APIP Antibodies
Background
APIP is a protein that plays a key role in apoptosis and inflammation regulation, and is mainly distributed in the tissues and cells of various mammals. The protein encoded by this gene affects the process of programmed cell death by participating in the regulation of the caspase signaling pathway, and can also maintain cellular homeostasis under oxidative stress conditions. Studies have shown that the expression changes of APIP are closely related to mitochondrial dysfunction and the development of metabolic diseases. This gene was initially identified as an apoptosis inhibitor in 2004. The analysis of its three-dimensional structure revealed its association with methyltransferase activity, providing a new perspective for understanding the interaction between proteins and metabolites. The continuous exploration of the mechanism of action of APIP not only deepens people's understanding of innate immune responses but also provides a molecular basis for the development of therapeutic targets for related diseases.
Structure of APIP
APIP is a protein with a molecular weight of approximately 35 kDa. Its precise weight may fluctuate slightly among different species due to subtle differences in amino acid composition.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Zebrafish |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 35.2 | 34.8 | 34.9 | 35.5 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Core functions are conserved, regulating apoptosis and metabolism | High homology with human | It is often used in disease model research | It has a fundamental conservative function |
This protein is composed of 298 amino acids and folds to form a typical spherical structure. The structure of APIP contains a key methyltransferase domain, which enables it to catalyze specific methylation reactions. The fundamental regulatory function of this gene in cells originates from this active domain. The tertiary structure of APIP is mainly composed of multiple α -helices and β -folds, which together form a hydrophobic active pocket to stabilize the binding of its substrates. The conserved amino acids in its active center are responsible for directly mediating the transfer of the methyl donor (S-adenosylmethionine), while the adjacent residues ensure the specificity of the reaction and prevent its inactivation.
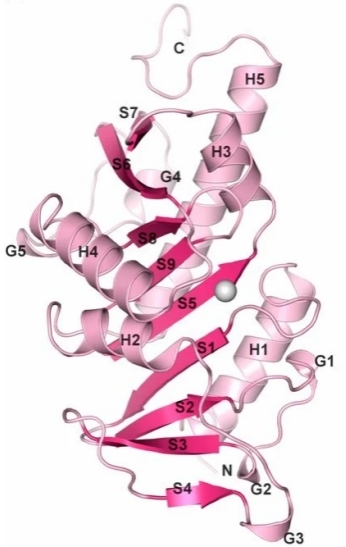 Fig. 1 The monomeric APIP/MtnB structure is sketched in ribbon representation.1
Fig. 1 The monomeric APIP/MtnB structure is sketched in ribbon representation.1
Key structural properties of APIP:
- Typical spherical methyltransferase folding conformation
- Composed of beta and alpha helix lamella common hydrophobic active center
- Conservative S - adenosine methionine combining structural domain is responsible for the catalytic methyl transfer
Functions of APIP
The core function of the APIP gene is to regulate apoptosis and inflammatory responses, and it is also involved in a variety of key cellular physiological processes, including energy metabolism balance and oxidative stress response.
| Function | Description |
| Apoptosis regulation | By inhibiting the activity of signaling pathways such as caspase-8, it prevents the excessive activation of programmed cell death and maintains cell survival. |
| Inflammatory regulation | Negatively regulate pathways such as the NLRP3 inflammasome to alleviate excessive inflammatory responses and related tissue damage. |
| Metabolic support | Participating in the methionine recovery metabolic pathway helps maintain the stability of methylation donors and energy metabolism balance within cells. |
| Oxidative stress protection | Under reactive oxygen species stress conditions, it helps maintain the integrity of mitochondrial function and protect cells from oxidative damage. |
| Developmental support | Through its pro-survival signaling function, it ensures the growth and remodeling of tissues during the normal development of embryos. |
Unlike the widely acting apoptosis-inducing factors, the scope of action of APIP is relatively concentrated, and its regulatory network shows a high degree of specificity, which indicates that it plays an irreplaceable and precise regulatory role in maintaining specific cellular homeostasis.
