CPT1A Antibodies
Background
The CPT1A gene encodes carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1A, a rate-limiting enzyme located on the outer mitochondrial membrane, which is mainly distributed in metabolically active tissues such as the liver, kidneys and pancreas. This enzyme regulates the key step of fatty acids entering mitochondria for β -oxidation by catalyzing the binding reaction between long-chain fatty acids and carnitine, thereby maintaining the homeostasis of energy metabolism in the body. Under conditions of starvation or high-fat diet, the upregulation of CPT1A expression plays an important regulatory role in ketone body formation and gluconeogenesis processes. This gene was first located and cloned in 1990. The mechanism by which its activity is inhibited by allosteric modification of malonyl-CoA has become A classic regulatory model in the field of metabolic research. The continuous exploration of the structure and function of CPT1A not only reveals the molecular basis of fatty acid metabolism but also provides a theoretical basis for the targeted treatment of metabolic syndromes such as obesity and diabetes.
Structure of CPT1A
CPT1A is a mitochondrial membrane protein with a molecular weight of approximately 88 kDa, and its precise molecular weight varies among different subtypes.
| Species | Human | Rat | Mouse | Chicken |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 88.2 | 87.9 | 88.1 | 89.5 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Containing about 773 amino acids, with N control domain | Highly homologous to the rat sequence | Catalytic core highly conservative | Specific variation was found in the C-terminal domain |
This protein is composed of approximately 773 amino acids, and its N-terminal contains a key regulatory domain responsible for sensing metabolic signals. The tertiary structure of CPT1A forms a dual-domain architecture: a smaller N-terminal domain is embedded in the outer mitochondrial membrane, and a larger C-terminal catalytic domain is oriented towards the cytoplasm. Its active center contains an arginine residue, which is crucial for binding carnitine substrates, while A channel crossing the membrane structure is responsible for accepting long-chain acyl-CoA. The catalytic mechanism of this enzyme relies on an arginine-glutamate charge relay system, a feature that has been highly conserved during evolution, ensuring the efficiency and specificity of fatty acid transport.
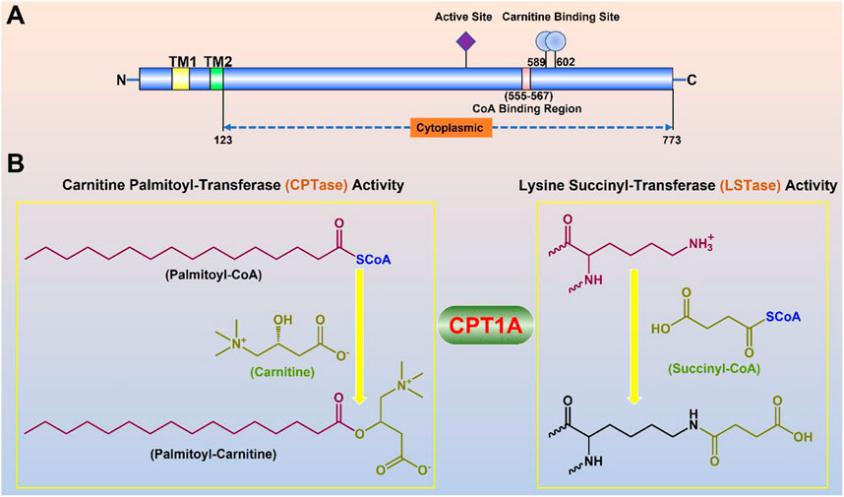 Fig. 1 Molecular properties and physiological functions of CPT1A.1
Fig. 1 Molecular properties and physiological functions of CPT1A.1
Key structural properties of CPT1A:
- Contains N end control domain and C end dual domain framework of catalytic domain
- Transmembrane helical anchors are located in the mitochondrial outer membrane
- The arginine-glutamate charge relay system forms the catalytic core
Functions of CPT1A
The core function of CPT1A protein is to regulate the entry of long-chain fatty acids into mitochondria for β -oxidation. Its main physiological functions include:
| Function | Description |
| Limiting rate of fatty acid oxidation | Catalyze the binding reaction between long-chain acyl-coA and carnitine, and control the speed at which fatty acids enter the mitochondrial matrix. |
| Regulation of energy metabolism | Under starvation conditions, its activity is upregulated, promoting the production of ketone bodies in the liver and providing alternative energy for brain tissue. |
| Balance of sugar and lipid metabolism | By malonyl-coa allosteric inhibition, the cross regulation of glucose metabolism and lipid metabolism was realized. |
| Thermogenic adaptation | Support decoupling and thermogenesis in brown adipose tissue to maintain stable body temperature. |
| Regulation of insulin sensitivity | By influencing lipid metabolic flow, it indirectly regulates the insulin signaling pathway in peripheral tissues. |
The activity of this enzyme exhibits a unique substrate concentration biphasic kinetic characteristic: it follows the Michaelis equation at low substrate concentrations, while at high concentrations, it is regulated by the membrane structure microenvironment, resulting in an activity plateau phase. This nonlinear dynamic characteristic enables it to sensitively respond to changes in the body's energy state and play a core role in maintaining metabolic homeostasis.
