XIAP Antibodies
Background
XIAP is an apoptosis inhibitor protein widely present in the cytoplasm and belongs to the IAP family. This protein specifically binds to and inhibits the activities of caspase-3, caspase-7 and caspase-9 through its BIR domain, thereby blocking the execution process of apoptosis. In terms of maintaining cellular homeostasis, XIAP participates in important physiological activities such as embryonic development and immune regulation by regulating programmed cell death. This gene was simultaneously discovered by multiple research teams in 1996. The three-dimensional structure analysis of it for the first time revealed the molecular mechanism of the interaction between the BIR domain and caspase. As a key regulatory factor of the apoptotic pathway, XIAP has become an important target in cancer treatment research. Its abnormal expression is closely related to pathological processes such as tumorigenesis and chemotherapy resistance, providing a theoretical basis for the development of targeted drugs.
Structure of XIAP
XIAP is an intracellular protein with a molecular weight of approximately 57 kDa. Its precise molecular weight fluctuates within the range of 55-60 kDa depending on the species of the organism and the splicing method of the transcript. This protein is composed of 426 amino acids, and its typical structural feature is the presence of three tandem BIR domains (BIR1-3) and a RING zinc finger domain at the carboxyl terminus.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Zebrafish |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 57.3 | 56.8 | 57.1 | 55.5 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains 3 BIR domains and RING domains | The BIR2 domain is highly conserved | The RING domain has two amino acid substitutions | Only 2 BIR domains are included to simplify the function |
The BIR domain constitutes the core framework of the protein, among which the BIR2 domain is mainly responsible for inhibiting caspase-3/7, while the BIR3 domain specifically binds to and inhibits caspase-9. The RING domain at the carboxyl terminus has E3 ubiquitin ligase activity and can regulate signal transduction and protein stability by catalyzing the ubiquitination modification of itself and the substrate. This combination of multiple domains enables XIAP to precisely regulate the apoptotic pathway through various molecular mechanisms.
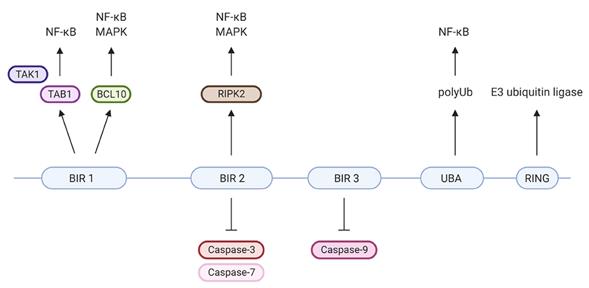 Fig. 1 XIAP's protein domains and their individual specific protein interactions and functions.1
Fig. 1 XIAP's protein domains and their individual specific protein interactions and functions.1
Key structural properties of XIAP:
- Contains three concatenated BIR domains
- BIR2 and BIR3 domains specifically inhibit caspase-3/7 and caspase-9, respectively
- The carboxyl terminus has a RING zinc finger domain
Functions of XIAP
The main function of XIAP is to inhibit apoptosis and regulate cell signal transduction. In addition, it is also involved in a variety of cellular physiological processes, including inflammatory responses, immune regulation and cell cycle regulation.
| Function | Description |
| Apoptosis inhibition | By directly binding to and inhibiting the activity of caspase-3/7/9 through the BIR domain, the apoptotic execution stage is blocked. |
| Activation of the NF-κB pathway | By interacting with receptors such as NOD through the BIR1 domain, the NF-κB signaling pathway is activated, promoting cell survival. |
| Ubiquitination regulation | Through the E3 ubiquitin ligase activity of the RING domain, it catalyzes the ubiquitination modification of itself and downstream proteins, affecting protein stability. |
| Inflammatory regulation | By regulating the NOD-like receptor signaling pathway, it affects the production and release of inflammatory factors. |
| Cell cycle influence | By interacting with the BMP pathway and others, it indirectly affects the cell cycle process and proliferation. |
Unlike the rapid activation characteristics of most pro-apoptotic proteins, the inhibition of caspase by XIAP exhibits rapid and reversible enzyme-inhibitor kinetic features, which enables it to act as a rapid molecular switch for cell fate rather than a simple long-term inhibitor.
