YAP1 Antibodies
Background
The YAP1 gene encodes a transcriptional co-activator, which serves as a core effector molecule of the Hippo signaling pathway and participates in developmental regulation by regulating cell proliferation, apoptosis and organ size. This protein binds to multiple transcription factors through the WW domain, activates the expression of downstream target genes, and plays a key role in tissue regeneration and stem cell self-renewal. Its abnormal expression is closely related to the occurrence of various tumors, especially showing a significantly high expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. The gene was first identified by scientist Sudol in 1994. Subsequent research gradually revealed its characteristics as a mechanosensitive transcription factor - it can sense the stiffness of the extracellular matrix and changes in cell shape, and convert physical microenvironment signals into biochemical signals. This unique mechanical transduction function makes YAP1 an important target in tissue engineering and cancer treatment research, and related studies continue to drive breakthroughs in understanding the mechanism of cell contact inhibition and the regulation of three-dimensional microenvironments.
Structure of YAP1
YAP1 is a relatively large transcriptional regulatory protein, and its molecular weight varies among different subtypes and post-translational modifications, typically ranging from 65 to 75 kDa. This difference mainly stems from its complex domain and variable phosphorylation state.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Zebrafish |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | ~65-75 | ~65-75 | ~65-75 | ~70 |
| Primary Structural Differences | The core of the Hippo pathway regulates proliferation and apoptosis | Highly homologous to humans and functionally conserved | Important disease model molecules | Role in embryonic development |
The YAP1 protein contains approximately 450 to 500 amino acids and interacts with multiple partners through its complex domain. The key to the protein structure is a WW domain, which acts like a molecular key, specifically recognizing and binding to transcription factors containing specific proline motifs (PPxY), such as the TEAD family. The activity of YAP1 is mainly regulated by phosphorylation: when the Hippo pathway is activated, upstream kinases (LATS1/2) phosphorylate multiple serine sites of YAP1 (such as S127), causing it to be retained in the cytoplasm and become inactive. Conversely, in the activated state, YAP1 enters the cell nucleus and combines with factors such as TEAD, jointly initiating the gene program that promotes cell proliferation and growth.
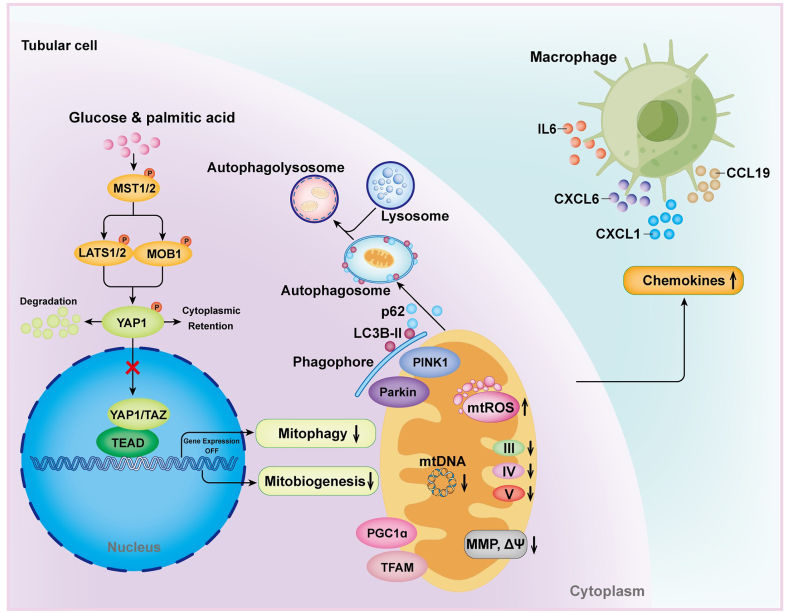 Fig. 1 YAP1 Dysfunction: Driving Diabetic Kidney Disease Progression.1
Fig. 1 YAP1 Dysfunction: Driving Diabetic Kidney Disease Progression.1
Key structural properties of YAP1:
- Contains multiple functional domains (WW, TEAD-binding domain, etc.)
- Disordered regions exist that mediate phase separation and transcriptional condensates formation
- Phosphorylation switches regulate its nucleoplasmic shuttle (key site Ser127)
- Mechanically sensitive modules sense cellular tension and microenvironmental signals
Functions of YAP1
The core function of YAP1 is to regulate gene expression as a transcriptional co-activator. However, its functions vary depending on the cellular environment and play different roles in development, cancer, and tissue regeneration.