Applications of CPT1A and CPT1A Antibody in Literature
1. Ma, Lei, et al. "Targeting carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1A (CPT1A) induces ferroptosis and synergizes with immunotherapy in lung cancer." Signal transduction and targeted therapy 9.1 (2024): 64. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-024-01772-w
This study reveals that in lung cancer, CPT1A forms a c-Myc positive feedback loop, activates the NRF2/GPX4 antioxidant system and down-regulates ACSL4, enhancing the resistance of tumor stem cells to ferroptosis and leading to the inactivation of CD8+ T cells. Targeting CPT1A can enhance the efficacy of immune checkpoint blockade and provide a new strategy for lung cancer immunotherapy.
2. Liang, Kai. "Mitochondrial CPT1A: Insights into structure, function, and basis for drug development." Frontiers in pharmacology 14 (2023): 1160440. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2023.1160440
This study reveals that CPT1A is a key rate-limiting enzyme in fatty acid oxidation, and its abnormal function is closely related to the occurrence and development of various cancers. Targeted inhibition of CPT1A can interfere with the metabolism of cancer cells, thereby inhibiting their proliferation and drug resistance, and it is a highly promising new strategy for cancer treatment. This review systematically summarizes the role of CPT1A in diseases and the prospects of targeted therapy.
3. Li, Rongqing, et al. "Mitochondrial STAT3 exacerbates LPS-induced sepsis by driving CPT1a-mediated fatty acid oxidation." Theranostics 12.2 (2022): 976. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.63751
This study found that STAT3 located in the mitochondria of macrophages can upregulate USP50 through NF-κB, thereby stabilizing CPT1A protein and reducing its degradation. This effect enhances the oxidation metabolism of fatty acids, thereby exacerbating LPS-induced sepsis. The research has revealed the key mechanism of the mitochondrial STAT3-CPT1A axis in sepsis.
4. Wang, Muyun, et al. "CPT1A‐IL‐10‐mediated macrophage metabolic and phenotypic alterations ameliorate acute lung injury." Clinical and Translational Medicine 14.8 (2024): e1785. https://doi.org/10.1002/ctm2.1785
This study reveals the key role of CPT1A in regulating macrophage metabolism and polarization in acute lung injury. CPT1A alleviates pulmonary inflammation by promoting fatty acid oxidation and inducing IL-10 expression, driving macrophages to polarize towards the anti-inflammatory M2 phenotype, and maintaining mitochondrial homeostasis. The CPT1A-IL-10 axis provides a new target for treatment.
5. Su, Wenyan, et al. "Restoration of CPT1A-mediated fatty acid oxidation in mesothelial cells protects against peritoneal fibrosis." Theranostics 13.13 (2023): 4482. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.84921
This study reveals the key role of CPT1A in peritoneal dialysis fibrosis. Long-term dialysis leads to a decrease in the expression of CPT1A in mesothelmal cells and damage to fatty acid oxidation, resulting in fibrosis. Overexpression or activation of CPT1A can restore cellular metabolic function, reverse the pro-fibrotic phenotype, and alleviate peritoneal lesions, suggesting that targeting CPT1A is a potential therapeutic strategy.
Creative Biolabs: CPT1A Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality CPT1A antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom CPT1A Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our CPT1A antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Liang, Kai. "Mitochondrial CPT1A: Insights into structure, function, and basis for drug development." Frontiers in pharmacology 14 (2023): 1160440. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2023.1160440
Anti-CPT1A antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-BRD3 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0801) (CBMAB-0804-YY)

-
Rabbit Anti-CCN1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJC-3580) (CBMAB-C4816WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0790) (CBMAB-0793-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-AZGP1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJZ-007) (CBMAB-Z0012-WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-DDC Recombinant Antibody (8E8) (CBMAB-0992-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ARSA Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A799) (CBMAB-A3679-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-dsRNA Recombinant Antibody (2) (CBMAB-D1807-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC3 Recombinant Antibody (16E63) (CBMAB-C3367-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-14-3-3 Pan Recombinant Antibody (V2-9272) (CBMAB-1181-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-APP Recombinant Antibody (5C2A1) (CBMAB-A3314-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-FAS2 Monoclonal Antibody (1D4) (CBMAB-0071-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-BLK Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0618) (CBMAB-0621-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ASB9 Recombinant Antibody (1D8) (CBMAB-A0529-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CARTPT Recombinant Antibody (113612) (CBMAB-C2450-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ABL1 (Phosphorylated Y185) Recombinant Antibody (V2-443434) (PTM-CBMAB-0001YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AHCYL1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180270) (CBMAB-A1703-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AGO2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-634169) (CBMAB-AP203LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACKR3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-261265) (CBMAB-C1023-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ATF4 Recombinant Antibody (D4B8) (CBMAB-A3872-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-GDF5 Recombinant Antibody (1F4) (CBMAB-G2740-LY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






