CYP1A2 Antibodies
Background
CYP1A2 is an important cytochrome P450 enzyme, mainly present in the human liver, responsible for metabolizing various exogenous substances (such as caffeine and drugs) and endogenous compounds. This enzyme promotes the biotransformation of substrates through oxidation reactions and plays a key role in drug metabolism and detoxification processes. Its activity is significantly influenced by genetic polymorphisms and environmental factors (such as smoking), leading to metabolic differences among individuals. In the 1990s, scientists first analyzed the gene sequence of CYP1A2. Subsequent studies on its structure and function have deepened our understanding of drug interactions and personalized medication. As a model molecule for drug metabolism research, CYP1A2 provides an important theoretical basis for the development of new drugs and the assessment of drug safety.
Structure of CYP1A2
CYP1A2 is a cytochrome P450 enzyme with a molecular weight of approximately 58 kDa. Its precise molecular weight may vary slightly due to species and post-translational modifications.
| Species | Human | Rats | Mice | Rabbits |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | ~58 | ~57.5 | ~57.8 | ~58.2 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Highly conserved, with stable key metabolic active sites | The substrate binding regions are slightly different | High similarity to human CYP1A2 | Differences between enzyme kinetics characteristics |
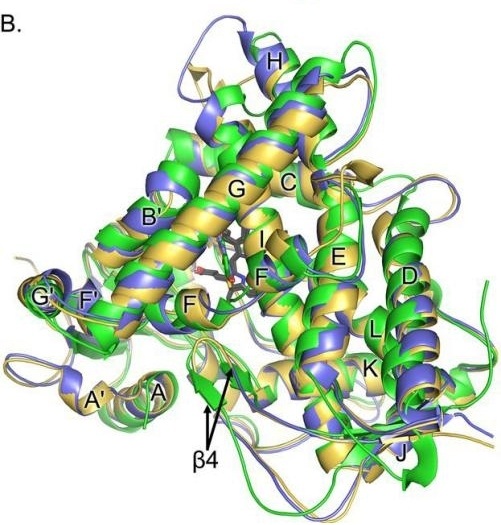 Fig. 1 Structural Superposition of CYP1A1 (Blue), CYP1A2 (Yellow), and CYP1B1 (Green) Aligned by Cα Atoms.1
Fig. 1 Structural Superposition of CYP1A1 (Blue), CYP1A2 (Yellow), and CYP1B1 (Green) Aligned by Cα Atoms.1
Key structural properties of CYP1A2:
- A spherical structure mixed with α -helix and β -fold
- Hydrophobic channels facilitate the binding of liposoluble substrates
- Heme-iron active centers catalyze oxidation reactions
- Highly variable substrate binding regions (affecting differences in drug metabolism)
- Susceptibility to genetic polymorphisms (e.g., changes in enzyme activity due to CYP1A21F mutation)
The structural study of CYP1A2 provides an important foundation for understanding drug metabolism, individualized medication and drug interactions.
Functions of CYP1A2
CYP1A2 is one of the most important drug-metabolizing enzymes in the liver, mainly responsible for the biotransformation of exogenous and endogenous compounds.
| Function | Description |
| Drug metabolism | Metabolize approximately 15% of commonly used clinical drugs, including various medications such as caffeine and chlorazine. |
| Prodrug activation | Convert certain prodrugs (such as cyclophosphamide) into active forms. |
| Detoxification of toxins | Participate in the detoxification process of carcinogens such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and aromatic amines. |
| Endogenous substance metabolism | Metabolize endogenous compounds such as melatonin and estradiol. |
| Regulation of drug interactions | Its activity is induced or inhibited by various drugs and it is an important target for drug interactions. |
Applications of CYP1A2 and CYP1A2 Antibody in Literature
1. Yu, Jianqing, et al. "CYP1A2 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma through antagonizing HGF/MET signaling." Theranostics 11.5 (2021): 2123. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.49368
This study reveals the tumor suppressor effect of CYP1A2 in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Through antibody detection techniques such as Western blot and immunohistochemistry, it was found that high expression of CYP1A2 was associated with a good prognosis. Mechanically, the CYP1A2 antibody confirmed that it binds to HIF-1α and promotes degradation, thereby inhibiting the HGF/MET signaling pathway. CYP1A2 can serve as an independent prognostic marker for HCC.
