AIM2 Antibodies
Background
AIM2 is a cytoplasmic DNA sensor encoded by the HIN-200 family genes, mainly expressed in immune cells and barrier tissues. This protein recognizes double-stranded DNA released by pathogens or damaged cells through its C-terminal HIN domain and recruits ASC adapter proteins with the N-terminal PYD domain, thereby assembling inflammasome complexes - this mechanism was simultaneously elucidated by three independent research teams in 2009. As an important regulatory factor of innate immunity, AIM2 can not only resist intracellular pathogen infections, but its abnormal activation is also closely related to autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus. In 2015, the analysis of its crystal structure revealed the key amino acid residues in the DNA-binding domain, providing a structural basis for the development of targeted therapies for inflammatory diseases.
Structure of AIM2
AIM2 is an inflammasome sensor protein with a molecular weight of approximately 39-42 kDa. There are minor differences in its molecular weight among different species, mainly due to species specific variations in the PYD domain and HIN domain sequences.
| Species | Human | Mice | Rhesus monkey | Rats |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 39.5 | 40.2 | 39.8 | 40.1 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains 581 amino acids | Contains 578 amino acids | Highly conserved PYD structure domain | HIN domain structure has three mutation loci |
The AIM2 protein is composed of the N-terminal pyrin domain (PYD) and the C-terminal HIN200 domain, and its functional structure is formed through typical α -helical bundle folding. Its HIN domain contains two OB folding mods, which can specifically recognize the phosphate skeleton of double-stranded DNA. Key functional sites include: the "death domain folding" of the PYD domain is responsible for the recruitment of ASC linker proteins, and the K248 and R310 residues of the HIN domain directly participate in DNA binding. This modular structure enables AIM2 to both sense pathogenic DNA and initiate immune responses through the inflammasome pathway.
Key structural properties of AIM2:
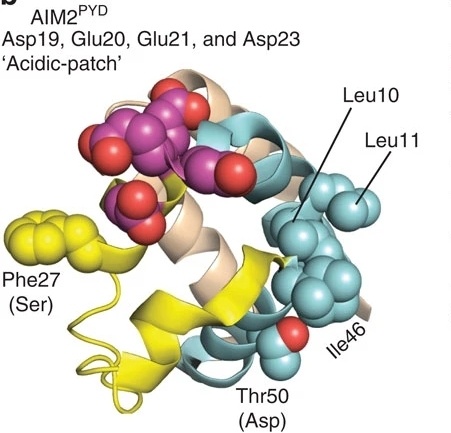 Fig. 1 The crystal structure of AIM2PYD (PDB ID: 3VD8).1
Fig. 1 The crystal structure of AIM2PYD (PDB ID: 3VD8).1
- Modular dual-domain architecture (N-end PYD domain + C-end HIN domain)
- HIN domain uses OB folding pattern to recognize double-stranded DNA
- PYD domain forms death domain fold to mediate protein interaction
Functions of AIM2
The main function of AIM2 is to act as a pattern recognition receptor for the innate immune system, detecting abnormal DNA in the cytoplasm and triggering inflammatory responses.
| Function | Description |
| DNA identification | Binding to double-stranded DNA in the cytoplasm (such as pathogen DNA or self-damaging DNA) activates the inflammasome signaling pathway. |
| Inflammasome activation | ASC and caspase-1 mediate the maturation and release of IL-1β and IL-18 to initiate anti-infective immune responses.. |
| Pyroptosis induction | Triggering the cleavage of Gasdermin D protein leads to cell membrane perforation and the release of pro-inflammatory factors, eliminating infected or cancerous cells. |
| Autoimmune regulation | Abnormal activation may be associated with autoimmune diseases (such as lupus erythematosus), and excessive inflammation needs to be prevented through negative feedback mechanisms. |
| Antiviral defense | Identify viral DNA (such as poxvirus), restrict viral replication and promote host cell death to block transmission. |
The activation of AIM2 depends on the direct binding of its HIN domain to DNA, while the PYD domain is responsible for downstream signal transduction. Its function is highly specific, and it is related to the localization of DNA receptors such as TLR9 (endosome vs. The cytoplasm and its functions complement each other.
Applications of AIM2 and AIM2 Antibody in Literature
1. Zhu, Huan, et al. "The complex role of AIM2 in autoimmune diseases and cancers." Immunity, Inflammation and Disease 9.3 (2021): 649-665. https://doi.org/10.1002/iid3.443
This article indicates that AIM2, as a key enzyme in the β -oxidation of short-chain fatty acids, its functional defects are associated with metabolic diseases (such as SCADD) and tumorigenesis. Research has found that abnormal expression of AIM2 affects the tumor microenvironment by altering lipid metabolism and exerts a tumor suppressor effect in various cancers such as liver cancer. Meanwhile, its gene polymorphism is significantly associated with the risk of metabolic syndrome.
2. Wang, Qi, et al. "AIM2 promotes renal cell carcinoma progression and sunitinib resistance through FOXO3a-ACSL4 axis-regulated ferroptosis." International journal of biological sciences 19.4 (2023): 1266. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.79853
This article indicates that AIM2 affects the energy supply of renal cancer cells by regulating the metabolism of short-chain fatty acids. The down-regulation of its expression promotes lipid accumulation and tumor progression, and is associated with resistance to targeted therapy, potentially becoming a new target for the treatment of renal cancer.
3. Huang, Yuan, et al. "Interaction between HCMV pUL83 and human AIM2 disrupts the activation of the AIM2 inflammasome." Virology journal 14 (2017): 1-10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12985-016-0673-5
This article confirmed through AIM2 antibody detection that the expression of AIM2 increased in the early stage of HCMV infection, but was inhibited by the viral pUL83 protein 24 hours later. pUL83 directly binds to AIM2 and blocks the activation of its inflammasome, revealing a new mechanism by which the virus evades host immunity.
4. Antiochos, Brendan, et al. "The DNA sensors AIM2 and IFI16 are SLE autoantigens that bind neutrophil extracellular traps." Elife 11 (2022): e72103. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.72103
This article's use of AIM2 antibody detection revealed that 31.3% of SLE patients had this autoantibody, which was significantly higher than that of the control group (4.1%). Research has found that AIM2 binds to neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) to form a DNase resistance complex, which may be involved in the pathogenesis of SLE by maintaining the interferon signaling pathway.
5. Chen, Yong, et al. "Expression of AIM2 in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Its Role on Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes." Mediators of Inflammation 2020.1 (2020): 1693730. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/1693730
This article research shows that the positive rate of AIM2 antibody detection in the synovial tissue of RA patients is significantly higher than that of the OA group (P<0.05), and the expression level of AIM2 is positively correlated with ESR and CRP (r=0.42). siRNA silencing of AIM2 can inhibit the proliferation of RA-FLS (P<0.01), suggesting that AIM2 antibody may serve as a novel biomarker for RA.
Creative Biolabs: AIM2 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality AIM2 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom AIM2 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our AIM2 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, please contact us.
Reference
- Morrone, Seamus R., et al. "Assembly-driven activation of the AIM2 foreign-dsDNA sensor provides a polymerization template for downstream ASC." Nature communications 6.1 (2015): 7827. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms8827
Anti-AIM2 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (HIS50) (CBMAB-C10123-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD2AP Recombinant Antibody (BR083) (CBMAB-BR083LY)