Applications of XIAP and XIAP Antibody in Literature
1. Tu, Huailu, and Max Costa. "XIAP's profile in human cancer." Biomolecules 10.11 (2020): 1493. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10111493
The article indicates that XIAP is an important apoptosis inhibitor protein that affects cell survival by regulating the caspase pathway. It is overexpressed in the occurrence and development of tumors, promoting malignant progression, and thus has become a key target in the research and development of anti-cancer drugs. This article reviews the cancer regulatory mechanism, targeted drugs and RNA interaction research of XIAP.
2. Mudde, Anne CA, Claire Booth, and Rebecca A. Marsh. "Evolution of our understanding of XIAP deficiency." Frontiers in pediatrics 9 (2021): 660520. https://doi.org/10.3389/fped.2021.660520
The article indicates that XIAP deficiency is a rare hereditary immune disease caused by mutations in the XIAP gene. Its characteristics are immune dysregulation, and the clinical manifestations are diverse, including hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, inflammatory bowel disease and various infections, etc. At present, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation is the only method that can cure this disease.
3. Abbas, Ruqaia, and Sarit Larisch. "Targeting XIAP for promoting cancer cell death—the story of ARTS and SMAC." Cells 9.3 (2020): 663. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030663
The article indicates that XIAP blocks apoptosis by directly inhibiting caspase, and its overexpression is closely related to the escape and death of tumor cells. The natural antagonist ARTS can specifically degrade XIAP. Based on this, developing anti-cancer drugs that respectively simulate Smac and ARTS has become a new strategy, aiming to target and degrade cIAPs or XIAP to overcome the drug resistance of different tumors.
4. Sun, Ning, et al. "XIAP promotes metastasis of bladder cancer cells by ubiquitylating YTHDC1." Cell Death & Disease 16.1 (2025): 205. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-025-07545-9
The article indicates that XIAP degrades the m6A reader YTHDC1 through ubiquitination in bladder cancer, thereby stabilizing the mRNA of matrix metalloproteinase MMP-2 and ultimately promoting cancer metastasis. This study revealed a new mechanism of the XIAP/YTHDC1/MMP-2 axis in tumor metastasis, providing a potential target for treatment.
5. Witt, Axel, et al. "XIAP deletion sensitizes mice to TNF-induced and RIP1-mediated death." Cell Death & Disease 14.4 (2023): 262. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-023-05793-1
The article indicates that the absence of XIAP significantly enhances TNF-mediated cell death and inflammatory responses through the RIP1 kinase pathway, leading to serious consequences such as tissue damage. Studies have shown that inhibiting RIP1 can effectively block this process, providing a new potential strategy for the treatment of XIAP defect-related diseases.
Creative Biolabs: XIAP Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality XIAP antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom XIAP Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our XIAP antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Mudde, Anne CA, Claire Booth, and Rebecca A. Marsh. "Evolution of our understanding of XIAP deficiency." Frontiers in pediatrics 9 (2021): 660520. https://doi.org/10.3389/fped.2021.660520
Anti-XIAP antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0790) (CBMAB-0793-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-EPO Recombinant Antibody (CBFYR0196) (CBMAB-R0196-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCS Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1093) (CBMAB-C1150-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACE2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179293) (CBMAB-A0566-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ABIN2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179106) (CBMAB-A0349-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-DLL4 Recombinant Antibody (D1090) (CBMAB-D1090-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BANF1 Recombinant Antibody (3F10-4G12) (CBMAB-A0707-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-HTLV-1 gp46 Recombinant Antibody (CBMW-H1006) (CBMAB-V208-1154-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD46 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0076) (CBMAB-C0085-FY)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Recombinant Antibody (CBC05) (CBMAB-CR005LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AHCYL1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180270) (CBMAB-A1703-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-1728) (CBMAB-2077-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-AK4 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180419) (CBMAB-A1891-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CCL18 Recombinant Antibody (64507) (CBMAB-C7910-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BLK Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0618) (CBMAB-0621-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-AQP2 Recombinant Antibody (G-3) (CBMAB-A3359-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP1A2 Recombinant Antibody (M7-PB-E9) (CBMAB-A4013-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BLNK Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0623) (CBMAB-0626-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD8 Recombinant Antibody (C1083) (CBMAB-C1083-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC3 Recombinant Antibody (315304) (CBMAB-1214-CN)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