2. Mahdavi, Sara, Paolo Palatini, and Ahmed El-Sohemy. "CYP1A2 genetic variation, coffee intake, and kidney dysfunction." JAMA network open 6.1 (2023): e2247868-e2247868. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-1331.2011.03353.x
This study explores the influence of CYP1A2 genotype (rs762551) on the association between coffee intake and renal function. The results show that people with slow coffee metabolism (AC/CC genotype) have a significantly increased risk of proteinuria, hyperfiltration and hypertension when they consume more than three cups of coffee daily, suggesting that CYP1A2 antibody testing may help assess caffeine metabolism capacity and kidney risk.
3. Fekete, Ferenc, et al. "CYP1A2 mRNA expression rather than genetic variants indicate hepatic CYP1A2 activity." Pharmaceutics 14.3 (2022): 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14030532
This study explored the influence of CYP1A2 gene polymorphisms (such as -163C>A) on enzyme activity and mRNA expression, and found that they had no significant association with CYP1A2 function. CYP1A2 antibody detection revealed that enzyme activity is more dependent on mRNA expression levels rather than genotypes, and the influence of non-genetic factors is limited. The conclusion is that the genotyping of CYP1A2 has limited predictive value for function, but the mRNA expression of white blood cells can reflect metabolic capacity.
4. Wang, Shushan, et al. "CYP1A2 polymorphism may contribute to agomelatine-induced acute liver injury: Case report and review of the literature." Medicine 100.45 (2021): e27736. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000027736
This study reports a case of acute liver injury in a 75-year-old male patient caused by taking agomelatine (metabolized by CYP1A2). Detection revealed that it carried the CYP1A2 rs762551 AA genotype, suggesting that the polymorphism of this enzyme gene might cause hepatotoxicity by affecting drug metabolism. It is recommended to regularly monitor liver function during the treatment period. CYP1A2 antibody testing may help assess individual metabolic risks.
5. Fekete, Ferenc, et al. "CYP1A2 expression rather than genotype is associated with olanzapine concentration in psychiatric patients." Scientific Reports 13.1 (2023): 18507. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-45752-6
This study confirmed that CYP1A2 (rather than CYP2D6) is the key enzyme in the metabolism of olanzapine. The detection of CYP1A2 antibody revealed that its mRNA expression level (rather than gene polymorphism) was significantly correlated with blood drug concentration. Smoking can induce the expression of CYP1A2, especially in those carrying the -163A variant. It is recommended to guide individualized medication by detecting the level of CYP1A2 mRNA in white blood cells.
Creative Biolabs: CYP1A2 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality CYP1A2 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom CYP1A2 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our CYP1A2 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, please contact us.
Reference
- Walsh, Agnes A., Grazyna D. Szklarz, and Emily E. Scott. "Human cytochrome P450 1A1 structure and utility in understanding drug and xenobiotic metabolism." Journal of Biological Chemistry 288.18 (2013): 12932-12943. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.452953
Anti-CYP1A2 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-APC Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A661) (CBMAB-A3036-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ALX1 Recombinant Antibody (96k) (CBMAB-C0616-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACVR1C Recombinant Antibody (V2-179685) (CBMAB-A1041-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CASQ1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0863) (CBMAB-C0918-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (HIS50) (CBMAB-C10123-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-C5AR1 Recombinant Antibody (R63) (CBMAB-C9553-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A950) (CBMAB-A4388-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ABIN2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179106) (CBMAB-A0349-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-DMD Recombinant Antibody (D1190) (CBMAB-D1190-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ADAM29 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179787) (CBMAB-A1149-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ANXA7 Recombinant Antibody (A-1) (CBMAB-A2941-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV-5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-503416) (CBMAB-V208-1402-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD164 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0077) (CBMAB-C0086-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-FN1 Monoclonal Antibody (71) (CBMAB-1241CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ACTB Recombinant Antibody (V2-179553) (CBMAB-A0870-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD19 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-1224) (CBMAB-C1491-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC3 Recombinant Antibody (16E63) (CBMAB-C3367-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-DLK1 Recombinant Antibody (9D8) (CBMAB-D1061-YC)

-
Rat Anti-ADAM10 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179741) (CBMAB-A1103-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ALOX5 Recombinant Antibody (33) (CBMAB-1890CQ)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






