ICAM1 Antibodies
Background
ICAM1 is a transmembrane glycoprotein widely expressed on the surface of vascular endothelial cells and immune cells. As a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, its structure contains multiple extracellular immunoglobulin-like domains. The protein encoded by this gene plays a core role in inflammatory responses and immune cell migration by mediating the adhesion of white blood cells to vascular endothelium. When tissues are infected or damaged, inflammatory factors will induce the upregulation of ICAM1 expression, promoting white blood cells to pass through the vascular wall and enter the lesion site. This gene was first identified in 1986. Subsequent studies have found that it not only participates in chronic inflammatory diseases such as atherosclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis, but also serves as the main cellular receptor for rhinoviruses. In-depth research on the mechanism of action of ICAM1 has greatly promoted the progress of immune response theory and targeted drug development.
Structure of ICAM1
ICAM1 is a transmembrane glycoprotein with a molecular weight of approximately 55-90 kDa, and its differences mainly stem from the varying degrees of glycosylation modification.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 55-90 | 48-60 | 52-65 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains five Ig sample structure domain and nine glycosylation sites | ICAM1 65% homology with people, less glycosylation sites | With 85% homology to the rat, the glycosylation pattern is different |
This protein is composed of 574 amino acids, and its extracellular segment contains five immunoglobulin-like domains (D1-D5). Among them, the D1 domain contains epitopes bound to the LFA-1 integrin, the D2 domain is involved in conformational stability, and the D3-D5 domain mediates the localization of the proximal and distal ends of the membrane. The transmembrane region is composed of 24 hydrophobic amino acids, and the intracellular segment contains 28 amino acid residues, which are connected to the actin cytoskeleton through ERM proteins. This multi-domain structure enables ICAM1 to undergo conformational changes in response to inflammatory stimuli, effectively regulating the leukocyte adhesion cascade reaction.
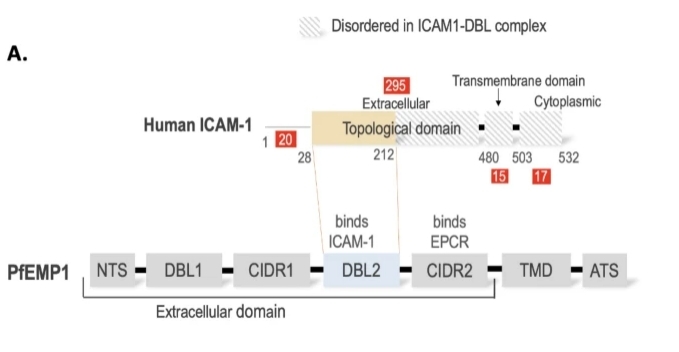 Fig. 1 Domain diagram of ICAM-1 and PfEMP1.1
Fig. 1 Domain diagram of ICAM-1 and PfEMP1.1
Key structural properties of ICAM1:
- Extracellular section contains five immunoglobulin sample structure domain (D1 - D5)
- Highly glycosylated rod-shaped transmembrane structure
- Integrin binding site of D1 domain (LFA-1/MAC-1)
- Intracellular segments are connected to the cytoskeleton through anchoring proteins
Functions of ICAM1
The main function of ICAM1 is to mediate the adhesion of white blood cells to vascular endothelium and signal transduction. In addition, it is also involved in various physiological and pathological processes such as the initiation of immune responses and the regulation of inflammation.
| Function | Description |
| Leukocyte adhesion | Binding to LFA-1/MAC-1 integrin through the D1 domain mediates firm adhesion of leukocytes to endothelial cells. |
| Migration of immune cells | Guide white blood cells to penetrate the walls of blood vessels at the site of inflammation and enter the tissue to carry out immune defense. |
| Immune synaptic formation | During the antigen presentation process, helper T cells maintain stable contact with APCs, enhancing the efficiency of immune responses. |
| Signal transduction | Intracellular segment with the cytoskeleton, start the downstream signaling pathways, regulating cell polarity and migration direction. |
| Disease-related functions | As the main receptor of rhinoviruses; Participate in chronic inflammatory lesions such as atherosclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis. |
The binding affinity of ICAM1 to ligands is regulated by inflammatory factors. It is expressed at a low level in the resting state, but can be rapidly upregulated under the stimulation of TNF-α, IL-1, etc. This dynamic regulatory characteristic makes it a key control node in the immune inflammatory process.
Applications of ICAM1 and ICAM1 Antibody in Literature
1. Taftaf, Rokana, et al. "ICAM1 initiates CTC cluster formation and trans-endothelial migration in lung metastasis of breast cancer." Nature communications 12.1 (2021): 4867. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-25189-z
This study reveals that in triple-negative breast cancer, the ICAM1 protein is significantly upregulated in lung metastases. It promotes metastasis by mediating the aggregation between tumor cells (forming circulating tumor cell clusters) and tumor-endothelial cell adhesion. Targeting ICAM1 can effectively inhibit metastasis initiation, indicating that it can serve as a potential therapeutic target.
2. Zhang, Ying, et al. "Fusobacterium nucleatum promotes colorectal cancer cells adhesion to endothelial cells and facilitates extravasation and metastasis by inducing ALPK1/NF-κB/ICAM1 axis." Gut Microbes 14.1 (2022): 2038852. https://doi.org/10.1080/19490976.2022.2038852
Research has found that Fusobacterium nucleatum upregulates the expression of ICAM1 in colorectal cancer cells by inducing the ALPK1/NF-κB signaling pathway. This enhances the adhesion between cancer cells and endothelial cells, promoting tumor extravasation and distant metastasis. High expression of ICAM1 indicates a poor prognosis for patients, revealing a new mechanism by which the gut microbiota promotes metastasis.
3. Tinajero-Rodríguez, José Manuel, et al. "ICAM1 (CD54) Contributes to the Metastatic Capacity of Gastric Cancer Stem Cells." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25.16 (2024): 8865. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25168865
Research has found that in gastric cancer stem cells, ICAM1 regulates their migration, invasion and metastasis abilities by activating STAT3 signaling. After knockout of ICAM1, although cancer cells' resistance to cisplatin increased, their migration and metastasis abilities were significantly lost. This indicates that ICAM1 is a key molecule regulating the metastasis of gastric cancer stem cells.
4. Tinajero-Rodríguez, José Manuel, et al. "ICAM1 (CD54) Contributes to the Metastatic Capacity of Gastric Cancer Stem Cells." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25.16 (2024): 8865. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1484483
Research has found that in periodontitis, ICAM1 marks a subpopulation of fibroblasts with inflammatory characteristics. This cell produces factors such as CCL2 through the NF-κB pathway, which in turn recruits macrophages and eliminates neutrophils, exerting a protective effect in the early stage of the disease and inhibiting bone resorption.
5. Zhou, Qin, et al. "Role of ICAM1 in tumor immunity and prognosis of triple-negative breast cancer." Frontiers in Immunology 14 (2023): 1176647. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1176647
Research has found that in triple-negative breast cancer, low expression of ICAM1 is associated with a poor prognosis for patients. The mechanism might be that the low expression of ICAM1 leads to immunosuppression, such as promoting the polarization of M2 macrophages and T cell exhaustion, thereby weakening anti-tumor immunity and possibly affecting the efficacy of immunotherapy.
Creative Biolabs: ICAM1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality ICAM1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom ICAM1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our ICAM1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Gill, Jasmita, Himmat Singh, and Amit Sharma. "Profiles of global mutations in the human intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) shed light on population-specific malaria susceptibility." BMC genomics 24.1 (2023): 773. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-023-09846-9
Anti-ICAM1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-CCND2 Recombinant Antibody (DCS-3) (CBMAB-G1318-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CTCF Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2371) (CBMAB-C2443-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL2L1 Recombinant Antibody (H5) (CBMAB-1025CQ)