-
Mouse Anti-dsDNA Recombinant Antibody (22) (CBMAB-AP1954LY)

-
Rat Anti-CCR2 Recombinant Antibody (475301) (CBMAB-C1338-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CRTAM Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2235) (CBMAB-C2305-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AKR1C3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-12560) (CBMAB-1050-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0790) (CBMAB-0793-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCN2 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2383) (CBMAB-C2456-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ABL1 (Phosphorylated Y185) Recombinant Antibody (V2-443434) (PTM-CBMAB-0001YC)

-
Mouse Anti-A2M Recombinant Antibody (V2-178822) (CBMAB-A0036-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CEMIP Recombinant Antibody (3C12) (CBMAB-K0296-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AK4 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180419) (CBMAB-A1891-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0216) (CBMAB-0217-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ASH1L Monoclonal Antibody (ASH5H03) (CBMAB-1372-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AP4E1 Recombinant Antibody (32) (CBMAB-A2996-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-CCL5 Recombinant Antibody (R0437) (CBMAB-R0437-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-ARID3A Antibody (A4) (CBMAB-0128-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AQP2 Recombinant Antibody (E-2) (CBMAB-A3358-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CECR2 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJC-2465) (CBMAB-C3533WJ)

-
Rabbit Anti-ALDOA Recombinant Antibody (D73H4) (CBMAB-A2314-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






