Alpha Tubulin Antibodies
Background
Alpha Tubulin, as a major component protein of the cellular microtubule system, is widely present in the cytoplasm and cytoskeleton of eukaryotes. This protein forms a microtubule structure through polymerization, which not only maintains cell morphology but also participates in key physiological processes such as mitosis and intracellular substance transport. Because the dynamic assembly of microtubules plays a core role in the growth of neuronal axons, Alpha Tubulin has attracted much attention in the field of neural development. Its three-dimensional structure was first analyzed by electron crystallography in the 1980s, revealing the molecular mechanism of the GTP binding domain in the regulation of microtubule polymerization. As highly conserved cytoskeletal proteins, the research on their structure and function has greatly promoted breakthroughs in fields such as cell division, ciliary movement, and anti-cancer drug targets.
Structure of Alpha Tubulin
Alpha Tubulin is a conserved structural protein with a molecular weight of approximately 50 kDa, and its precise molecular weight varies slightly among different species.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Yeast | Arabidopsis thaliana | Bovine |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 50.1 | 49.9 | 49.8 | 49.7 | 50.0 |
| Primary Structural Differences | There are multiple post-translational modification sites at the C-terminal tail | Highly homologous to the human sequence | Core structure domain highly conservative | Adapt to the unique microtubule functions of plants | As a commonly used experimental material, it has a stable structure |
This protein is composed of approximately 450 amino acids, and its primary structure folds to form a hollow spherical core structure composed of alternating β -sheets and α -helices. This GTP-binding domain acts as a "molecular switch" to regulate the polymerization and depolymerization kinetics of tubulin dimers through the hydrolysis of GTP. Its functional activity is highly dependent on the heterodimer formed with β-tubulin, and this composite conformation provides the basic structural unit for microtubule assembly.
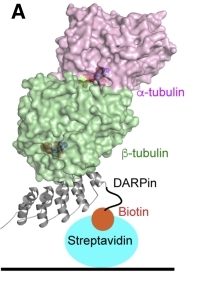 Fig. 1 Strategy for the selection of α-tubulin-specific αReps.1
Fig. 1 Strategy for the selection of α-tubulin-specific αReps.1
Key structural properties of Alpha Tubulin:
- Hollow globular GTPase domain composed of β-lamellar and α-helix
- Exposed acidic C-terminal tail
- Conservative GTP binding site
- The heterodimer interface formed with β-Tubulin
Functions of Alpha Tubulin
The core function of Alpha Tubulin is to form cellular microtubules and regulate their dynamic assembly. In addition, it is also involved in a variety of key cellular activities, including intracellular transport and regulation of cell division.
| Function | Description |
| Microtubule polymerization | With beta Tubulin heterologous dimers, longitudinal as basic unit assembly, forming hollow structure of microtubules. |
| Maintenance of cell morphology | By forming a cytoskeletal network, it provides mechanical support for cells and determines their morphology and polarity. |
| Mitotic regulation | Assemble to form a spindle, accurately capture and arrange chromosomes, and ensure their equal separation into daughter cells. |
| Intracellular transport | Provides tracks for motor proteins such as kinesin, dynein, and mediates the directed transport of vesicles and organelles. |
| Signal transduction | As a molecular platform, it participates in the transduction and regulation processes of multiple key signaling pathways such as Hedgehog and Hippo. |
The growth of microtubules stems from the continuous addition of GTP-bound αβ -heterodimers at the end, while the hydrolysis of GTP triggers structural instability and contraction. This "dynamic instability" enables the microtubule network to rapidly reconstruct to adapt to changes in the cell cycle and external environment.
Applications of Alpha Tubulin and Alpha Tubulin Antibody in Literature
1. Iuzzolino, Angela, et al. "The α-tubulin acetyltransferase ATAT1: structure, cellular functions, and its emerging role in human diseases." Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences 81.1 (2024): 193. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-024-05227-x
The article indicates that acetylation at the K40 site of α -tubulin can enhance the stability of microtubules. Its acetyltransferase ATAT1 plays a significant role in cell movement, mitosis and other processes, and is related to human diseases. Research on related inhibitors is also ongoing.
2. Diao, Lei, et al. "Cryo-EM of α-tubulin isotype-containing microtubules revealed a contracted structure of α4A/β2A microtubules: α4A/β2A microtubules display contracted lattices." Acta Biochimica et Biophysica Sinica 55.10 (2023): 1551. https://doi.org/10.3724/abbs.2023130
