ACTN3 Antibodies
Background
ACTN3 gene encoding alpha-actinin-3, it is a mainly expressed in these fibers of cytoskeleton proteins. This protein maintains the structural integrity of myofibrils and enhances muscle contraction strength by binding to actin filaments, especially playing a key role in sports that require explosive power. In 2003, the team led by Australian scientist Kathryn North first discovered the R577X functional mutation in the ACTN3 gene. This mutation led to a complete loss of alpha-actinin-3 expression in approximately 18% of the Asian population. As a model gene in sports genetics research, the polymorphism of ACTN3 has been confirmed to be significantly associated with the athletic performance of explosive power events such as sprinting and weightlifting. The study of its molecular mechanism provides an important theoretical basis for understanding muscle type differentiation and sports adaptability.
Structure of ACTN3
The ACTN3 gene encodes alpha-actinin-3 (ACTN3), with a molecular weight of approximately 100 kDa, and belongs to the spectrin protein family. This protein has a high degree of conservation among different species, but there are certain structural differences:
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Cattle |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 100 | 99 | 100 | 101 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Containing R577X mutation (non-functional in some populations) | No loss-of-function mutations | Highly conservative | Highly similar to humans |
This protein is mainly expressed in fast-twitch muscle fibers (type II) and enhances muscle contractility by binding to F-actin. The R577X mutation (C→T, stop codon) leads to a complete deficiency of functional ACTN3 protein in approximately 18% of the Asian population, affecting explosive power performance. Its structural characteristics make it an important target for research in sports genetics and muscle diseases.
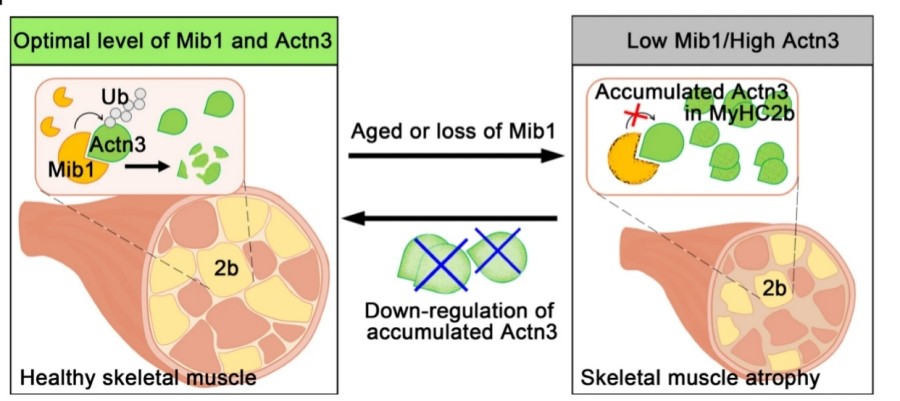 Fig. 1 ACTN3 Accumulation Drives Age-Related Muscle Atrophy.1
Fig. 1 ACTN3 Accumulation Drives Age-Related Muscle Atrophy.1
Key structural properties of ACTN3:
- N-terminal CH domain
- Central Repeat Zone
- C-terminal EF hand-type domain
Functions of ACTN3
The main function of the ACTN3 gene is to regulate the type of muscle fibers and contractile performance, especially playing a key role in fast muscle fibers (type II). In addition, it is also involved in a variety of physiological and pathological processes, including exercise adaptation, muscle injury repair and metabolic regulation.
| Function | Description |
| Enhanced muscle contraction | By binding with F-actin, it stabilizes the structure of myofibrils and enhances the explosive power and rapid contraction ability of muscles. |
| Fast-twitch muscle fiber maintenance | Promote the development and function of type II muscle fibers (fast muscles), and influence anaerobic exercise performance (such as sprinting, weightlifting). |
| Exercise adaptive regulation | Genetic polymorphisms (such as R577X) affect the differences in an individual's response to strength training or endurance training. |
| Muscle injury repair | Participate in regeneration process after muscle damage, affects the recovery rate and reshaping of muscle fiber. |
| Metabolic regulation | May be affected by muscle energy use efficiency, regulate glycolysis and oxidative metabolism balance. |
The R577X mutation of ACTN3 (resulting in protein deficiency) is widely present in the population. Approximately 18% of East Asians are homozygous deletion type (577XX), and their muscles tend to have slow muscle (type I) characteristics, which may affect explosive power but enhance endurance potential. This characteristic makes ACTN3 an important target for research in sports genetics and personalized training.