Applications of APIP and APIP Antibody in Literature
1. Lim, Bitna, et al. "Cardioprotective role of APIP in myocardial infarction through ADORA2B." Cell Death & Disease 10.7 (2019): 511. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-1746-3
The article indicates that in ischemic hearts, APIP inhibits the lysosomal degradation of ADORA2B protein by binding to it, enhances the activity of the PKA-CREB signaling pathway, thereby stabilizing ADORA2B and exerting cardiac protective effects. This mechanism reveals the key function of APIP in alleviating myocardial ischemic injury.
2. Hong, Se-Hoon, et al. "APIP, an ERBB3-binding partner, stimulates erbB2-3 heterodimer formation to promote tumorigenesis." Oncotarget 7.16 (2016): 21601. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.7802
The article indicates that in gastric cancer, the level of APIP is significantly elevated. It continuously activates the ERK and AKT signaling pathways by binding to the ERBB3 receptor, enhancing the formation of ERBB2/ERBB3 heterodimers, and ultimately promoting the proliferation of cancer cells and tumor growth. This indicates that APIP is a key positive regulatory factor for ERBB3-driven tumorigenesis.
3. Mary, Camille, et al. "Functional identification of APIP as human mtnB, a key enzyme in the methionine salvage pathway." PloS one 7.12 (2012): e52877. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0052877
Studies have confirmed that APIP plays a key role in the human methionine recovery pathway and is responsible for catalyzing the dehydrating enzyme step. The absence of APIP will directly impair the cell's ability to regenerate methionine using the metabolite MTA, and its activity depends on a potential zinc binding site.
4. Tang, Min, et al. "What may cause fetus loss from acute pancreatitis in pregnancy: Analysis of 54 cases." Medicine 97.7 (2018): e9755. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000009755
This article develops a highly sensitive fluorescence-based biosensor using quantum dots conjugated with plastic antibodies to detect myoglobin at femtomolar concentrations, providing a cost-effective, selective, and stable alternative for early myocardial infarction diagnosis in human serum.
5. Kang, Wonchull, et al. "Structural and biochemical basis for the inhibition of cell death by APIP, a methionine salvage enzyme." Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 111.1 (2014): E54-E61. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1308768111
Studies have shown that human APIP protein has catalytic activity as an MtnB enzyme, but its function of inhibiting apoptosis is not related to the activity of this enzyme. However, when inhibiting Caspase-1-mediated pyroptosis, it depends on its MtnB enzyme function. This reveals the dual mechanism of APIP in regulating different cell death patterns.
Creative Biolabs: APIP Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality APIP antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom APIP Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our APIP antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Kang, Wonchull, et al. "Structural and biochemical basis for the inhibition of cell death by APIP, a methionine salvage enzyme." Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 111.1 (2014): E54-E61. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1308768111
Anti-APIP antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Rabbit Anti-CCL5 Recombinant Antibody (R0437) (CBMAB-R0437-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-ADAM12 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179752) (CBMAB-A1114-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AHCYL1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180270) (CBMAB-A1703-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO2 Recombinant Antibody (85F11) (CBMAB-0276CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ACE2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179293) (CBMAB-A0566-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ABL2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179121) (CBMAB-A0364-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CCL18 Recombinant Antibody (64507) (CBMAB-C7910-LY)

-
Rat Anti-FABP3 Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-2299) (CBMAB-F1612-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ARG1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYCL-103) (CBMAB-L0004-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-C5B-9 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYA-0216) (CBMAB-X0304-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD59 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-2097) (CBMAB-C4421-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BLK Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0618) (CBMAB-0621-YY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ABL1 (Phosphorylated Y245) Recombinant Antibody (V2-505716) (PTM-CBMAB-0465LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AGK Recombinant Antibody (V2-258056) (CBMAB-M0989-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-CBL Recombinant Antibody (D4E10) (CBMAB-CP0149-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-1728) (CBMAB-2077-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (HIS50) (CBMAB-C10123-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ENPP1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYE-0159) (CBMAB-E0375-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-DISP2 Monoclonal Antibody (F66A4B1) (CBMAB-1112CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP1B3 Recombinant Antibody (1E9) (CBMAB-A4021-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






