APMAP Antibodies
Background
The APMAP gene encodes a protein related to adipocyte membranes, which is mainly present in adipose tissue and participates in regulating adipocyte differentiation and energy metabolism balance. Its expression products can affect insulin signaling pathways and inflammatory responses, and play an important role in maintaining metabolic homeostasis. This gene was first identified in 2008. Subsequent studies have revealed that it is closely related to the occurrence and development of metabolic diseases such as obesity and type 2 diabetes. Due to its involvement in the regulatory mechanisms of various cellular processes, APMAP has become an important molecular target in the study of metabolic diseases, providing a new perspective for understanding the regulation of energy metabolism and pathophysiological mechanisms.
Structure of APMAP
APMAP is a protein encoded by multiple known transcripts, and its molecular weight varies by subtype, with the main subtypes approximately ranging from 30 to 45 kDa. This value varies among different species, mainly due to gene splicing and natural sequence variations.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 43 | 42 | 42 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains typical signal peptides and domains | High homology with human and highly conserved sequence | High homology with human and highly conserved sequence |
The APMAP protein is composed of hundreds of amino acids. Its primary structure includes an N-terminal signaling peptide, a major domain, and a transmembrane region, ultimately forming a type II transmembrane protein. Its spatial conformation enables it to interact with a variety of proteins within cells, and these interactions depend on its specific domain, which plays a key regulatory role in physiological processes such as adipocyte differentiation and inflammatory responses.
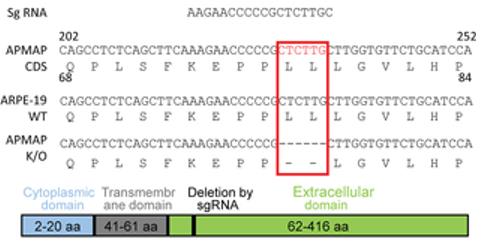 Fig. 1 Sequencing Identifies a Two-Amino Acid Deletion in the APMAP Gene of Knockout Cells.1
Fig. 1 Sequencing Identifies a Two-Amino Acid Deletion in the APMAP Gene of Knockout Cells.1
Key structural properties of APMAP:
- Contains the typical signal peptide sequence and a single transmembrane domain structure
- Extracellular region contains the function of the conservative domain involved in molecular recognition
- Form of homologous dimers ability is very important to its function
Functions of APMAP
The main function of APMAP (adipocyte membrane-associated protein) is to participate in the regulation of adipocyte differentiation and energy metabolism, and it also plays a role in inflammatory responses and cellular stress processes.
| Function | Description |
| Regulation of fat production | In front of the fat cells to mature key regulatory role during the process of adipocyte differentiation, the accumulation of lipid droplets and. |
| Regulation of insulin sensitivity | By participating in the regulation of insulin signaling pathways and influencing the response of adipocytes to insulin, it is closely related to metabolic health. |
| Involvement of inflammatory response | Under the condition of obesity, it participates in regulating the infiltration of macrophages and the release of inflammatory factors in adipose tissue. |
| Cellular stress response | Under metabolic stress conditions such as endoplasmic reticulum stress, its expression level changes and may play a protective role. |
| Extracellular matrix remodeling | Affect the composition of extracellular matrix and reconstruction of adipose tissue and indirect regulation of adipose tissue plasticity. |
APMAP plays a core role in maintaining metabolic homeostasis through its specific molecular interaction network, and its dysfunction is directly related to the development of insulin resistance and obesity-related metabolic diseases.
Applications of APMAP and APMAP Antibody in Literature
1. Zhu, et al. "APMAP promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of cervical cancer cells by activating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway." Journal of Cancer 12.20 (2021): 6265. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.59595
Studies have found that APMAP is highly expressed in cervical cancer and predicts a poor prognosis. It promotes cancer cell migration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by activating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, and is a potential prognostic marker and therapeutic target.
2. Gerber, Hermeto, et al. "The APMAP interactome reveals new modulators of APP processing and beta-amyloid production that are altered in Alzheimer’s disease." Acta neuropathologica communications 7.1 (2019): 13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40478-019-0660-3
Research reveals that the APMAP protein in the brain is associated with γ -secretase and affects the progression of Alzheimer's disease. Mouse experiments have shown that the absence of APMAP exacerbates memory deficits and promotes the generation and deposition of β -amyloid protein (Aβ), and its effect is related to the autophagy-lysosomal system.
3. Luo, Gang, et al. "FTO regulated intramuscular fat by targeting APMAP gene via an m6A-YTHDF2-dependent manner in Rex rabbits." Cells 12.3 (2023): 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12030369
Research reveals that in rabbit muscle fat deposition, FTO, through m6A demethylation and recognition by YTHDF2, enhances the expression of the APMAP gene, thereby promoting adipocyte differentiation. The expression level of APMAP is positively correlated with fat content, providing a new target for breeding.
4. Pessentheiner, Ariane R., et al. "APMAP interacts with lysyl oxidase–like proteins, and disruption of Apmap leads to beneficial visceral adipose tissue expansion." The FASEB Journal 31.9 (2017): 4088. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201601337R
Research has found that knocking out the APMAP gene can improve insulin sensitivity in obese mice and reduce collagen deposition and fibrosis in white adipose tissue. APMAP has become a potential therapeutic target for obesity by regulating extracellular matrix components such as lysyl oxidase.
5. Su, Fangyu, et al. "Endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced CRELD2 promotes APMAP-mediated activation of TGF-β/SMAD and NF-κB pathways in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma." Frontiers in Immunology 16 (2025): 1616201. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1616201
Research has found that in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, endoplasmic reticulum stress induces CRELD2 expression through the PERK-ATF4 pathway. CRELD2 promotes the localization of APMAP to the cell membrane, thereby activating the TGF-β/SMAD and NF-κB signaling pathways and driving the malignant progression of tumors.
Creative Biolabs: APMAP Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality APMAP antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom APMAP Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our APMAP antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Ye X, Gui X, et al. "Identification of adipocyte plasma membrane-associated protein as a novel modulator of human cytomegalovirus infection." PLoS pathogens 15.7 (2019): e1007914. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1007914
Anti-APMAP antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-CCN2 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2383) (CBMAB-C2456-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CIITA Recombinant Antibody (CBLC160-LY) (CBMAB-C10987-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CASP7 Recombinant Antibody (10-01-62) (CBMAB-C2005-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL2L1 Recombinant Antibody (H5) (CBMAB-1025CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CD83 Recombinant Antibody (HB15) (CBMAB-C1765-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CSPG4 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYM-1050) (CBMAB-M1203-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO2 Recombinant Antibody (85F11) (CBMAB-0276CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CEMIP Recombinant Antibody (3C12) (CBMAB-K0296-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CGAS Recombinant Antibody (CBFYM-0995) (CBMAB-M1146-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BAD (Phospho-Ser136) Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0138) (CBMAB-0139-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATG5 Recombinant Antibody (9H197) (CBMAB-A3945-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ACTB Recombinant Antibody (V2-179553) (CBMAB-A0870-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ATM Recombinant Antibody (2C1) (CBMAB-A3970-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ASH1L Monoclonal Antibody (ASH5H03) (CBMAB-1372-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-ADRA1A Recombinant Antibody (V2-12532) (CBMAB-1022-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-ACE2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179293) (CBMAB-A0566-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL6 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0435) (CBMAB-0437-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ARSA Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A799) (CBMAB-A3679-YC)

-
Rat Anti-(1-5)-α-L-Arabinan Recombinant Antibody (V2-501861) (CBMAB-XB0003-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-APOH Recombinant Antibody (4D9A4) (CBMAB-A3249-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