Applications of ACTN3 and ACTN3 Antibody in Literature
1. Pickering, Craig, and John Kiely. "ACTN3: more than just a gene for speed." Frontiers in physiology 8 (2017): 1080. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2017.01080
The article indicates that the ACTN3 gene (R577X polymorphism) affects athletic performance, especially speed and strength. The R allele can enhance muscle function, training adaptation and injury recovery, while the relationship between the XX genotype and endurance is not clear. The distribution of this gene varies significantly among different races and may contribute to the formulation of personalized training programs.
2. Pickering, Craig, and John Kiely. "ACTN3, morbidity, and healthy aging." Frontiers in genetics 9 (2018): 15.https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2018.00015
The article indicates that the ACTN3 gene (R577X polymorphism) affects the muscle function, bone density and metabolic health of the elderly. The XX genotype may increase the risk of sarcopenia, while the R allele may help maintain muscle strength and delay the decline of aging-related functions, providing a basis for personalized health management.
3. Ma, Fang, et al. "The association of sport performance with ACE and ACTN3 genetic polymorphisms: a systematic review and meta-analysis." PloS one 8.1 (2013): e54685. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0054685
The article indicates that the ACTN3 R577X polymorphism is associated with the performance of explosive power sports, and the RR genotype significantly enhances the performance of power-based events (OR=1.21). However, the overall analysis did not find a significant association between this genotype and exercise capacity (OR=1.03), suggesting that the influence of the gene has sports-specific specificity.
4. Silvino, Valmir Oliveira, et al. "The frequency of the ACTN3 polymorphism in Brazil: a systematic review and meta-analysis." BMC Medical Genomics 18.1 (2025): 79. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12920-025-02136-1
The article indicates that the ACTN3 R577X polymorphism study in the Brazilian population shows that the RX genotype has the highest proportion (46.2%), followed by RR (35.2%) and XX (18.6%). Although the frequency of the R allele was relatively high (58.3%), the meta-analysis did not confirm a stable association between this genotype and athletic performance, suggesting that athletic ability is influenced by multiple factors.
5. Gutiérrez-Hellín, Jorge, et al. "Effect of actn3 r577x genotype on injury epidemiology in elite endurance runners." Genes 12.1 (2021): 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12010076
The article indicates that the ACTN3 R577X polymorphism affects the injury characteristics of endurance runners: The RR type injury rate is the highest (3.2 times per 1000 hours), and the proportion of Achilles tendon injury is higher; Type XX did not show a higher risk of muscle injury, but the proportion of groin injury increased. Genotype does not affect the type and severity of injury.
Creative Biolabs: ACTN3 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality ACTN3 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom ACTN3 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our ACTN3 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Seo, Ji-Yun, et al. "Maintenance of type 2 glycolytic myofibers with age by Mib1-Actn3 axis." Nature Communications 12.1 (2021): 1294. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-21621-6
Anti-ACTN3 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Rabbit Anti-Acetyl-Histone H4 (Lys16) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623415) (CBMAB-CP1021-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-APP Recombinant Antibody (5C2A1) (CBMAB-A3314-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-APOH Recombinant Antibody (4D9A4) (CBMAB-A3249-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-ATF4 Recombinant Antibody (D4B8) (CBMAB-A3872-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CRTAM Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2235) (CBMAB-C2305-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL6 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0435) (CBMAB-0437-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-AKT1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180546) (CBMAB-A2070-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ENPP1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYE-0159) (CBMAB-E0375-FY)

-
Rat Anti-(1-5)-α-L-Arabinan Recombinant Antibody (V2-501861) (CBMAB-XB0003-YC)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S1 Monoclonal Antibody (CBFYR-0120) (CBMAB-R0120-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CA9 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-2079) (CBMAB-C0131-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CTNND1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2414) (CBMAB-C2487-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADGRL2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-58519) (CBMAB-L0166-YJ)

-
Mouse Anti-CD1C Recombinant Antibody (L161) (CBMAB-C2173-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CARD11 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0811) (CBMAB-C0866-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BMI1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-P026) (CBMAB-P0108-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ADIPOR2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179983) (CBMAB-A1369-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC5 Recombinant Antibody (6E4) (CBMAB-CP2646-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ABL1 (Phosphorylated Y245) Recombinant Antibody (V2-505716) (PTM-CBMAB-0465LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACTB Recombinant Antibody (V2-179553) (CBMAB-A0870-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








