BSND Antibodies
Background
The BSND gene encodes a protein called Barttin, which is a transmembrane subunit found mainly in the epithelial cells of the kidney and inner ear. This protein, as an auxiliary subunit of the chloride ion channel, is crucial for maintaining the reabsorption of sodium chloride in the renal tubules and the ionic balance of lymph fluid in the inner ear. Abnormal function can lead to Bartter syndrome type IV, which is characterized by renal dysfunction and congenital sensorineural deafness. The BSND gene was first identified in 2001, and the clarification of its function revealed the core role of ion channels in fluid balance and auditory physiology. In-depth research on this gene not only enhances human understanding of the ion transport mechanisms in the kidneys and inner ears, but also provides a molecular basis for the diagnosis and treatment of related genetic diseases.
Structure of BSND
The Barttin protein encoded by the BSND gene is a small transmembrane subunit with a molecular weight of approximately 10-12 kDa. This protein is highly conserved among different species, and the subtle differences in its molecular weight mainly result from slight changes in the amino acid sequence of the transmembrane region.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Bovine |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | ~10.5 | ~10.3 | ~10.4 | ~10.6 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains two transmembrane domains | Highly conserved across the membrane area | The N-terminal sequence is slightly different | The cytoplasmic regions at the C-terminal are similar |
The Barttin protein is composed of 320 amino acids and forms a basic topological structure of four transmembrane α -helices. This protein binds to the chloride ion channel CLC-K through two specific transmembrane domains to form a functional complex. Both its N-terminal and C-terminal are located on the cytoplasmic side, and the tail of the C-terminal contains multiple phosphorylation sites, which are responsible for regulating the activity of the channel and membrane transport. Two conserved extracellular cysteine residues form disulfide bonds, which are crucial for maintaining the stable conformation and normal function of proteins.
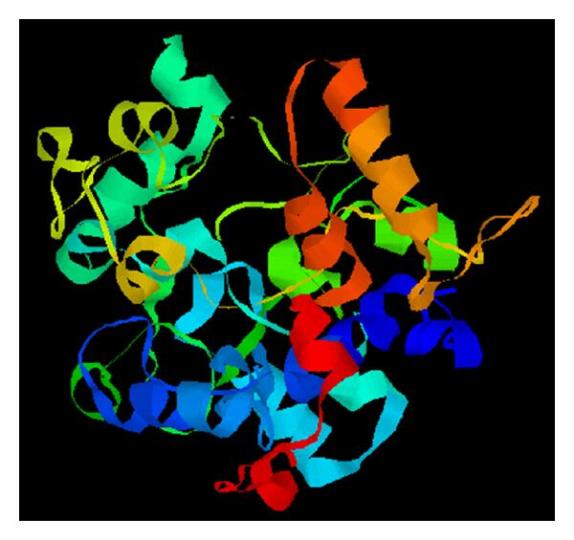 Fig. 1 Protein models of BSND.1
Fig. 1 Protein models of BSND.1
Key structural properties of BSND:
- Double transmembrane topology
- Conserved extracellular disulfide bonds
- The C-terminal cytoplasmic domain contains regulatory sites
Functions of BSND
The core function of the protein Barttin encoded by the BSND gene is to serve as an essential auxiliary subunit of the chloride ion channel CLC-K and maintain the ionic balance of the body. In addition, it is also involved in the regulation of various physiological processes.
| Function | Description |
| Activation of chlorine channels | Binding to CLC-Ka/CLC-Kb channels is required for its membrane localization and normal function, and regulates renal tubular chloride reabsorption. |
| Kidney salt balance | The transepithelial transport of sodium chloride mediated in the coarse segment of the ascending branch of the Heinz loop is crucial for maintaining fluid and electrolyte homeostasis. |
| Inner ear potassium circulation | Potassium circulation in the endolymphatic fluid is ensured in the stria vascularis and peripheral cells of the inner ear, and the high potassium environment required for auditory signal transduction is maintained. |
| Cellular pH regulation | By influencing the chloride ion flow across the membrane, epithelial cells of indirect participation in the pH of the steady state. |
| Association with genetic diseases | The loss of its function directly leads to Bartter syndrome type IV, which is characterized by salt consumption, hypotension and congenital deafness. |
The complex formed by Barttin and the CLC-K channel exhibits a unique voltage-dependent chloride ion conductivity, and its activation characteristics are crucial for efficient ion transport in the renal tubules and inner ear.
Applications of BSND and BSND Antibody in Literature
1. Himmerkus, Nina, et al. "Viewing cortical collecting duct function through phenotype-guided single-tubule proteomics." Function 1.1 (2020): zqaa007. https://doi.org/10.1093/function/zqaa007
In this study, by combining the functional and proteomic analysis of a single renal tubular in mouse CCDS, it was found that BSND (Barttin) was significantly downregulated in pendrin knockout mice. This, along with the expression changes of other ion transporters, jointly revealed the potential mechanism of the salt-loss phenotype of Pendred syndrome.
2. Sayed-Ahmed, Mohammed M., et al. "Molecular and Clinical Characterization of a Cohort of Autosomal Recessive Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Egyptian Patients." Journal of Molecular Neuroscience 74.4 (2024): 102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-024-02279-3
This study conducted genetic analysis on 13 patients with congenital severe hearing loss and discovered new pathogenic mutations in seven known deafness-causing genes such as BSND, further confirming that BSND gene mutations are one of the important causes of autosomal recessive hereditary deafness.
3. Shinmura, Kazuya, et al. "BSND and ATP6V1G3: novel immunohistochemical markers for chromophobe renal cell carcinoma." Medicine 94.24 (2015): e989. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000000989
This study, through database screening, found that the BSND gene is specifically highly expressed in renal chromophobe cell carcinoma. Immunohistochemistry confirmed that the BSND protein was widely positive in this type of cancer, but negative in other subtypes of renal cell carcinoma and lung cancer, indicating that it is an excellent new biomarker for differentiating chromophobe cell carcinoma of the kidney.
4. Iqbal, Hina, et al. "Identification of missense mutation (I12T) in the BSND gene and bioinformatics analysis." BioMed Research International 2011.1 (2011): 304612. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/304612
The article indicates that in a study of a close relative family in Pakistan, it was found that the p.I12T mutation of the BSND gene could lead to non-syndromic hearing loss without kidney abnormalities. This confirms that BSND mutations can not only cause Barth syndrome but also lead to deafness alone, and expands its pathogenic variant spectrum.
5. Renauld, Justine M., et al. "Lmx1a is essential for marginal cell differentiation and stria vascularis formation." Frontiers in cell and developmental biology 13 (2025): 1537505. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2025.1537505
Studies have shown that the absence of the transcription factor Lmx1a can lead to severe abnormal development of the inner ear, with complete loss of protein expression in specific regions of the stria vascularis, including BSND, which is crucial for hearing. This reveals the crucial role of Lmx1a in shaping the structure and function of the inner ear.
Creative Biolabs: BSND Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality BSND antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom BSND Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our BSND antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Iqbal, Hina, et al. "Identification of missense mutation (I12T) in the BSND gene and bioinformatics analysis." BioMed Research International 2011.1 (2011): 304612. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/304612
Anti-BSND antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-CD8 Recombinant Antibody (C1083) (CBMAB-C1083-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-C5b-9 Recombinant Antibody (aE11) (CBMAB-AO138LY)