| Function | Description |
| Cell proliferation driver | Repressed when cells are crowded, they enter the nucleus and bind to the TEAD transcription factor when there is enough space to initiate a genetic program that promotes cell division and drives tissue growth. |
| Mechanical signal transduction | Unique perception cells by physical pressure and extracellular matrix hardness, biochemical signals, convert mechanical stimulation to guide cell proliferation or apoptosis. |
| Damage repair and regeneration | Activated after tissue damage, it promotes the proliferation of progenitor cells to repair tissues and plays a particularly crucial role in liver regeneration and heart repair. |
| Tumorigenesis promotion | When the Hippo pathway is inactivated, YAP1 remains abnormally activated continuously, driving uncontrolled growth, invasion and metastasis of cancer cells by resisting cell contact inhibition. |
| Maintenance of stem cell characteristics | In a variety of adult stem cells increased, through regulating specific target genes to sustain self-renewal capacity of stem cells, prevent the premature differentiation. |
The activity of YAP1 is mainly regulated by its intracellular localization: after phosphorylation, it remains in the cytoplasm and is in a "closed" state; after dephosphorylation, it enters the nucleus and is in an "open" state. This unique "spatial regulation" mechanism enables it to efficiently integrate multiple upstream signals
Applications of YAP1 and YAP1 Antibody in Literature
1. Ye, Siyang, et al. "YAP1 preserves tubular mitochondrial quality control to mitigate diabetic kidney disease." Redox Biology 78 (2024): 103435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2024.103435
The article indicates that in diabetic nephropathy, the inactivation of YAP1 in renal tubular cells leads to the loss of control over mitochondrial quality regulation, causing abnormal mitochondrial function, and promotes the polarization of M1 in macrophages by secreting CXCL1, accelerating disease progression. Activation of YAP1 can improve mitochondrial function and alleviate kidney damage.
2. Sadhukhan, Pritam, et al. "YAP1 induces bladder cancer progression and promotes immune evasion through IL-6/STAT3 pathway and CXCL deregulation." The Journal of Clinical Investigation 135.2 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI171164
The article indicates that in bladder cancer, YAP1 shapes the immunosuppressive microenvironment by activating the IL-6/STAT3 pathway and regulating chemokines, thereby promoting the characteristics of tumor stem cells. Inhibiting YAP1 can reduce immunosuppressive cells such as M2 macrophages and, when used in combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors, has potential therapeutic value.
3. Li, Huiying, et al. "Mir-484 contributes to diminished ovarian reserve by regulating granulosa cell function via YAP1-mediated mitochondrial function and apoptosis." International journal of biological sciences 18.3 (2022): 1008. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.68028
The article indicates that in diminished ovarian function (DOR), the expression of miR-484 in granulosa cells is upregulated. It directly targets and inhibits YAP1, inducing mitochondrial dysfunction, thereby reducing cell proliferation, promoting cell apoptosis, and ultimately leading to a decline in ovarian reserve function. Replenishing YAP1 can reverse this damage.
4. Li, Yuexian, et al. "ITGB1 enhances the radioresistance of human non-small cell lung cancer cells by modulating the DNA damage response and YAP1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition." International journal of biological sciences 17.2 (2021): 635. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.52319
The article indicates that in non-small cell lung cancer, integrin ITGB1 enhances the radioresistance of cancer cells by promoting the expression and nuclear translocation of YAP1 and inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Targeting ITGB1 can inhibit YAP1 and enhance radiotherapy sensitivity.
5. Calvet, Loreley, et al. "YAP1 is essential for malignant mesothelioma tumor maintenance." Bmc Cancer 22.1 (2022): 639. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-022-09686-y
The article indicates that in malignant pleural mesotheliomas with abnormal Hippo signaling pathways, the continuous activation of YAP1 is the key to maintaining tumor growth. Inhibiting YAP1 can block the transcription of YAP1/TEAD, induce apoptosis of cancer cells and lead to the regression of already formed tumors, which provides a basis for targeting the YAP1-TEAD complex to treat this cancer.
Creative Biolabs: YAP1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality YAP1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom YAP1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our YAP1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Ye, Siyang, et al. "YAP1 preserves tubular mitochondrial quality control to mitigate diabetic kidney disease." Redox Biology 78 (2024): 103435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2024.103435
Anti-YAP1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-CTCF Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2371) (CBMAB-C2443-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ESR1 Recombinant Antibody (Y31) (CBMAB-1208-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-14-3-3 Pan Recombinant Antibody (V2-9272) (CBMAB-1181-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ADRA1A Recombinant Antibody (V2-12532) (CBMAB-1022-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-ACKR3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-261265) (CBMAB-C1023-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCN2 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2383) (CBMAB-C2456-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-FeLV g27 Recombinant Antibody (1) (CBMAB-V208-1714-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO2 Recombinant Antibody (H14) (CBMAB-E1341-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP1A2 Recombinant Antibody (M7-PB-E9) (CBMAB-A4013-YC)

-
Rat Anti-ADGRE4 Recombinant Antibody (V2-160163) (CBMAB-F0011-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-APCS Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A663) (CBMAB-A3054-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CEMIP Recombinant Antibody (3C12) (CBMAB-K0296-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-FLI1 Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-0733) (CBMAB-F0435-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ACTG1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179597) (CBMAB-A0916-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD59 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-2097) (CBMAB-C4421-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-AGK Recombinant Antibody (V2-258056) (CBMAB-M0989-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CASP8 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0987) (CBMAB-C2424-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-BZLF1 Recombinant Antibody (BZ.1) (CBMAB-AP705LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACE2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179293) (CBMAB-A0566-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ELAVL4 Recombinant Antibody (6B9) (CBMAB-1132-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