In this study, the microtubule structures composed of different α -tubulin isotypes (α1A, α1C, α4A) and β2A were resolved by cryo-electron microscopy. The results showed that the α4A/β2A microtubules contracted longitudinally between heterodimers, revealing for the first time that the α -tubulin isotype could determine the structural differences of microtubules, providing direct evidence for the "tubulin code" hypothesis.
3. Alonso, Victoria Lucia, et al. "Alpha-tubulin acetylation in Trypanosoma cruzi: a dynamic instability of microtubules is required for replication and cell cycle progression." Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology 11 (2021): 642271. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2021.642271
In this study, in Trypanosoma cruzii, the acetylation of the α -tubulin K40 site is crucial for maintaining the stability of the cytoskeleton. Research has found that its acetyltransferase TcATAT is located in the cytoskeleton and flagella. Its overexpression can disrupt cellular structures such as mitochondria, hinder the cell cycle process, and enhance the parasite's resistance to microtubule depolymerization drugs.
4. Campanacci, Valérie, et al. "Selection and characterization of artificial proteins targeting the tubulin α subunit." Structure 27.3 (2019): 497-506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2018.12.001
In this study, artificial proteins specifically binding to α -tubulin were screened out from the αRep library. These αRep can dose-dependent inhibit microtubule assembly and specifically block the growth of the negative end of microtubules by targeting the longitudinal interface of α -tubulin, providing a new tool for studying the dynamic mechanism of microtubules.
5. Ryan, Louise A., et al. "Fasciola hepatica expresses multiple α-and β-tubulin isotypes." Molecular and biochemical parasitology 159.1 (2008): 73-78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molbiopara.2008.02.001
The article indicates that five types of α -tubulin isotypes have been identified in liver fluke, and their amino acid sequence similarity ranges from 72% to 95%. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that two of the α -tubulin proteins were significantly different from those derived from other flukes.
Creative Biolabs: Alpha Tubulin Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality Alpha Tubulin antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom Alpha Tubulin Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our Alpha Tubulin antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Campanacci, Valérie, et al. "Selection and characterization of artificial proteins targeting the tubulin α subunit." Structure 27.3 (2019): 497-506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2018.12.001
Anti-Alpha Tubulin antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-CD164 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0077) (CBMAB-C0086-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-CCN1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJC-3580) (CBMAB-C4816WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-BLK Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0618) (CBMAB-0621-YY)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Recombinant Antibody (CR3022) (CBMAB-CR014LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ABL2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179121) (CBMAB-A0364-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-ABL1 (Phosphorylated Y185) Recombinant Antibody (V2-443434) (PTM-CBMAB-0001YC)

-
Mouse Anti-A2M Recombinant Antibody (V2-178822) (CBMAB-A0036-YC)

-
Rat Anti-C5AR1 Recombinant Antibody (8D6) (CBMAB-C9139-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD83 Recombinant Antibody (HB15) (CBMAB-C1765-CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-ALOX5AP Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-1219) (CBMAB-F0750-CQ)

-
Rat Anti-ADGRE4 Recombinant Antibody (V2-160163) (CBMAB-F0011-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0216) (CBMAB-0217-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-AGO2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-634169) (CBMAB-AP203LY)

-
Rat Anti-(1-5)-α-L-Arabinan Recombinant Antibody (V2-501861) (CBMAB-XB0003-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO2 Recombinant Antibody (85F11) (CBMAB-0276CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-B2M Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0059) (CBMAB-0059-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-APP Recombinant Antibody (DE2B4) (CBMAB-1122-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-8-oxoguanine Recombinant Antibody (V2-7697) (CBMAB-1869CQ)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S1 Monoclonal Antibody (CBFYR-0120) (CBMAB-R0120-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ARSA Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A799) (CBMAB-A3679-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