-
Rat Anti-C5AR1 Recombinant Antibody (8D6) (CBMAB-C9139-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-APOA1 Monoclonal Antibody (CBFYR0637) (CBMAB-R0637-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-F11R Recombinant Antibody (402) (CBMAB-0026-WJ)

-
Rabbit Anti-ALDOA Recombinant Antibody (D73H4) (CBMAB-A2314-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BBS2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0253) (CBMAB-0254-YY)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Recombinant Antibody (CBC05) (CBMAB-CR005LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALPL Antibody (B4-78) (CBMAB-1009CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ACE2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179293) (CBMAB-A0566-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC5 Recombinant Antibody (6E4) (CBMAB-CP2646-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ELAVL4 Recombinant Antibody (6B9) (CBMAB-1132-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-CCL5 Recombinant Antibody (R0437) (CBMAB-R0437-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-DHFR Recombinant Antibody (D0821) (CBMAB-D0821-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV8 Recombinant Antibody (V2-634028) (CBMAB-AP022LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AHCYL1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180270) (CBMAB-A1703-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CIITA Recombinant Antibody (CBLC160-LY) (CBMAB-C10987-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD164 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0077) (CBMAB-C0086-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ABL1 (Phosphorylated Y245) Recombinant Antibody (V2-505716) (PTM-CBMAB-0465LY)

-
Rat Anti-(1-5)-α-L-Arabinan Recombinant Antibody (V2-501861) (CBMAB-XB0003-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