-
Rat Anti-CCR2 Recombinant Antibody (475301) (CBMAB-C1338-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-C5b-9 Recombinant Antibody (aE11) (CBMAB-AO138LY)

-
Mouse Anti-HTLV-1 gp46 Recombinant Antibody (CBMW-H1006) (CBMAB-V208-1154-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ENO2 Recombinant Antibody (BA0013) (CBMAB-0272CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ALOX5 Recombinant Antibody (33) (CBMAB-1890CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CSPG4 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYM-1050) (CBMAB-M1203-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ALK (Phosphorylated Y1278) Recombinant Antibody (D59G10) (PTM-CBMAB-0035YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AKT1/AKT2/AKT3 (Phosphorylated T308, T309, T305) Recombinant Antibody (V2-443454) (PTM-CBMAB-0030YC)

-
Mouse Anti-C5AR1 Recombinant Antibody (R63) (CBMAB-C9553-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD19 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-1224) (CBMAB-C1491-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-B2M Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0050) (CBMAB-0050-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-dsDNA Recombinant Antibody (22) (CBMAB-AP1954LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADIPOR2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179983) (CBMAB-A1369-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AZGP1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJZ-007) (CBMAB-Z0012-WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-DLL4 Recombinant Antibody (D1090) (CBMAB-D1090-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD46 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0076) (CBMAB-C0085-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD63 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-1200) (CBMAB-C1467-CQ)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






