit the AR pathway.
3. Yamaguchi, Takashi, et al. "Smad3 phospho-isoform signaling in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23.11 (2022): 6270. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23116270
The article indicates that in NAFLD/NASH, TGF-β signaling mediates liver fibrosis and carcinogenesis through different phosphorylated Smad3. pSmad3L (mediated by JNK) promotes the occurrence of liver cancer and antagonizes the tumor suppressor pSmad3C pathway. These phosphorylated isomers of Smad3 may become key biomarkers for predicting the risk of HCC.
4. Piloto, Ana Margarida, et al. "Plastic antibodies tailored on quantum dots for an optical detection of myoglobin down to the femtomolar range." Scientific reports 8.1 (2018): 4944. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI152394
Research has found that EZH2 methylates SMAD3 at the K53/K333 site, and this modification is a key step in the activation of SMAD3 by TGFB1, which in turn drives cancer metastasis. Inhibiting this methylated peptide segment can effectively suppress tumor metastasis, indicating its potential as a therapeutic target.
5. Aziz, Ubair, and Ishrat Jabeen. "Probing the binding hypothesis of Smad3 modulators by molecular dynamic simulations for Atherosclerosis Cardiovascular Disease (ASCVD)." PLoS One 20.6 (2025): e0324677. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0324677
Research reveals that targeting Smad3 (rather than TGF-β receptors) can provide more precise treatment for atherosclerosis. Molecular simulation has revealed that Asn320 and others are key sites for inhibiting the binding of Smad3-FoxH1, and a potential regulatory site composed of Tyr323 has been newly discovered, providing a new direction for drug optimization.
Creative Biolabs: SMAD3 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality SMAD3 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom SMAD3 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our SMAD3 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Kim, Jung Yun, et al. "Jagged1 intracellular domain/SMAD3 complex transcriptionally regulates TWIST1 to drive glioma invasion." Cell Death & Disease 14.12 (2023): 822.https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-023-06356-0
Anti-SMAD3 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Rabbit Anti-ALOX5AP Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-1219) (CBMAB-F0750-CQ)

-
Rat Anti-FABP3 Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-2299) (CBMAB-F1612-CQ)

-
Rat Anti-ADGRE4 Recombinant Antibody (V2-160163) (CBMAB-F0011-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-FOSB Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-3593) (CBMAB-F2522-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-AQP2 Recombinant Antibody (E-2) (CBMAB-A3358-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-FeLV g27 Recombinant Antibody (1) (CBMAB-V208-1714-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AKR1C3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-12560) (CBMAB-1050-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-CRYAB Recombinant Antibody (A4345) (CBMAB-A4345-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BrdU Recombinant Antibody (IIB5) (CBMAB-1038CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-C5b-9 Recombinant Antibody (aE11) (CBMAB-AO138LY)

-
Mouse Anti-Acetyl SMC3 (K105/K106) Recombinant Antibody (V2-634053) (CBMAB-AP052LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-B2M Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0059) (CBMAB-0059-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-dsDNA Recombinant Antibody (22) (CBMAB-AP1954LY)

-
Mouse Anti-B2M Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0050) (CBMAB-0050-YY)

-
Rabbit Anti-AP2M1 (Phosphorylated T156) Recombinant Antibody (D4F3) (PTM-CBMAB-0610LY)

-
Armenian hamster Anti-CD40 Recombinant Antibody (HM40-3) (CBMAB-C10365-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD247 Recombinant Antibody (6B10.2) (CBMAB-C1583-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-8-oxoguanine Recombinant Antibody (V2-7697) (CBMAB-1869CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-ABL1 (Phosphorylated Y185) Recombinant Antibody (V2-443434) (PTM-CBMAB-0001YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-1728) (CBMAB-2077-YY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








