ASCL1 Antibodies
Background
The ASCL1 gene encodes a protein belonging to the basic helical ring-helix (bHLH) transcription factor family, which is mainly expressed in the nervous system during embryonic development. This protein plays a core role in the differentiation of neuroendocrine cells and the formation of the autonomic nervous system by regulating the transcription of downstream target genes. Its abnormal expression is closely related to the occurrence and development of neuroendocrine tumors. For example, it can serve as a key diagnostic marker in small cell lung cancer. As an important research object in developmental neurobiology, ASCL1 has become a hot target in cell reprogramming and cancer treatment research due to its dual role in cell fate determination and tumorigenesis.
Structure of ASCL1
The ASCL1 protein is a basic helical-ring-helix (bHLH) transcription factor with a molecular weight of approximately 30-35 kDa. This protein has a highly conserved bHLH domain in mammals, and its C-terminal region shows certain differences among different species, which may lead to different specificities of target gene regulation.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | About33 | About32 | About33 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Containing 238 amino acids, the typical bHLH structure domain | The bHLH domain is highly homologous to that of humans | Species-specific variation exists in the C-terminal transcriptional activation domain |
The ASCL1 protein is composed of approximately 238 amino acids, and its core functional domain is the C-terminal bHLH motif, which is responsible for DNA binding and dimerization. The N-terminal of the protein is rich in proline and acidic amino acids, forming a transcriptional activation domain. The bHLH domain contains two highly conserved α -helices, which are connected through a circular region. One of the α -helices contains a basic amino acid residue that directly binds to the E-box (CANNTG) on the target DNA sequence. This structural feature enables ASCL1 to recognize and bind to specific gene promoter regions, thereby initiating the transcriptional cascade of neuroendocrine differentiation.
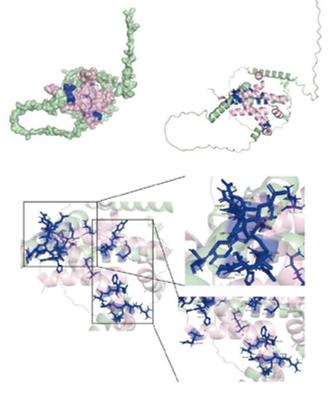 Fig. 1 Protein docking map and binding site of ASCL1 to CREB1.1
Fig. 1 Protein docking map and binding site of ASCL1 to CREB1.1
Key structural properties of ASCL1:
- Contains a conserved basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) domain
- The N-terminal acidic trans-activated domain is rich in proline
- Alkaline regions mediate the recognition and binding of specific DNA sequences
- Helix-loop-helix module promotes protein dimerization and nuclear localization
Functions of ASCL1
The core function of the ASCL1 gene is to regulate the differentiation of cells into neuroendocrine lineages. In addition, this gene is also involved in key biological processes such as cell cycle regulation, tumorigenesis and cell reprogramming.
| Function | Description |
| Regulation of neuroendocrine differentiation | By binding to the E-box cis-element to activate downstream target genes, it drives cells to differentiate directally towards neuroendocrine phenotypes. |
| Cell fate determination | Regulate the development and specialization of the autonomic nervous system and neuroendocrine cells during the embryonic period. |
| Tumorigenesis promotion | In abnormally high expression in small cell lung cancer and other malignant tumors, promoting tumor proliferation and malignant progression. |
| Cell reprogramming mediation | Can be used as a key transcription factor inducing fibroblast cell transdifferentiation of neuron cells. |
| Cell cycle intervention | The process of G1/S phase transition of the cell cycle is affected by regulating factors such as Cyclin D. |
ASCL1 forms homologous or heterodimers through its basic helical-ring-helical domain, specifically recognizing the E-box sequence (CANNTG) in the promoter region of the target gene, and thereby initiating the transcriptional program of neuroendocrine differentiation. The functional differences between it in normal tissues and tumors mainly depend on the expression level, interacting proteins and epigenetic regulatory status.
Applications of ASCL1 and ASCL1 Antibody in Literature
1. Nouruzi, Shaghayegh, et al. "ASCL1 regulates and cooperates with FOXA2 to drive terminal neuroendocrine phenotype in prostate cancer." JCI insight 9.23 (2024): e185952. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.185952
Studies have shown that the transcription factor ASCL1 and FOXA2 work in synergy to drive the neuroendocrinalization of prostate cancer. Its downstream target, prospero homeobox 1, is a key effector molecule. Targeting this molecule can inhibit tumor growth, providing a new target for treatment.
2. Romero, Rodrigo, et al. "The neuroendocrine transition in prostate cancer is dynamic and dependent on ASCL1." Nature Cancer 5.11 (2024): 1641-1659. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43018-024-00838-6
Studies have revealed that the absence of Rb1 in prostate cancer can drive KRT8+ lumen cells to transform into ASCL1+ neuroendocrine phenotypes in vivo. ASCL1 is a key factor in neuroendocrine transformation. Its early deficiency can block this transformation, suggesting that the timing of treatment is of crucial importance.
3. Wohlschlegel, Juliette, et al. "ASCL1 induces neurogenesis in human Müller glia." Stem cell reports 18.12 (2023): 2400-2417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stemcr.2023.10.021
Studies have shown that the transcription factor ASCL1 can successfully reprogram Muller glial cells in the human fetal retina and organoids into neurons in vitro. This provides a potential strategy for treating human retinal diseases through cell reprogramming.
4. Myers, Bianca L., et al. "Transcription factors ASCL1 and OLIG2 drive glioblastoma initiation and co-regulate tumor cell types and migration." Nature communications 15.1 (2024): 10363. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-54750-9
Research reveals that in glioblastoma, the transcription factors ASCL1 and OLIG2 mutually regulate each other and jointly drive tumorigenesis. Among them, high expression of ASCL1 can determine the neural stem cell/astrocyte-like identity of tumor cells, making them highly migratory and resistant to treatment.
5. Yang, Xiaolu, et al. "An integrative analysis of ASCL1 in breast cancer and inhibition of ASCL1 increases paclitaxel sensitivity by activating ferroptosis via the CREB1/GPX4 axis." Frontiers in Immunology 16 (2025): 1546794. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1546794
Research has found that the transcription factor ASCL1 is highly expressed in breast cancer and promotes the malignant progression of tumors. It inhibits ferroptosis by regulating the CREB1/GPX4 signaling axis, thereby reducing paclitaxel sensitivity, suggesting that it can serve as a potential therapeutic target.
Creative Biolabs: ASCL1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality ASCL1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom ASCL1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our ASCL1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Yang, Xiaolu, et al. "An integrative analysis of ASCL1 in breast cancer and inhibition of ASCL1 increases paclitaxel sensitivity by activating ferroptosis via the CREB1/GPX4 axis." Frontiers in Immunology 16 (2025): 1546794. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1546794
Anti-ASCL1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Rat Anti-EPO Recombinant Antibody (16) (CBMAB-E1578-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (D9S6V) (CBMAB-CP0017-LY)

-
Rat Anti-ADAM10 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179741) (CBMAB-A1103-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AKR1C3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-12560) (CBMAB-1050-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-ACE2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179293) (CBMAB-A0566-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ALB Recombinant Antibody (V2-363290) (CBMAB-S0173-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-FOXA3 Recombinant Antibody (2A9) (CBMAB-0377-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CAT Recombinant Antibody (724810) (CBMAB-C8431-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD59 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-2097) (CBMAB-C4421-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-C4B Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C2996) (CBMAB-C4439-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CORO1A Recombinant Antibody (4G10) (V2LY-1206-LY806)

-
Mouse Anti-ALPL Antibody (B4-78) (CBMAB-1009CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ADV Recombinant Antibody (V2-503423) (CBMAB-V208-1364-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACO2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179329) (CBMAB-A0627-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-DMPK Recombinant Antibody (CBYCD-324) (CBMAB-D1200-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ATG5 Recombinant Antibody (9H197) (CBMAB-A3945-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-dsRNA Recombinant Antibody (2) (CBMAB-D1807-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD1C Recombinant Antibody (L161) (CBMAB-C2173-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-DHFR Recombinant Antibody (D0821) (CBMAB-D0821-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-FN1 Monoclonal Antibody (71) (CBMAB-1241CQ)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








